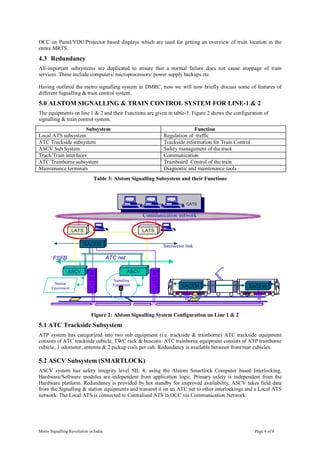
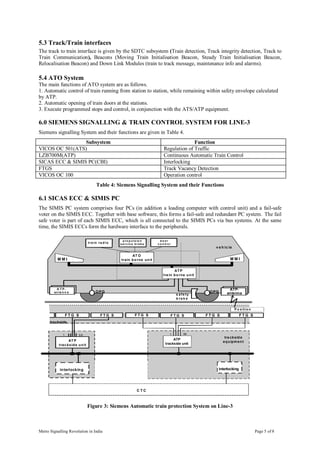
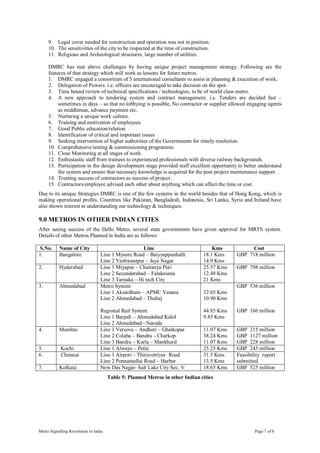
This document provides a case study of the development of metro signalling systems in India. It details how Delhi Metro Rail Corporation introduced the latest ERTMS level 2 signalling and train control system, the first of its kind in India. The document describes the features of DMRC's signalling and train control system and the challenges faced in implementing this modern technology. It also summarizes the signalling requirements of upcoming metro systems in India and important issues around achieving interoperability as urban transport expands rapidly.