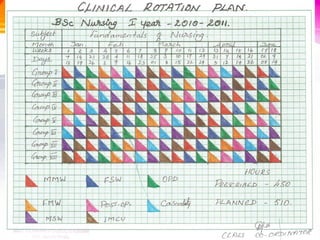
The master rotation plan outlines the systematic rotation of nursing students through various clinical and theoretical blocks in an educational institution, aiming to enhance coordination between theory and practice. It is designed to prepare students and faculty for a seamless educational experience and facilitate the effective evaluation of the curriculum. Key principles include advance planning, clear objectives, and ensuring all students have equitable clinical experiences.