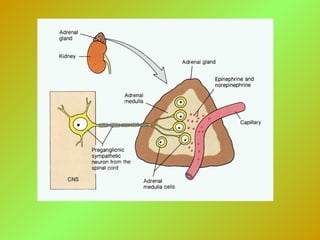
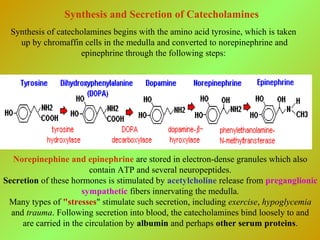
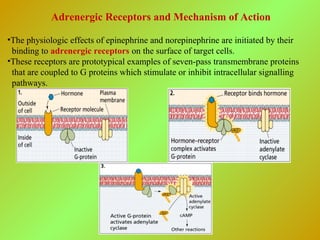
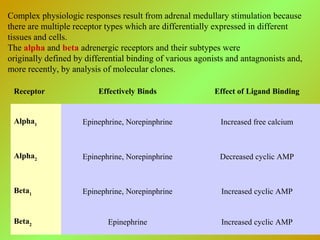
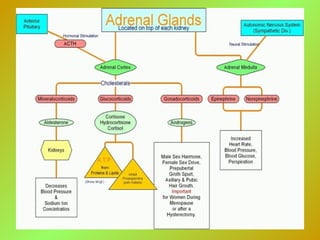
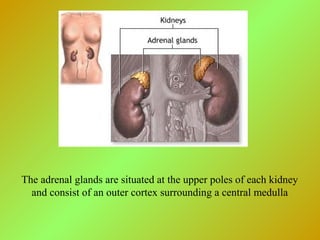
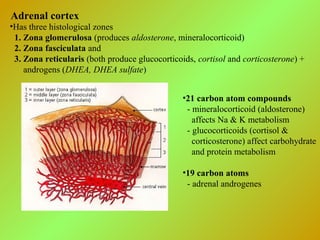
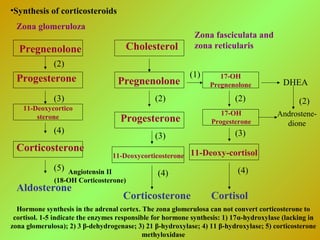
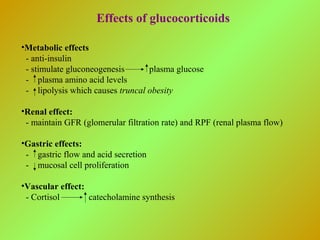
The adrenal glands consist of an outer cortex and inner medulla. The cortex produces mineralocorticoids like aldosterone and glucocorticoids like cortisol. Cortisol regulates metabolism and immune function. Aldosterone regulates sodium and potassium levels. Their release is controlled by the HPA axis and renin-angiotensin system. The medulla produces catecholamines like epinephrine and norepinephrine which increase heart rate and blood pressure through adrenergic receptors. Together these hormones help regulate vital processes and the stress response.




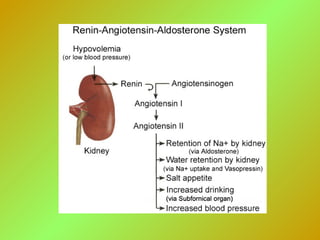
![Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone (control system)Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone (control system)
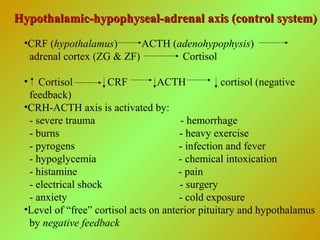
•Renin, a proteolytic enzyme, secreted by juxtaglomerular cells (JG) of the
juxtaglomerular apparatus (JGA)
•Baroreceptors and chemoreceptors of JGA are sensitive to:
- hypovolemia renin
- concentration of Na renin
•The renin-angiotensin system is also stimulated by:
- sympathetic nervous system renin
•Hypotension renin
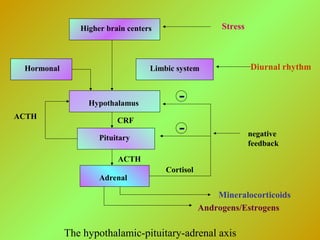
•Aldosterone secretion is controlled by: ECF volume BP or Na
renin (JGA) angiotensin (plasma) angiotensin I
angiotensin II aldosterone (zona glomerulosa) [“converting enzyme”
converts ANG I to ANG II]
• K adrenal zona glomerulosa aldosterone](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adrenalgland-140427101732-phpapp02/85/Adrenalgland-11-320.jpg)