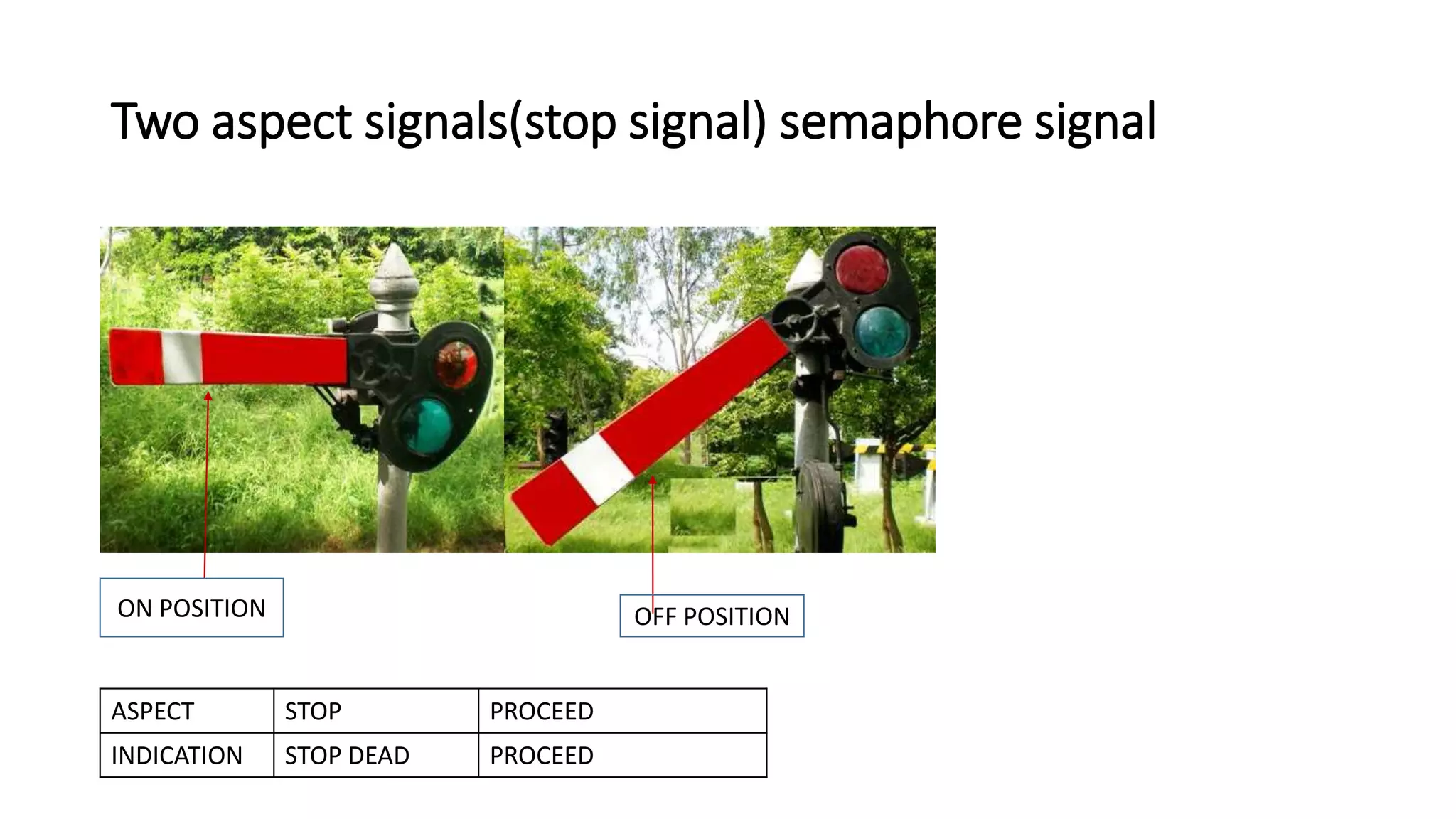
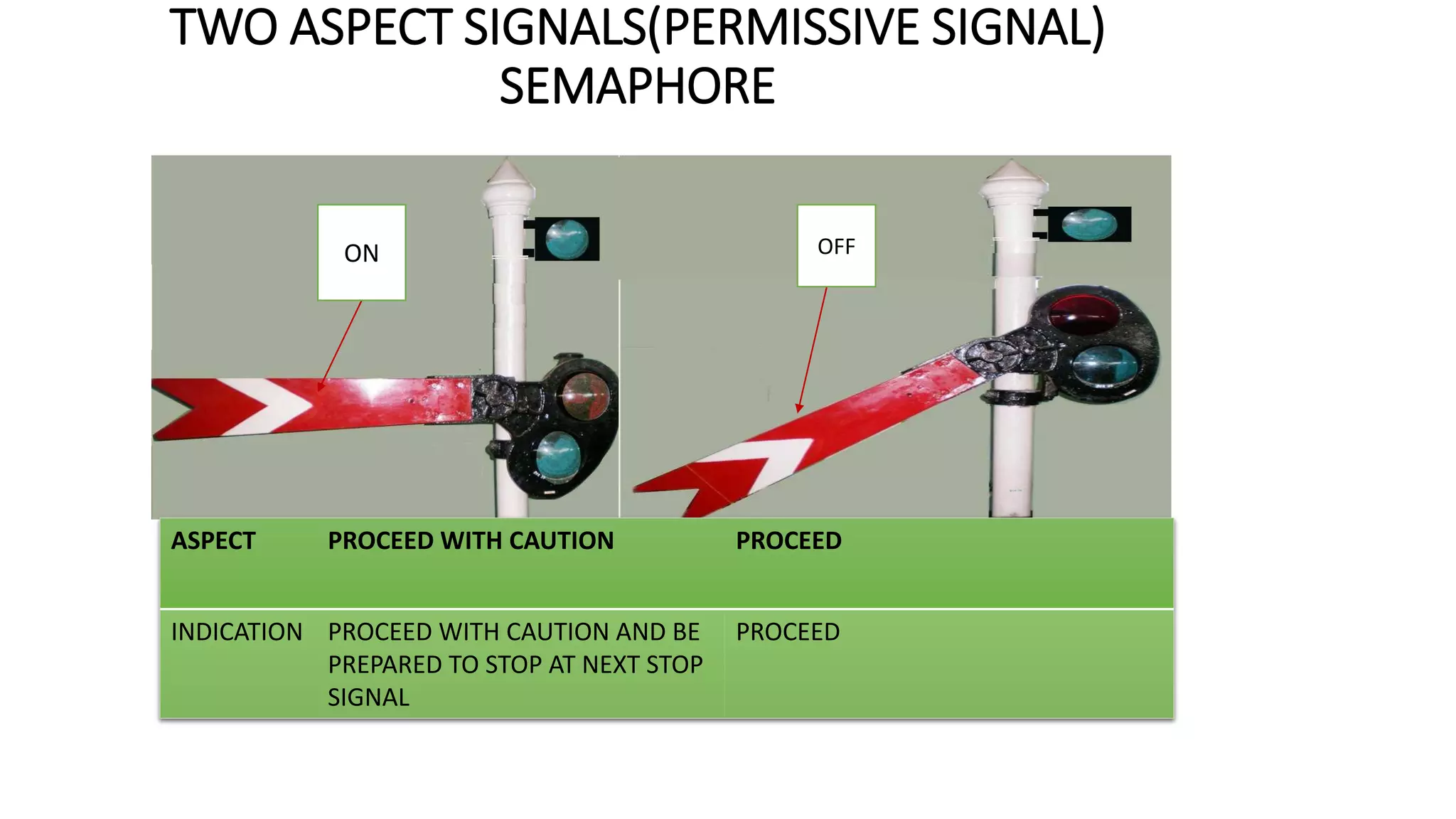
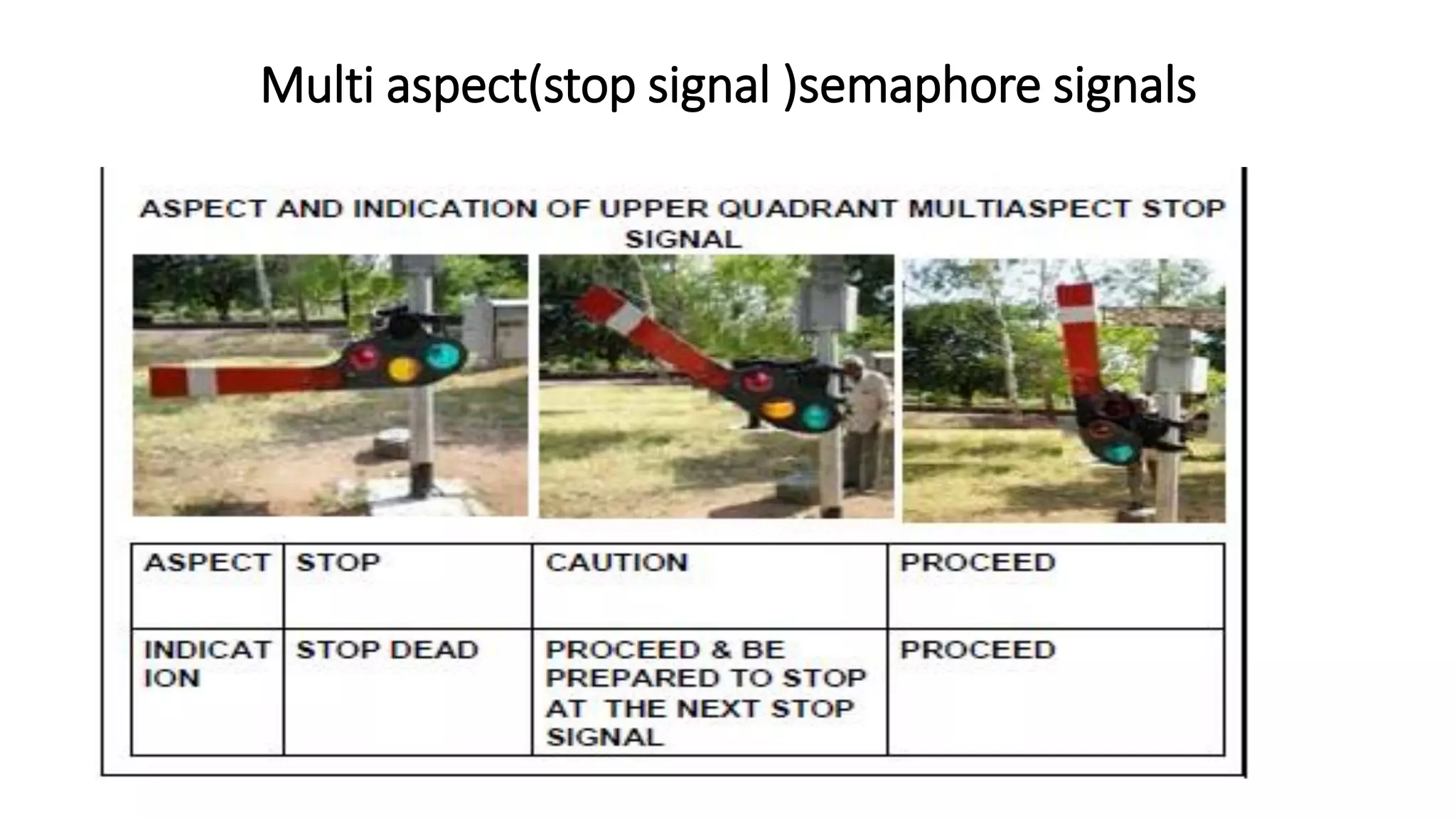
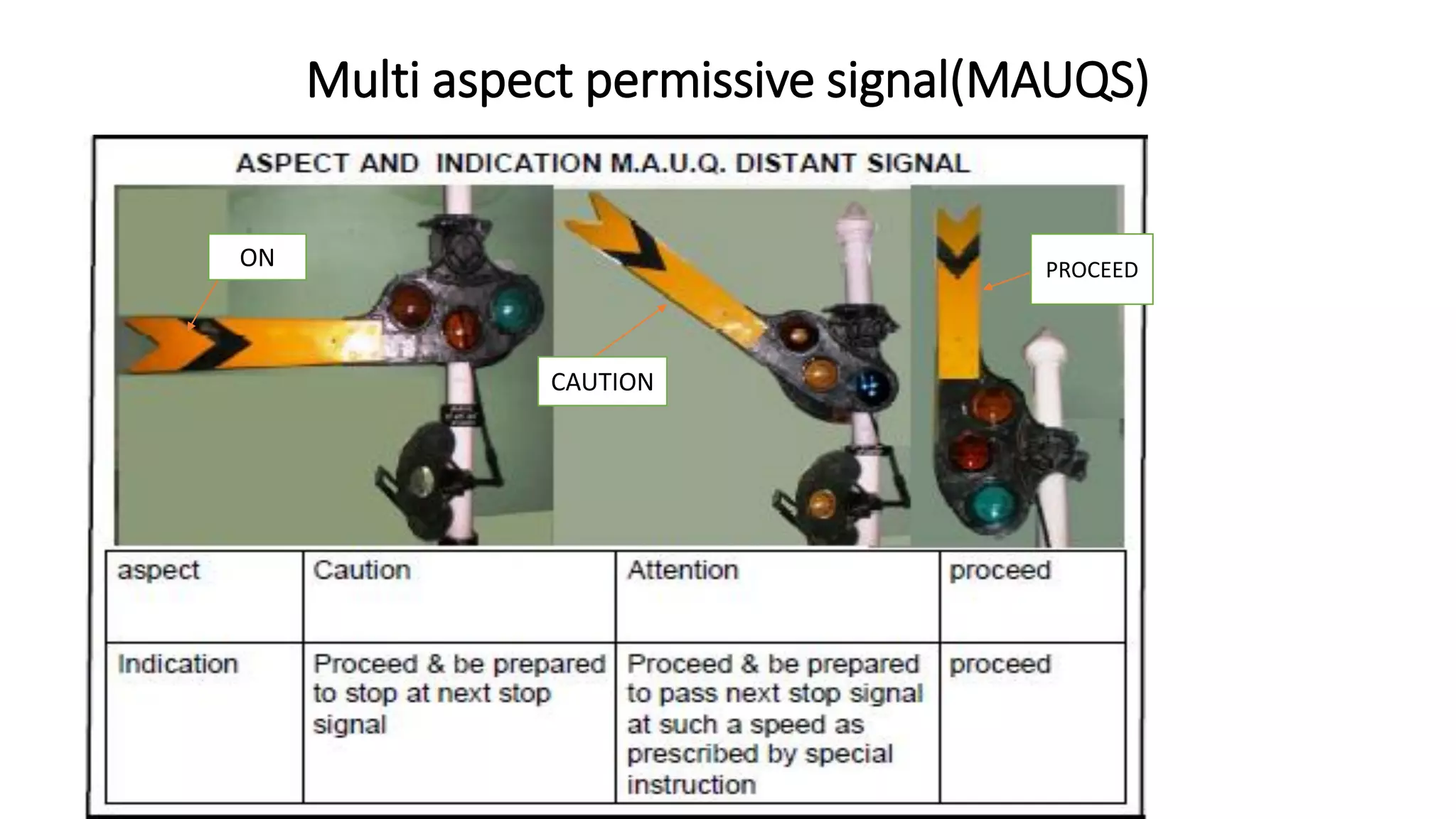
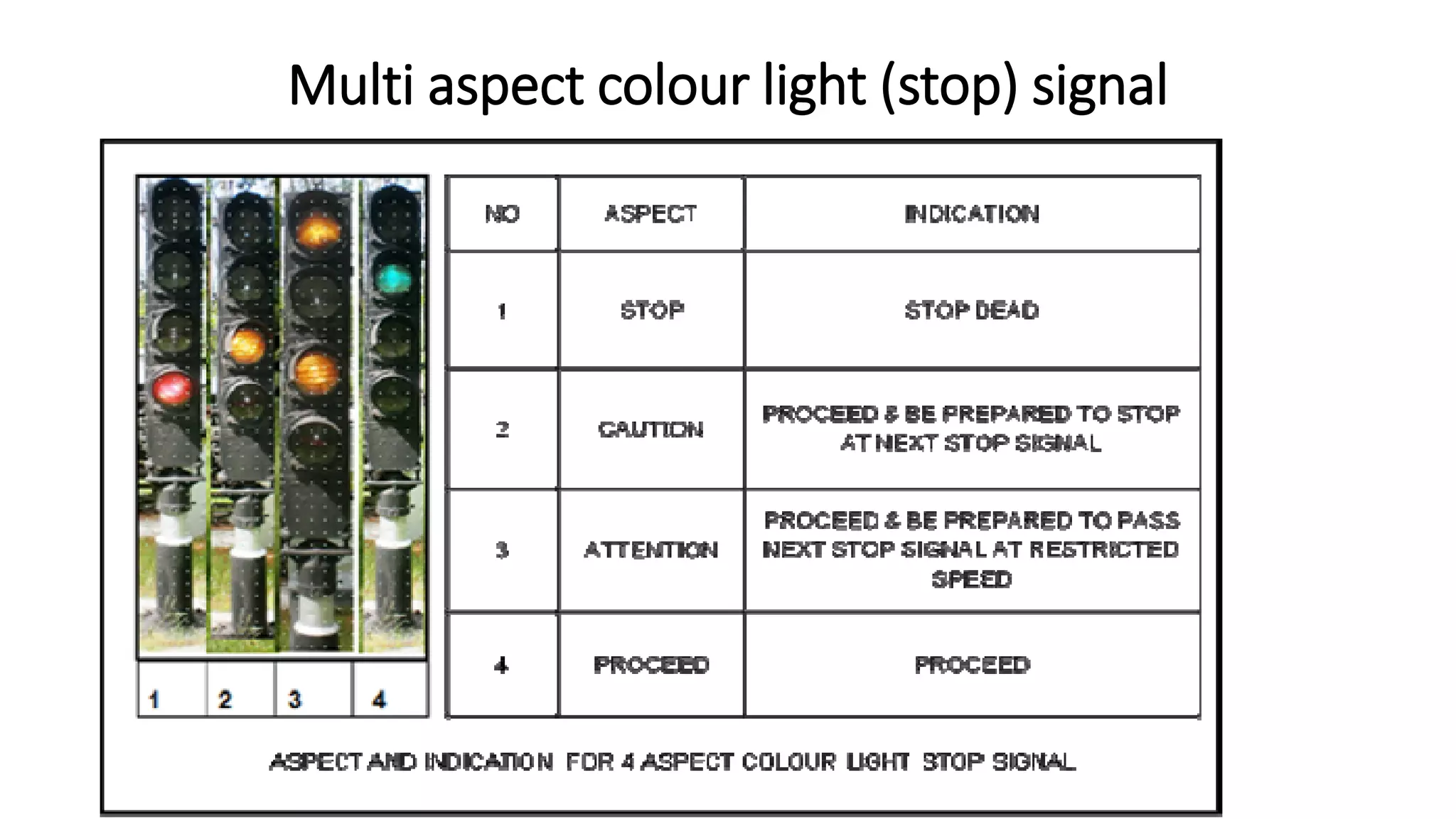
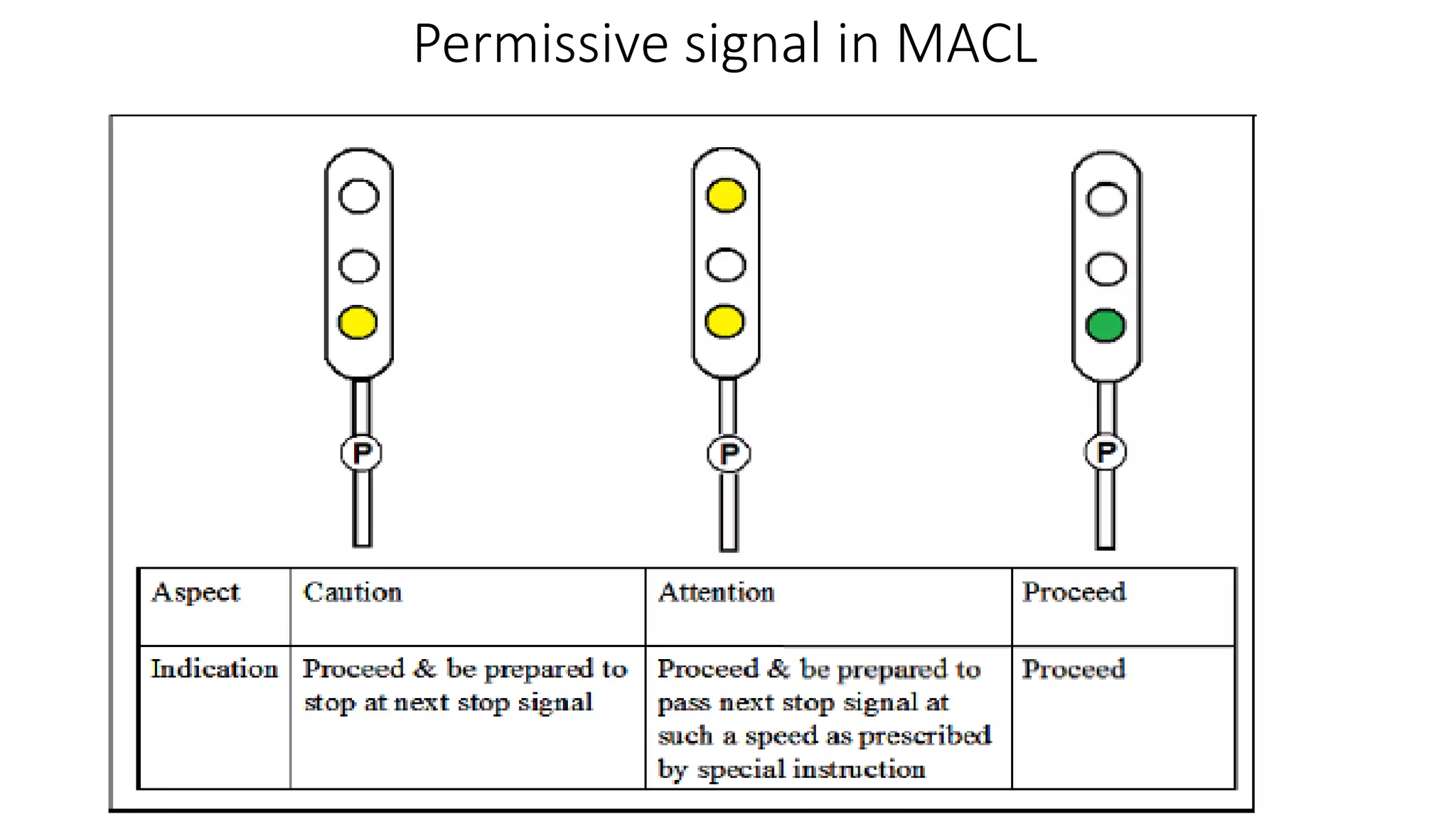
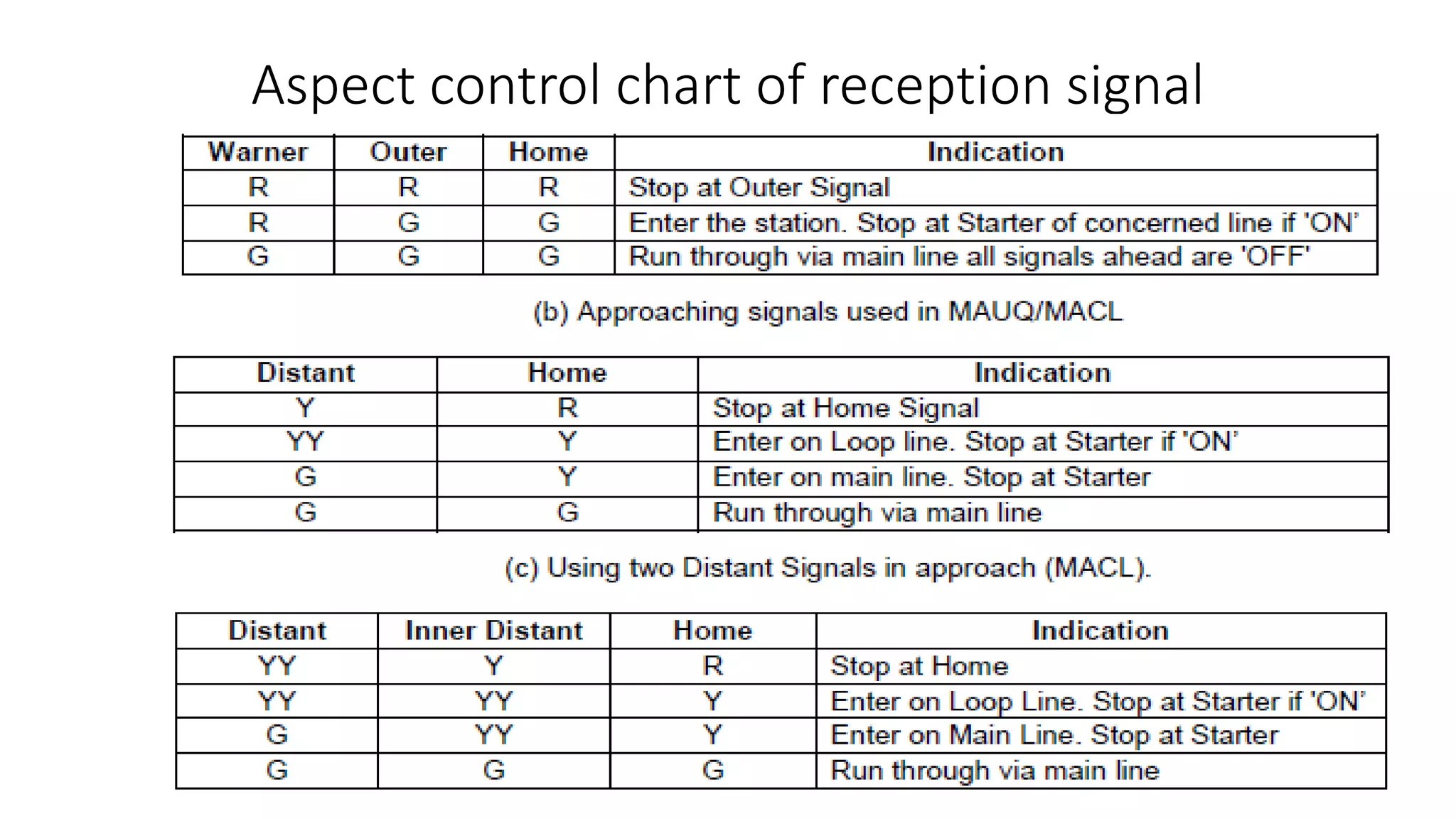
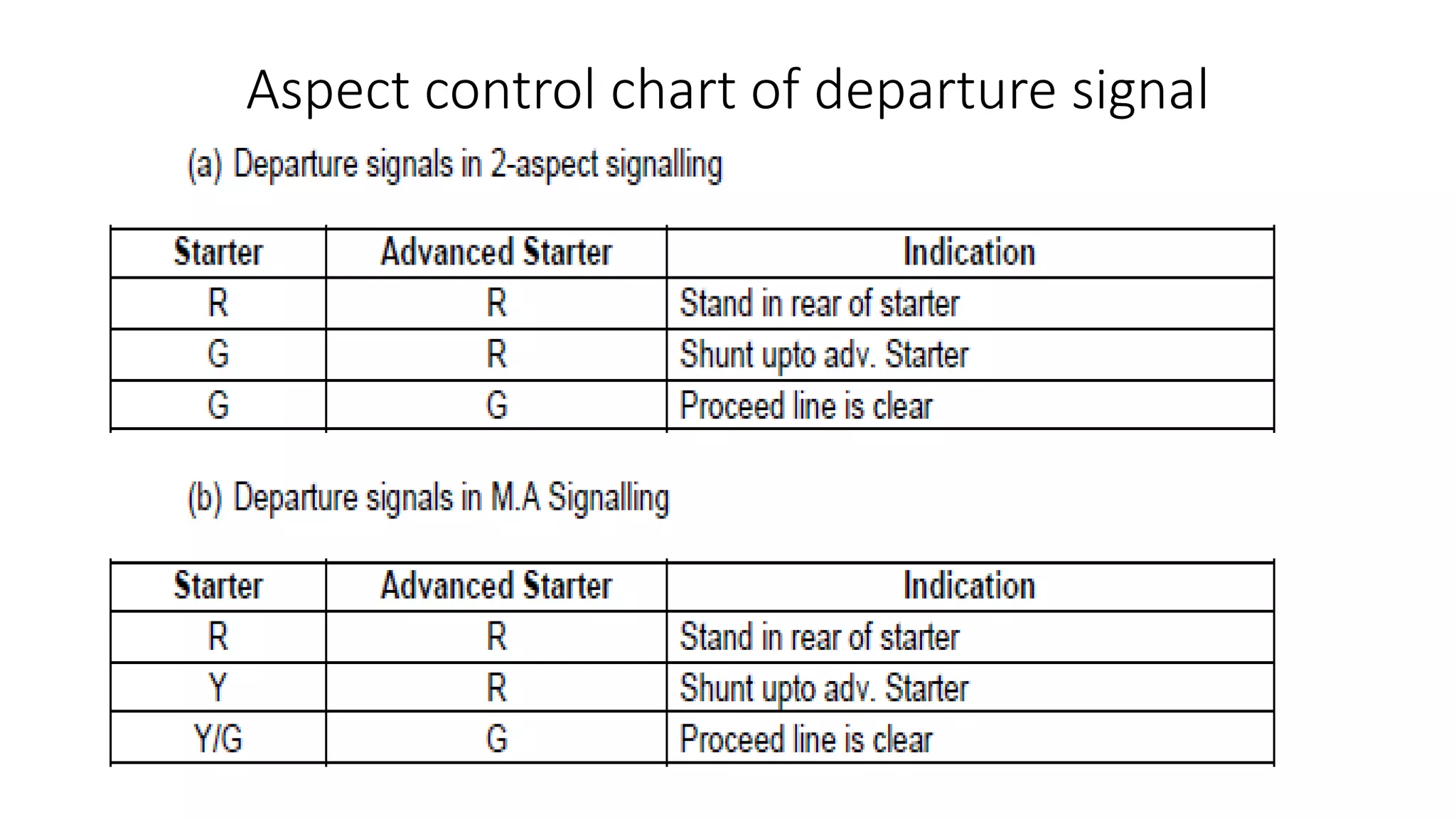
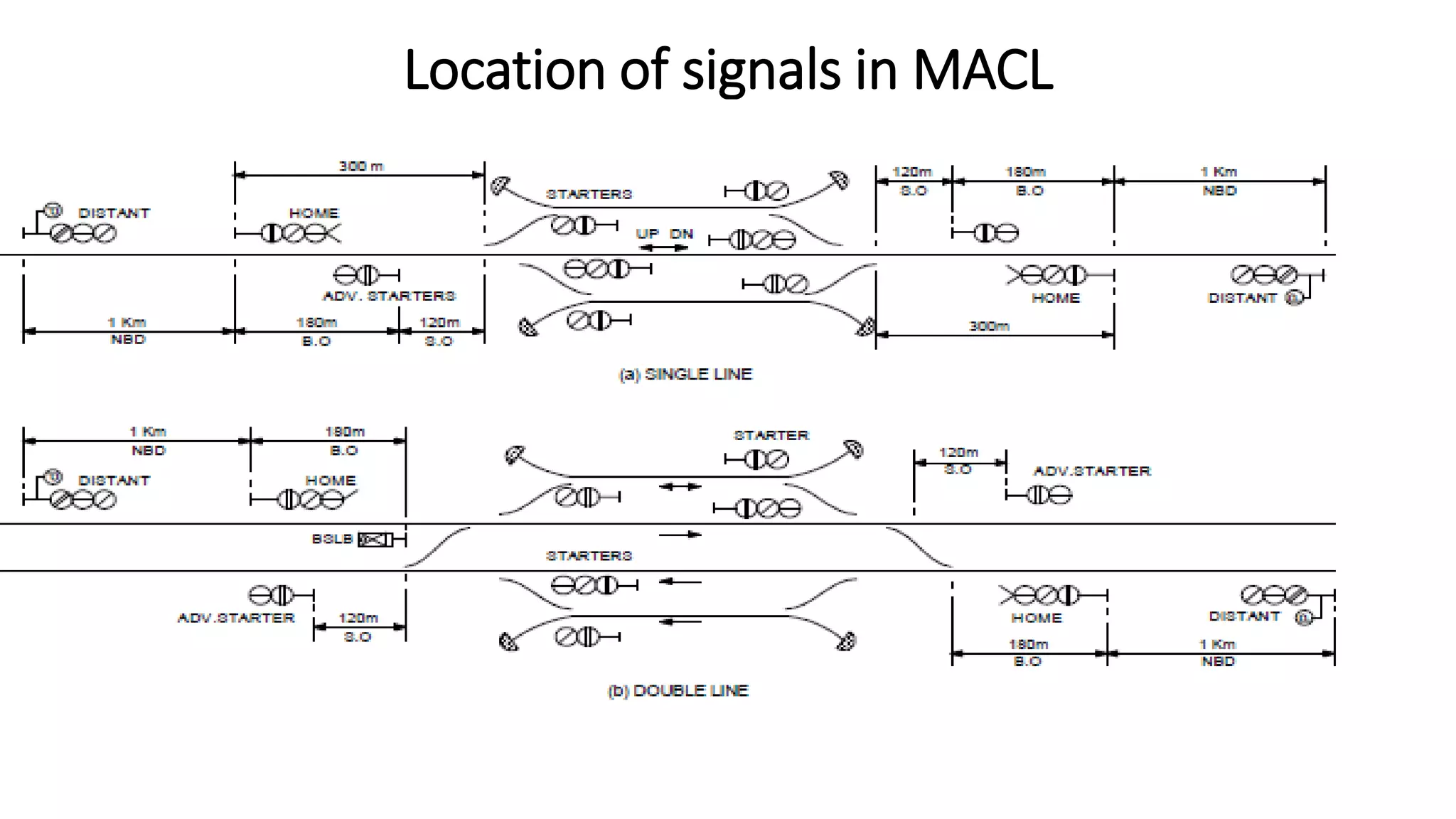
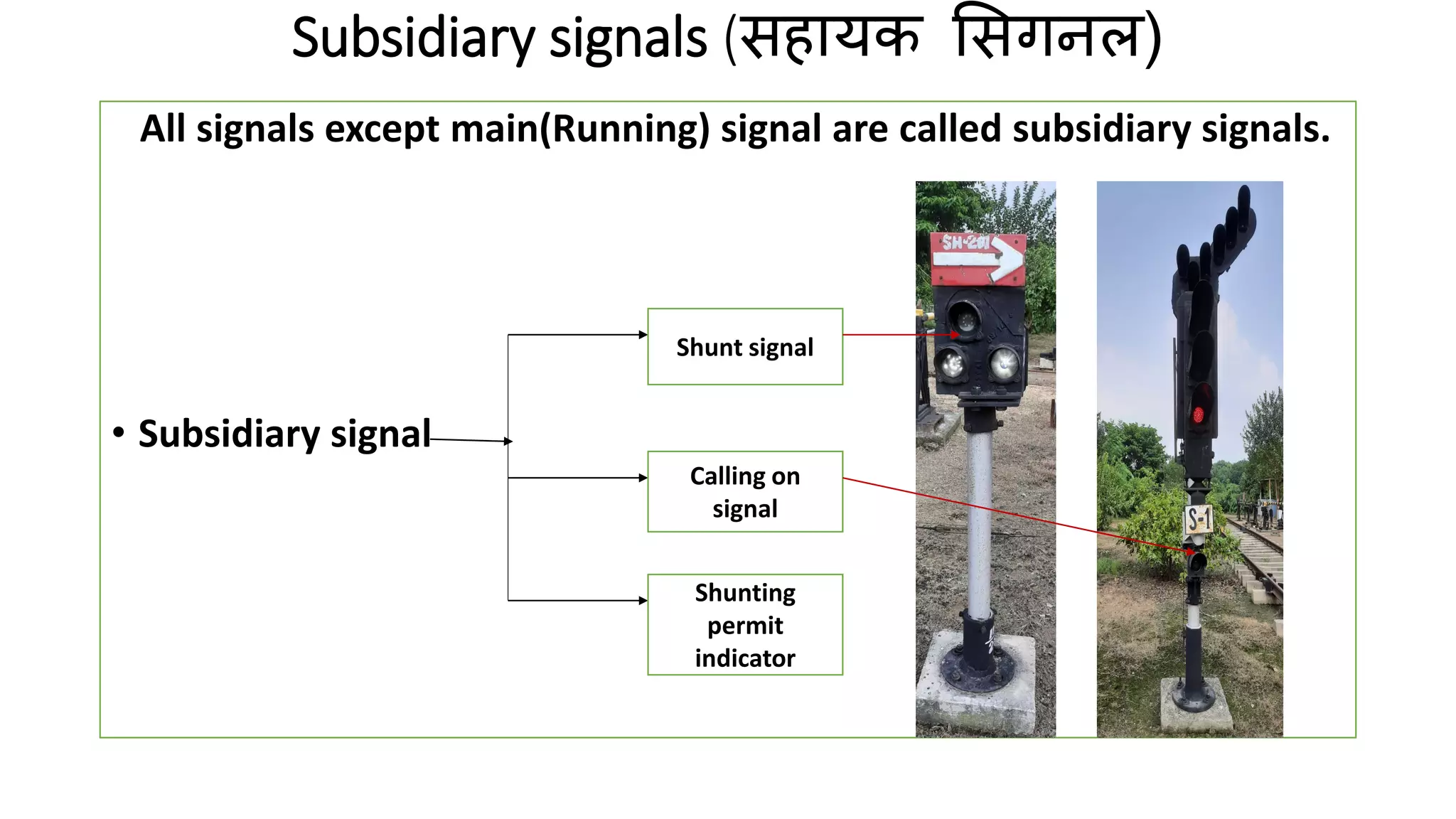
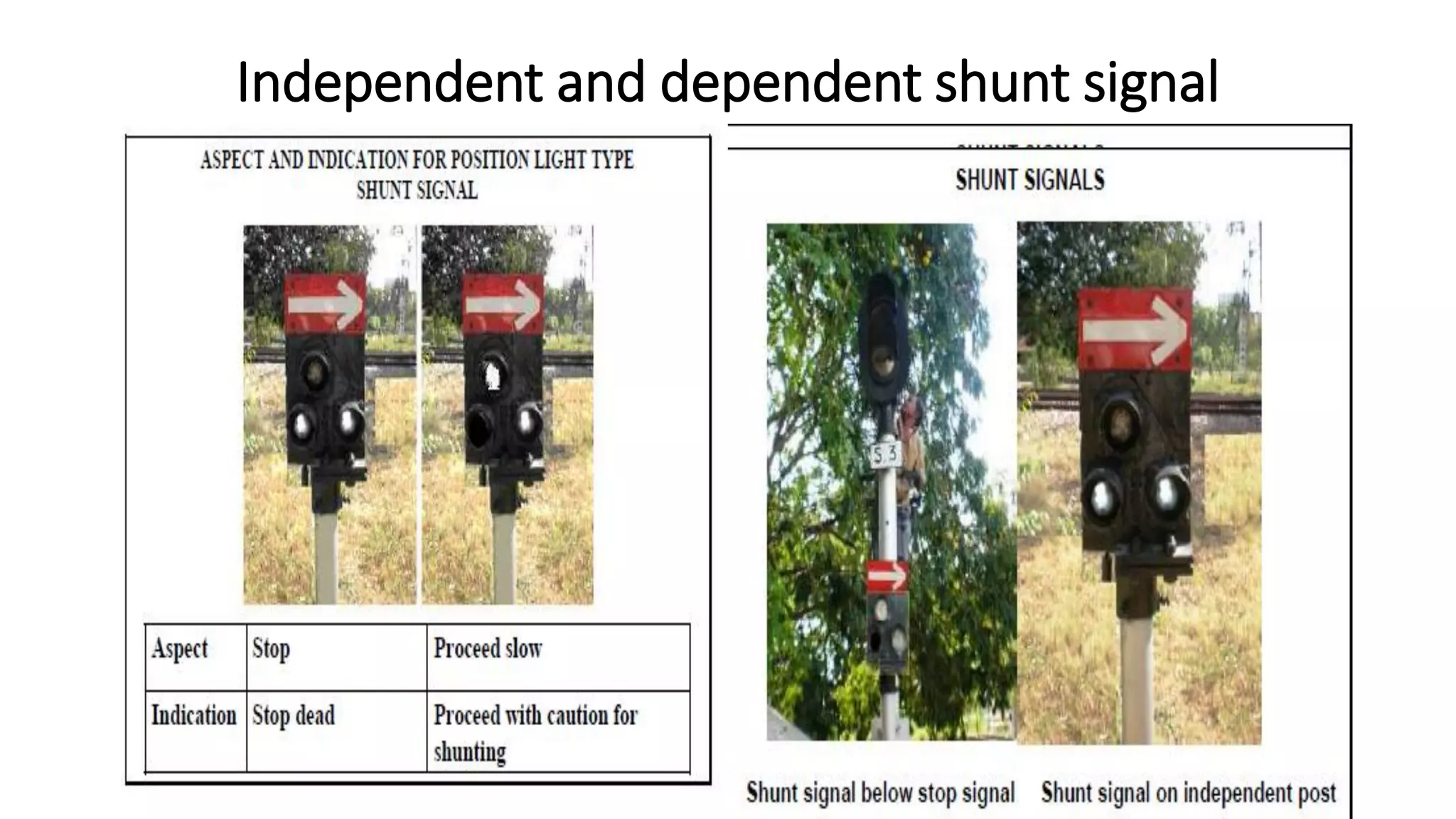
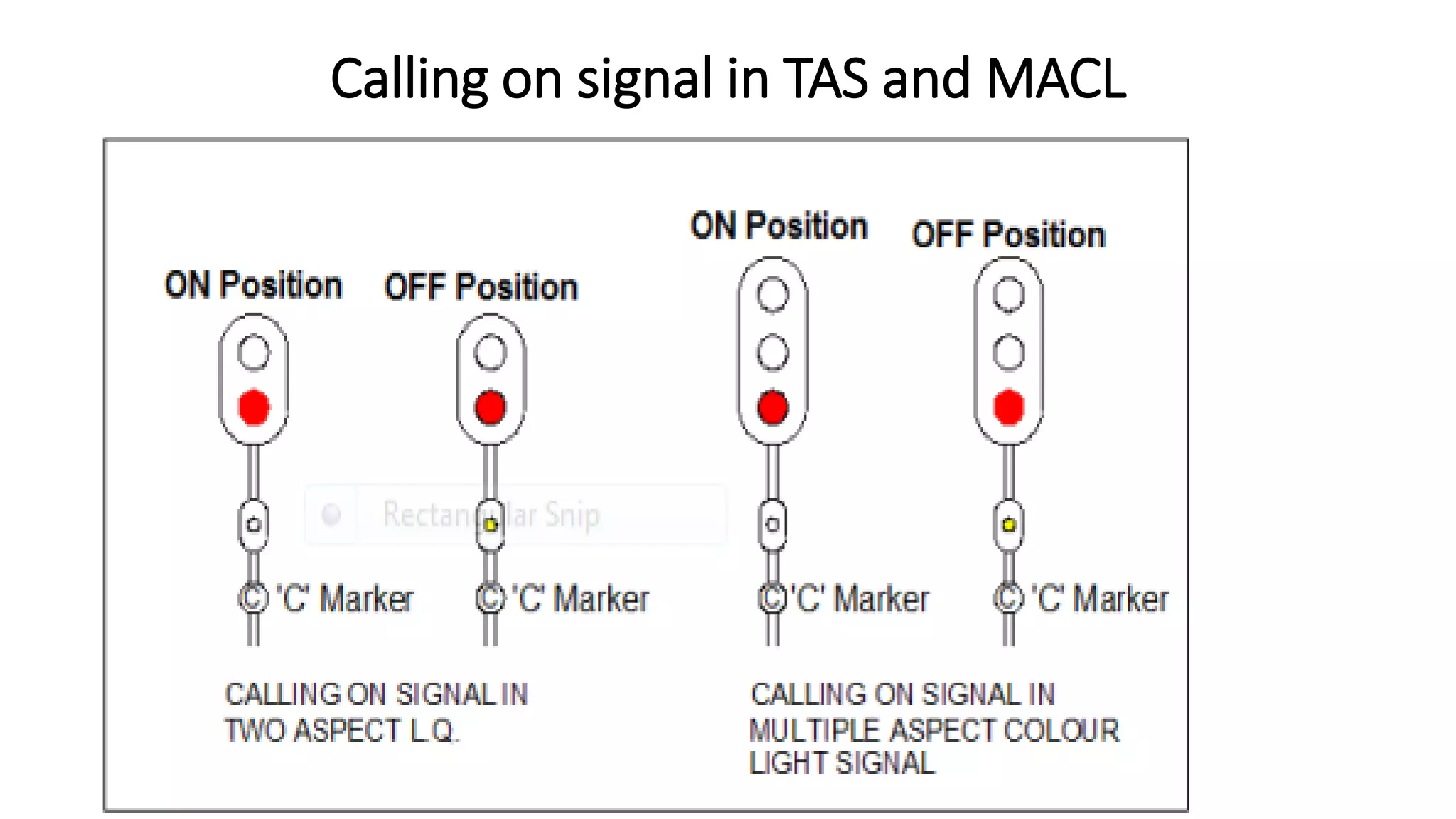
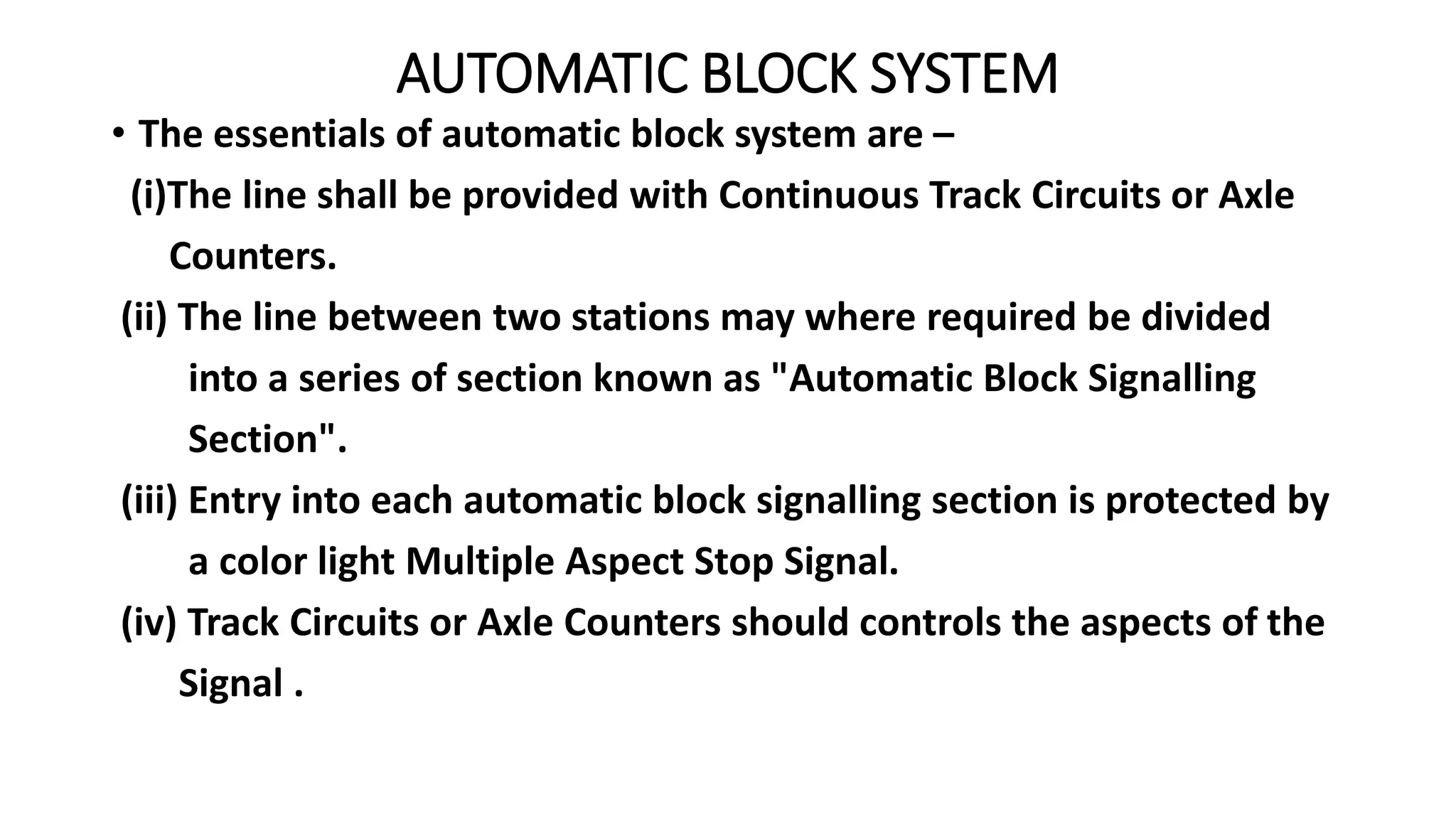
Fixed signals like home signals, starter signals and distant signals are used to control train movements on the railway track. Signals can be two-aspect or multi-aspect and include semaphore signals and colour light signals. The absolute block system is used for train working where line clear is obtained from the next block station and adequate distance beyond signals is kept clear. Automatic block system uses track circuits and axle counters to control signal aspects for train movement between stations.

![CLASSIFICATION OF SIGNAL IN I.R
VISIUL AUDIABLE
MOVABLE
FLAG SIGNAL
FIXED
SIGNAL
FLARE
SIGNAL
DETONATOR
SIGNAL
VOICE WHISTLE
RUNNING
SIGNAL
SUBSIDARY
SIGNAL
TWO ASPECT MULTI
ASPECT SIGNAL
SEMAPHORE
SGNAL
CLS
SEMAPHORE
SGNAL CLS
MINIATURE
ARM
DISC TYPE
POSITION
LIGHT TYPE
CLS TYPE
[d1]
SIGNALS](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/signalsystempptbasicintro-230717060656-fbabddcd/75/signal-system-ppt-basic-intro-pdf-2-2048.jpg)