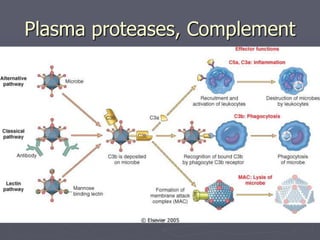
Leukocytes play a key role in the inflammatory response through activation, increased movement, and expression of adhesion molecules. Once activated, they kill pathogens using granule contents, oxidative burst, and inflammatory mediators. Key mediators that promote inflammation include histamine, bradykinin, arachidonic acid metabolites, plasma proteases, complement, platelet activating factor, cytokines like interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor, chemokines, interferons, and nitric oxide. Together these mediators induce vasodilation, increased permeability, leukocyte recruitment, fever, and other systemic inflammatory responses to fight infection and promote healing.