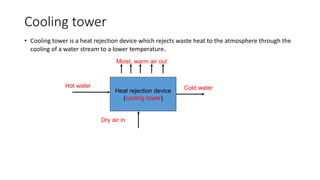
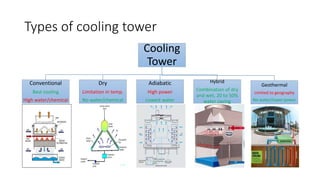
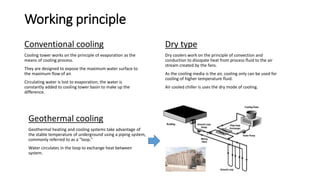
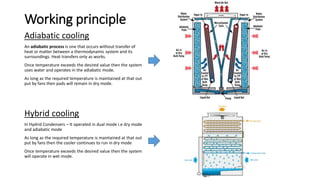
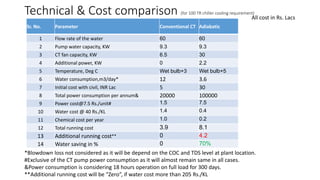
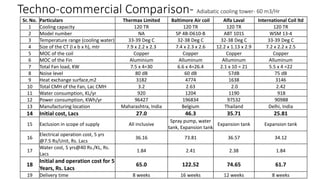
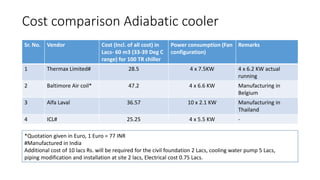
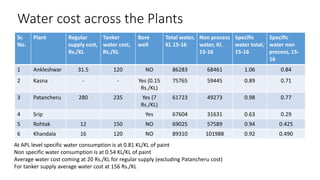
This document discusses options for replacing the existing conventional cooling tower at Asian Paints Limited (APL) with an adiabatic cooling tower. It provides an overview of different cooling tower types, their working principles, and compares the technical specifications, costs, water and energy savings of conventional versus adiabatic cooling towers. Based on its analysis of four vendor options for an adiabatic cooling tower for APL's 100TR chiller cooling requirement, the document recommends installing a tower from International Coil Limited due to its technical capabilities, lowest cost, and satisfactory customer feedback on existing large-scale installations.