Embed presentation
Download to read offline
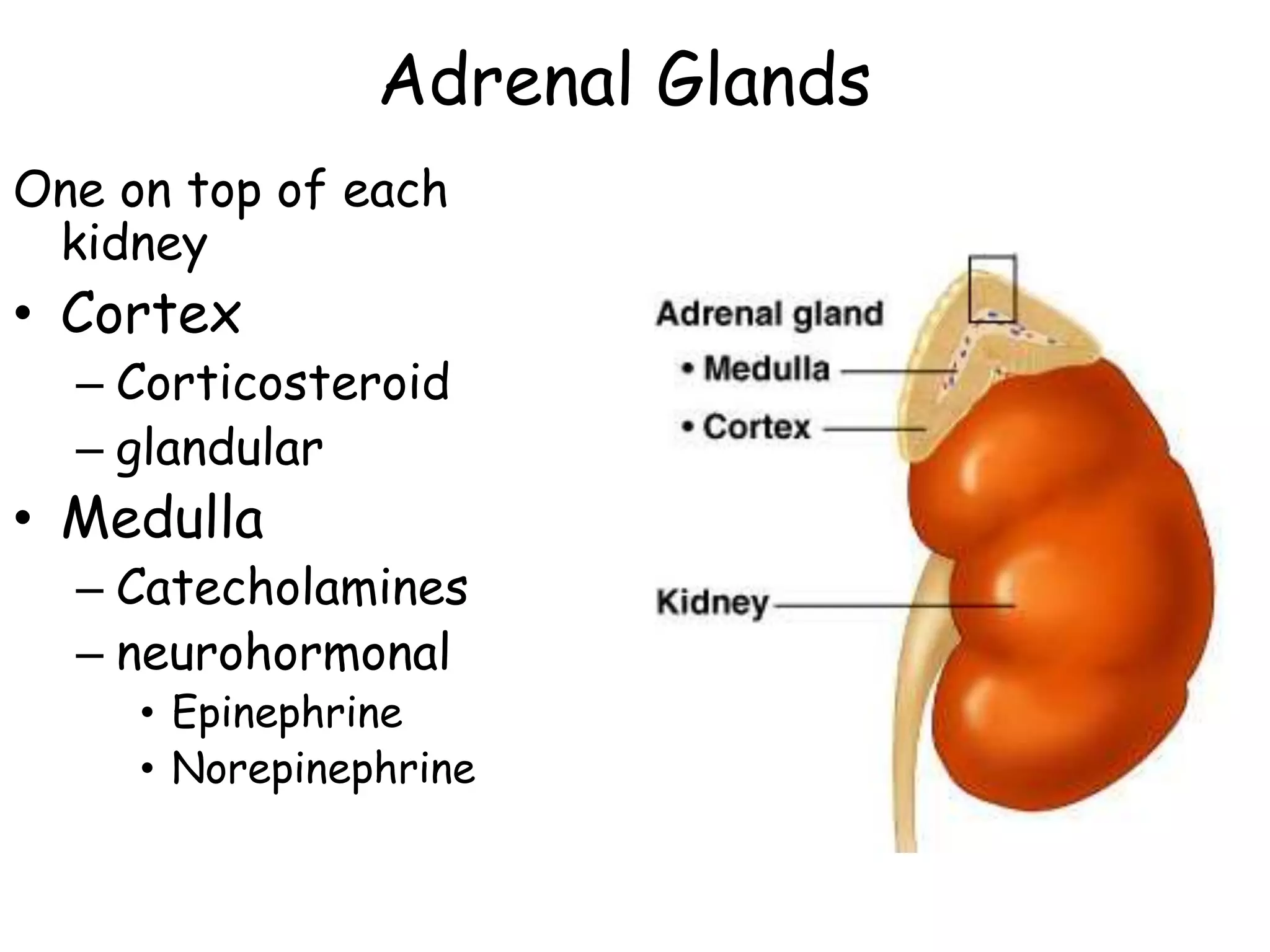
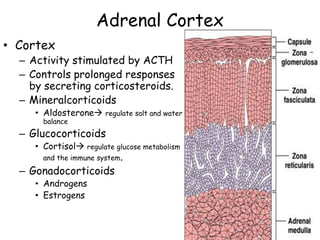
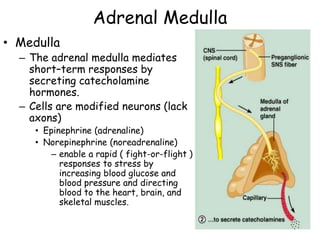
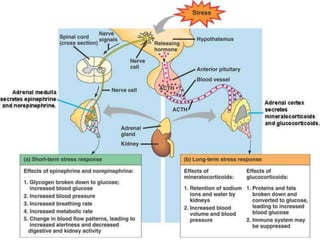

The adrenal glands are located on top of each kidney and consist of an outer cortex and inner medulla. The cortex secretes corticosteroids like cortisol and aldosterone which regulate processes like glucose metabolism, immune function, and salt/water balance. The medulla secretes catecholamines like epinephrine and norepinephrine to enable rapid fight-or-flight stress responses that increase blood glucose, blood pressure, and blood flow to major organs.



