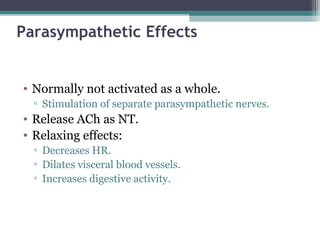
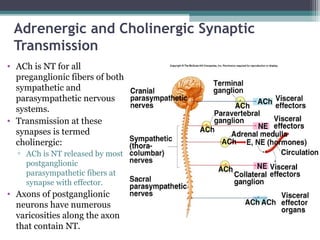
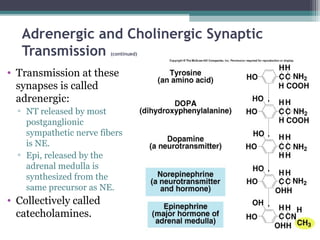
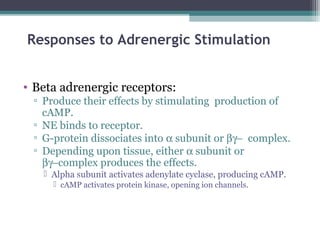
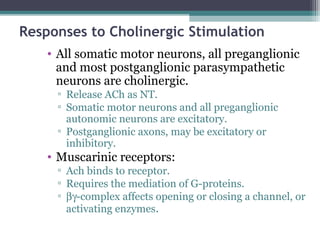
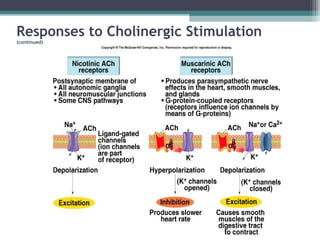
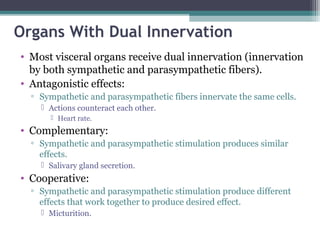
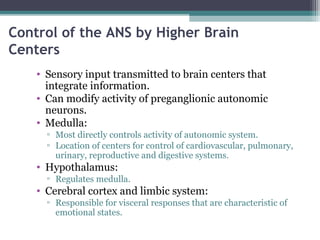
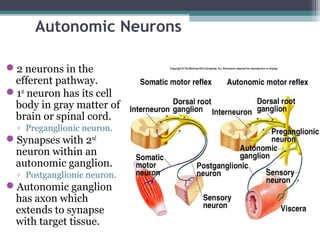
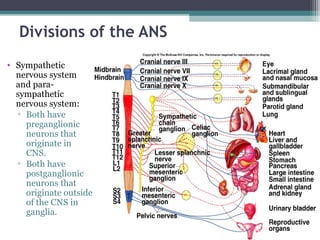
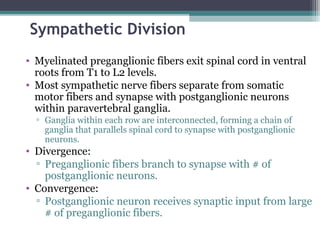
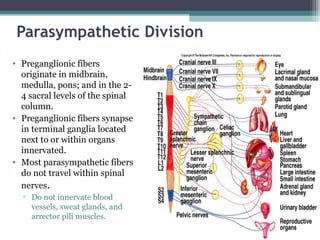
The autonomic nervous system (ANS) controls involuntary organs and consists of the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions. The sympathetic division activates the fight or flight response while the parasympathetic division elicits relaxing effects. Both divisions have two-neuron pathways, with the first neuron synapsing in an autonomic ganglion. The sympathetic system uses norepinephrine as its neurotransmitter while the parasympathetic system uses acetylcholine. Organs can receive dual innervation from both divisions, leading to antagonistic, complementary, or cooperative effects. Higher brain centers integrate sensory input to control autonomic function.





![Sympathetic Effects
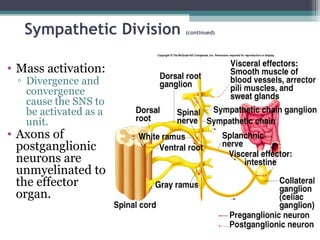
• Fight or flight response.
• Release of norepinephrine (NT) from
postganglionic fibers and epinephrine (NT)
from adrenal medulla.
• Mass activation prepares for intense activity.
▫ Heart rate (HR) increases.
▫ Bronchioles dilate.
▫ Blood [glucose] increases.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chp9theautonomicnervoussystem-151007042708-lva1-app6892/85/The-autonomic-nervous-system-12-320.jpg)