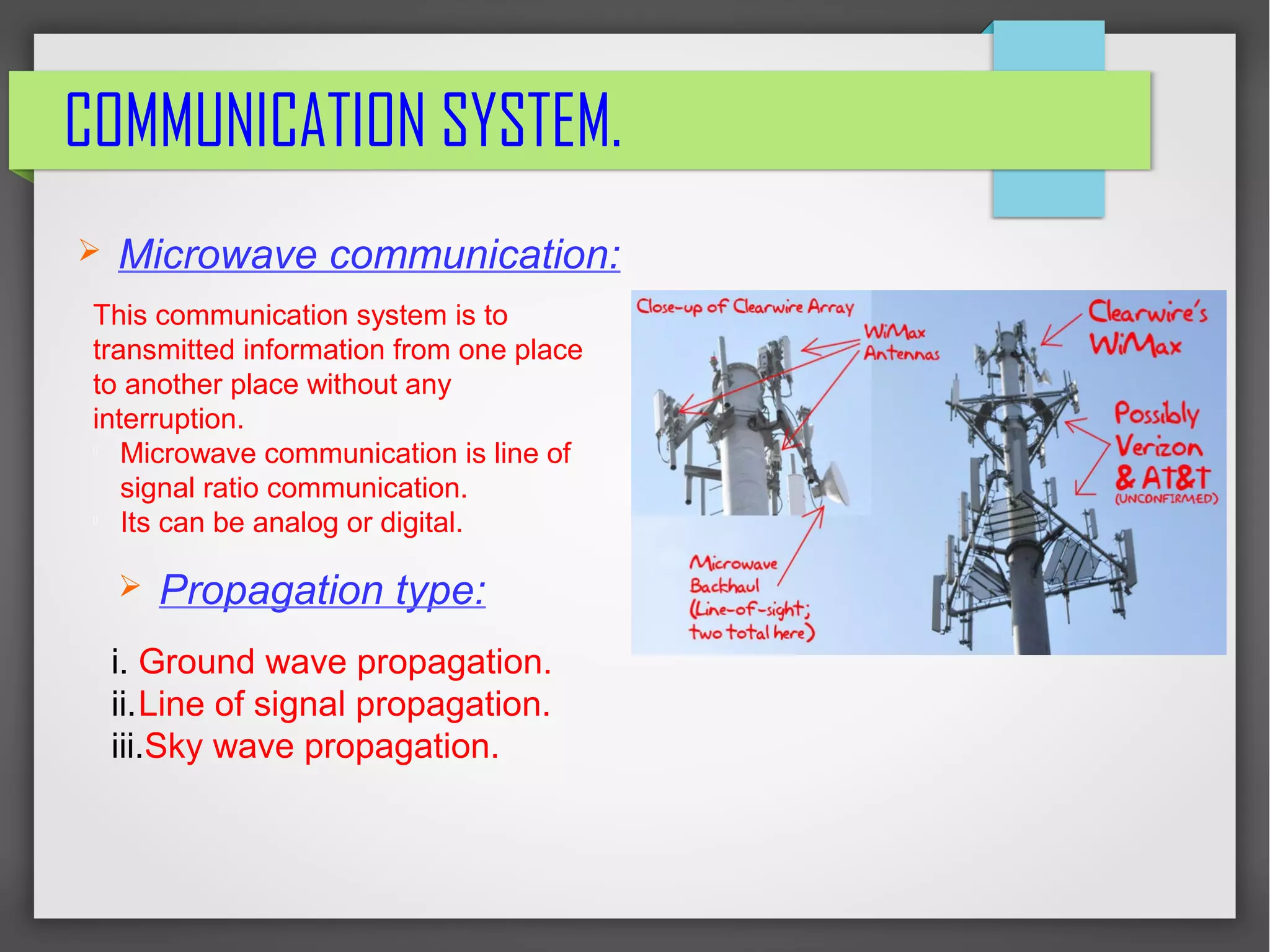
This presentation summarizes the Indian railway signal system. It introduces the Indian railway network as the 4th largest in the world comprising over 115,000 km of track. It then describes the key components of the railway signaling system including block signals, fixed signals, mechanical signals, color light signals and cab signals. It also discusses interlocking systems which use mechanical and electrical devices to coordinate signaling and ensure safe train movements. The presentation concludes by covering communication systems used for train traffic control such as microwave transmission and optical fiber communication.