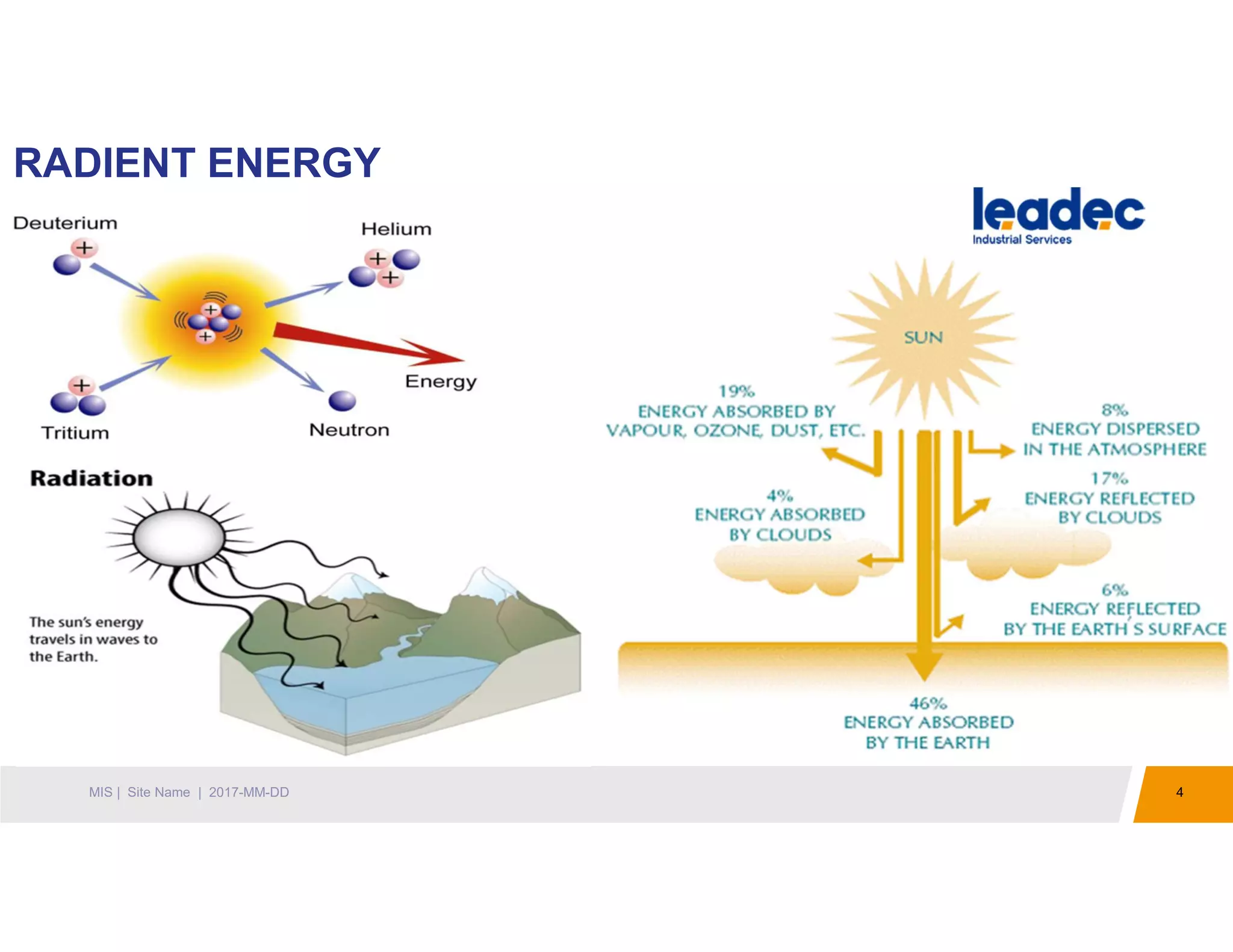
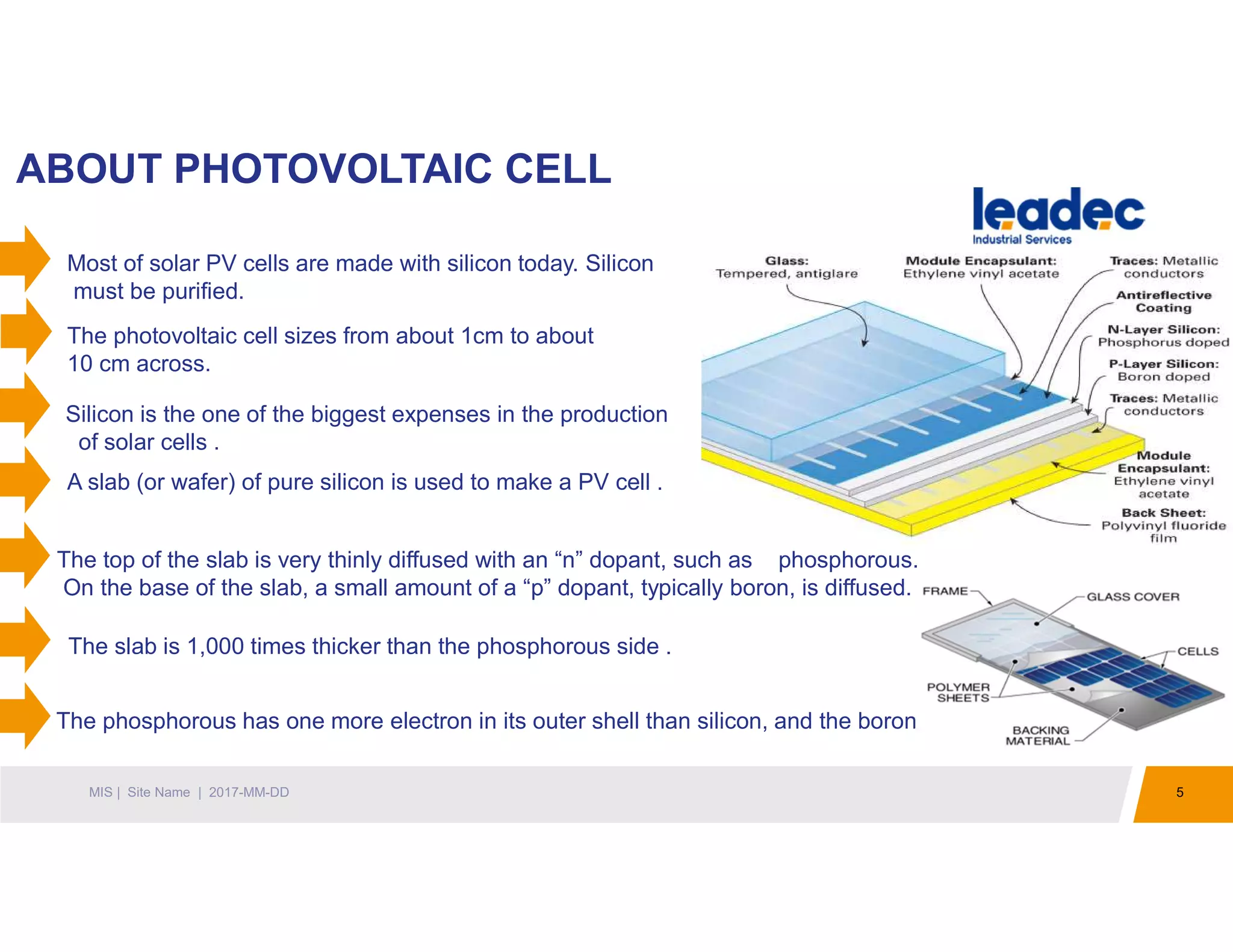
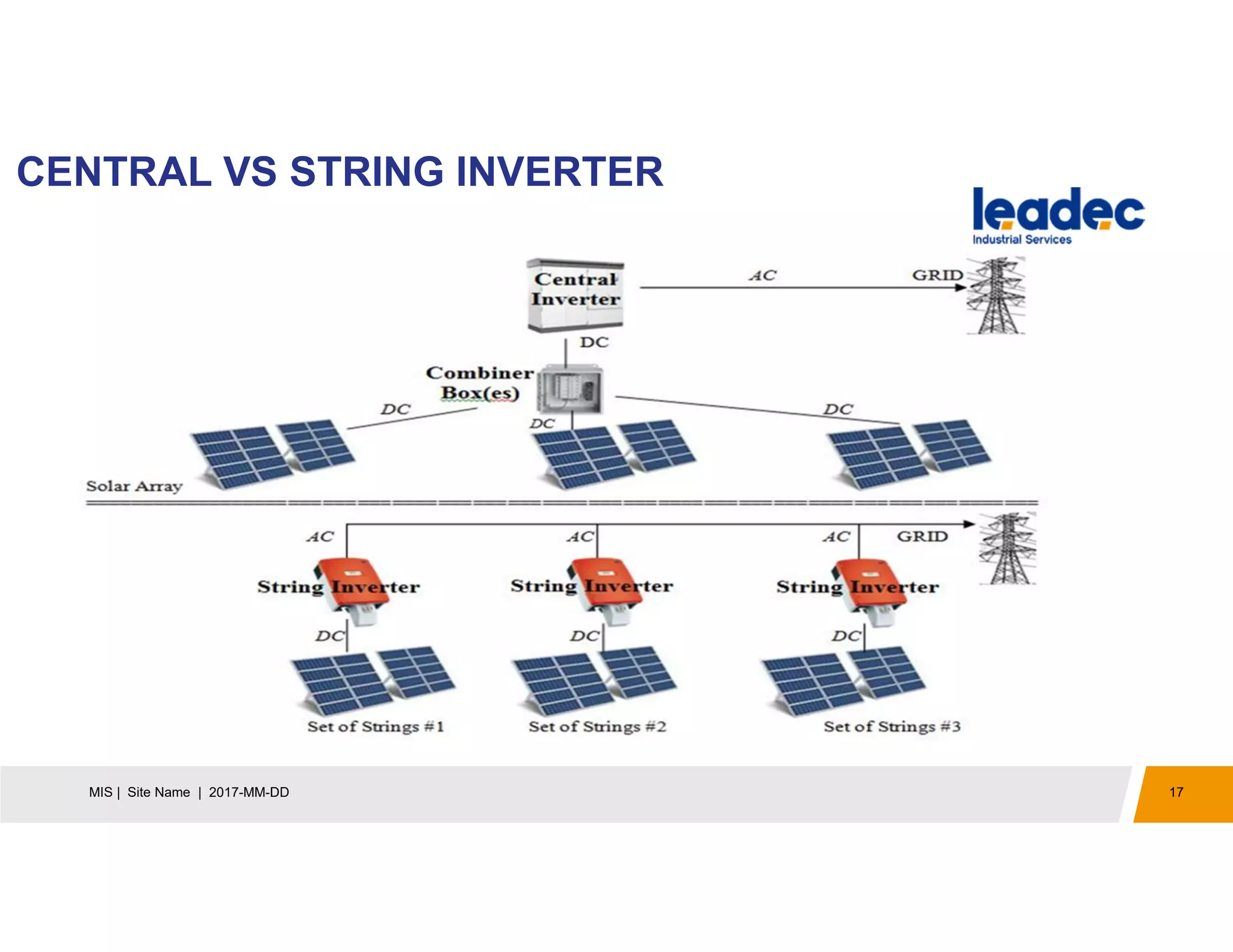
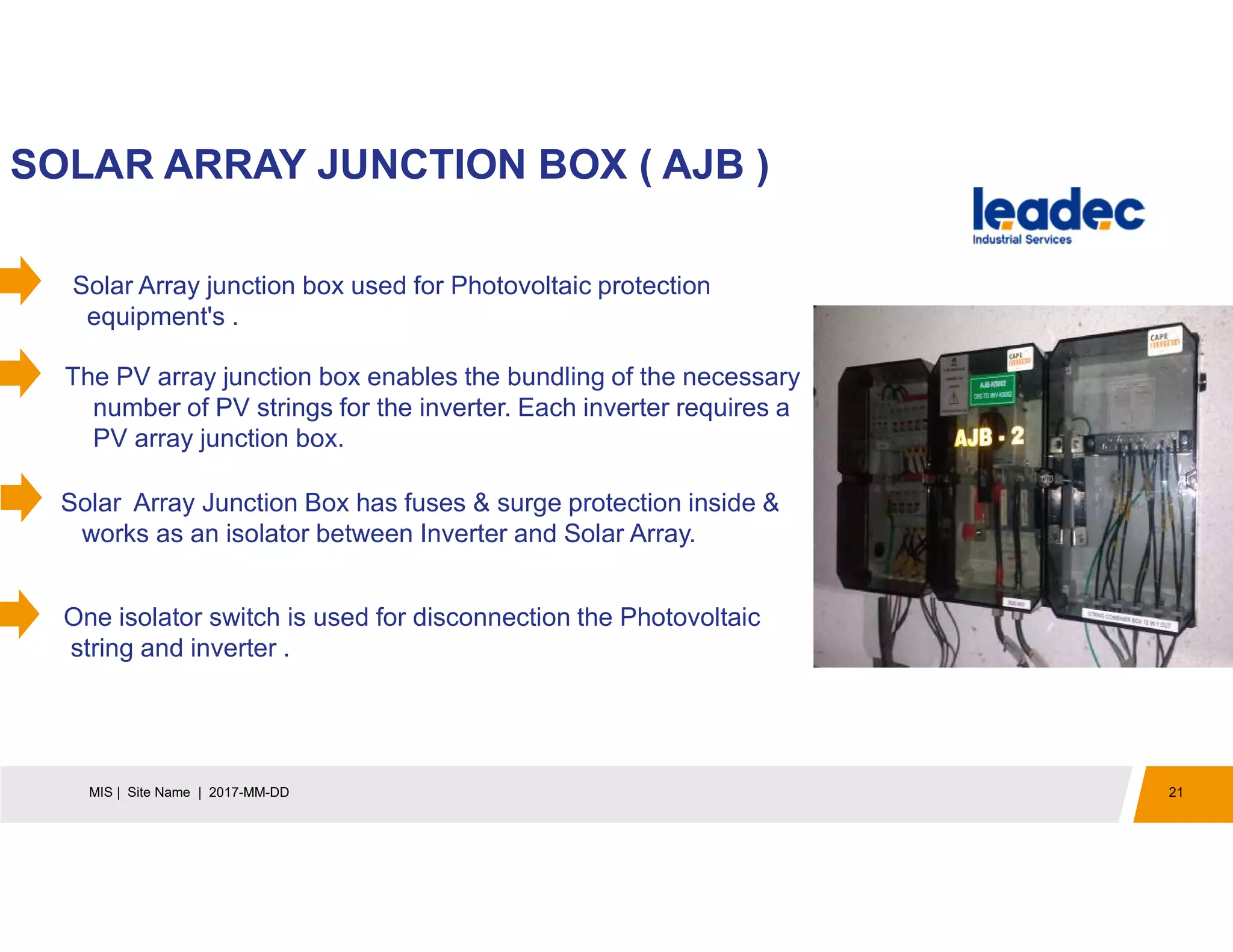
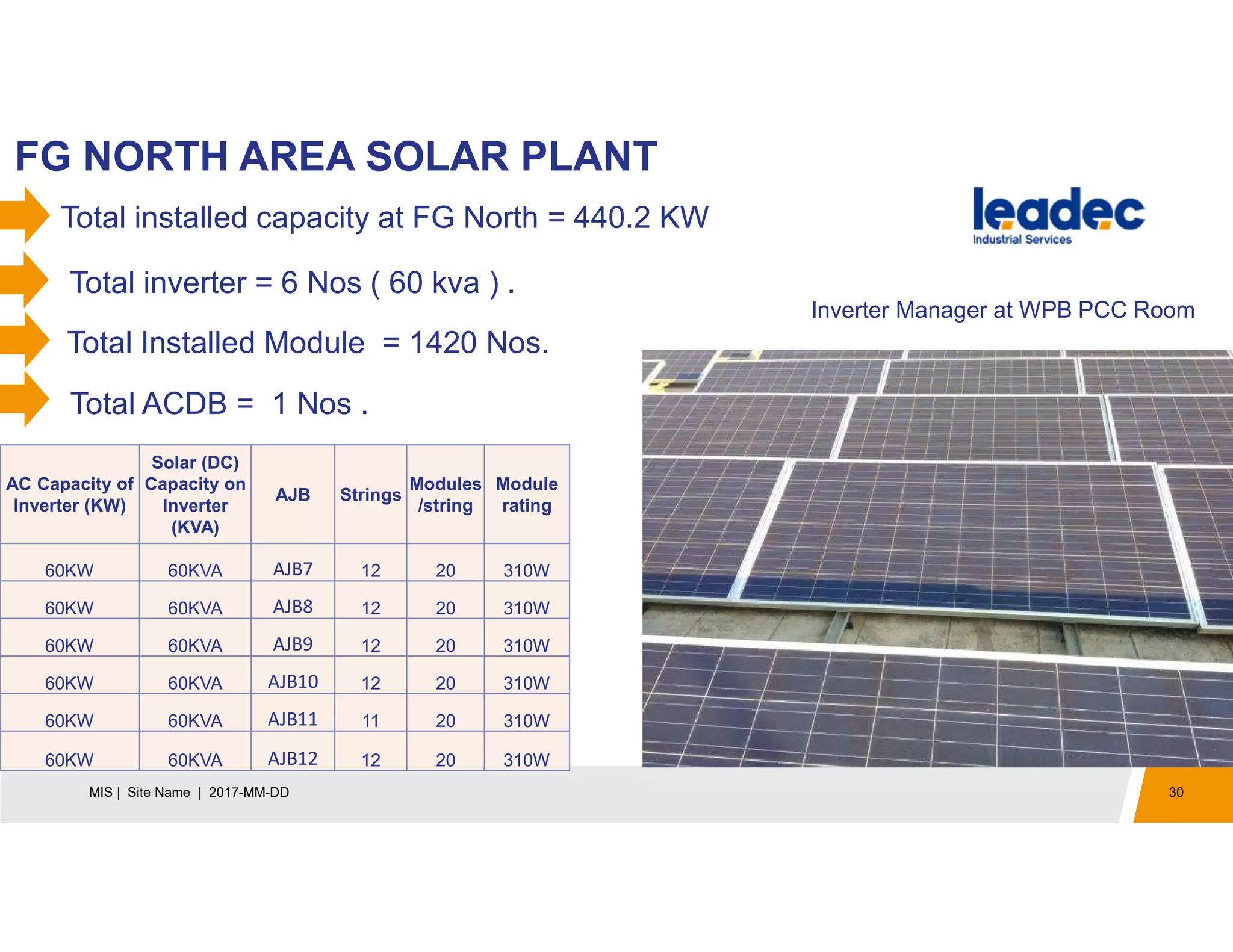
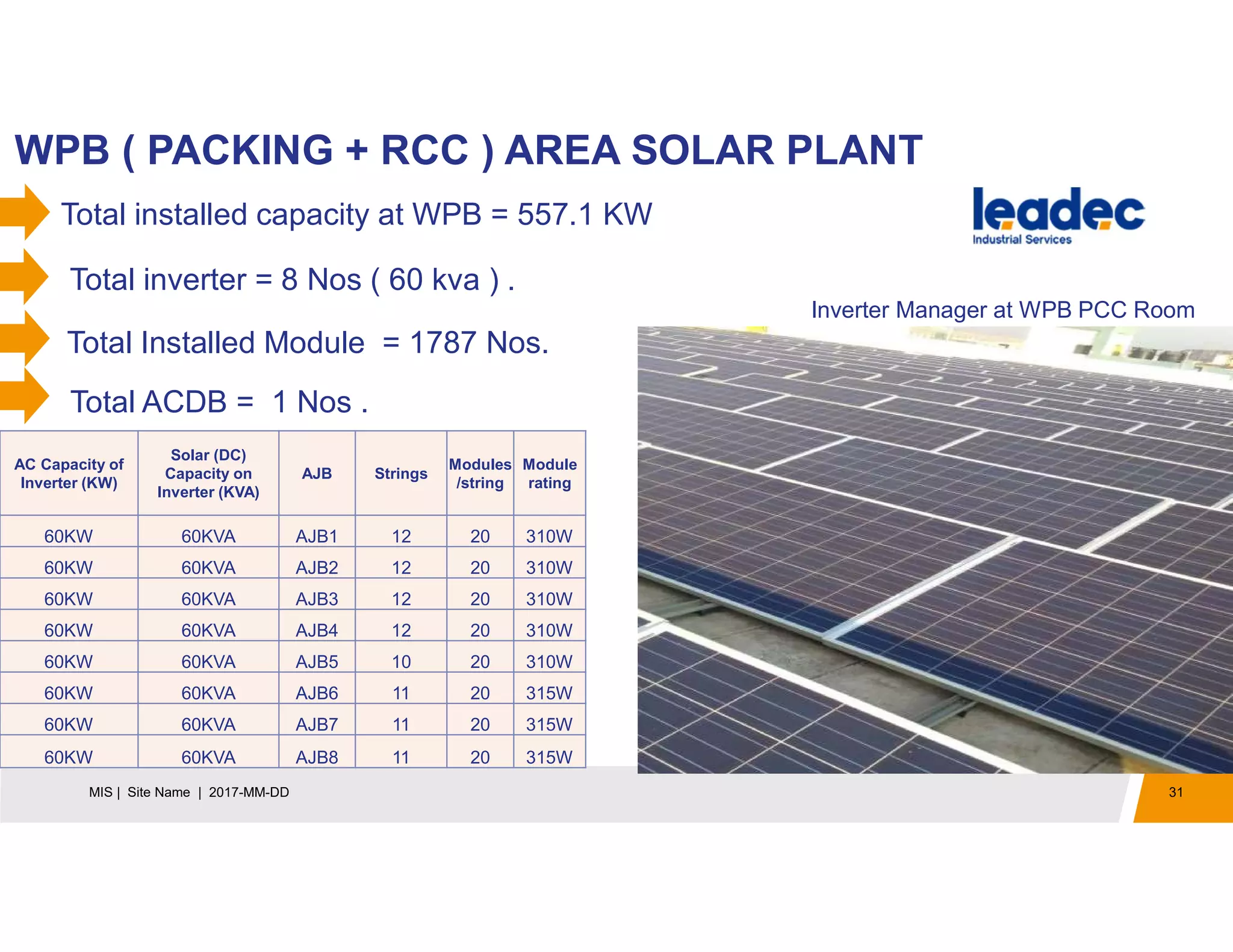
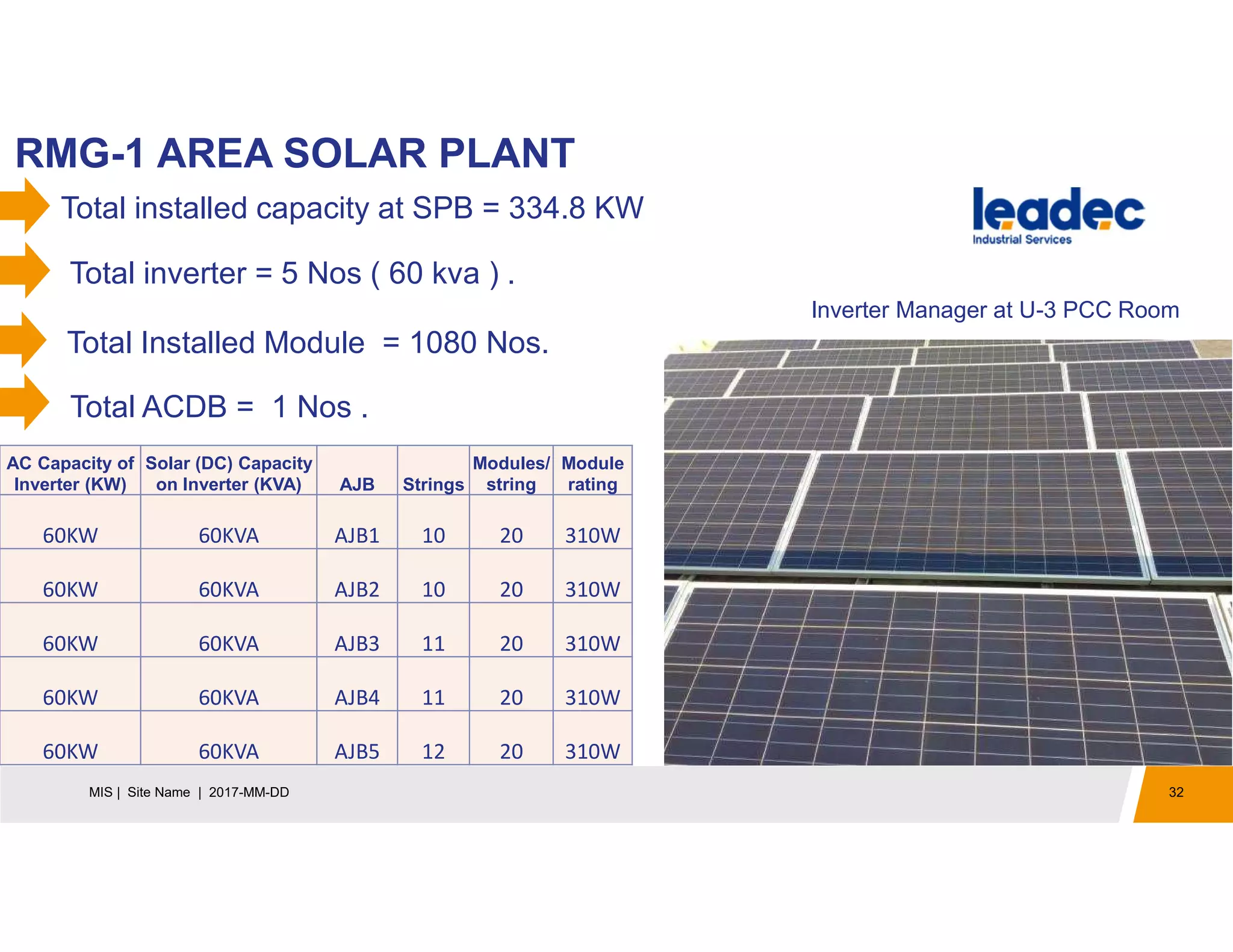
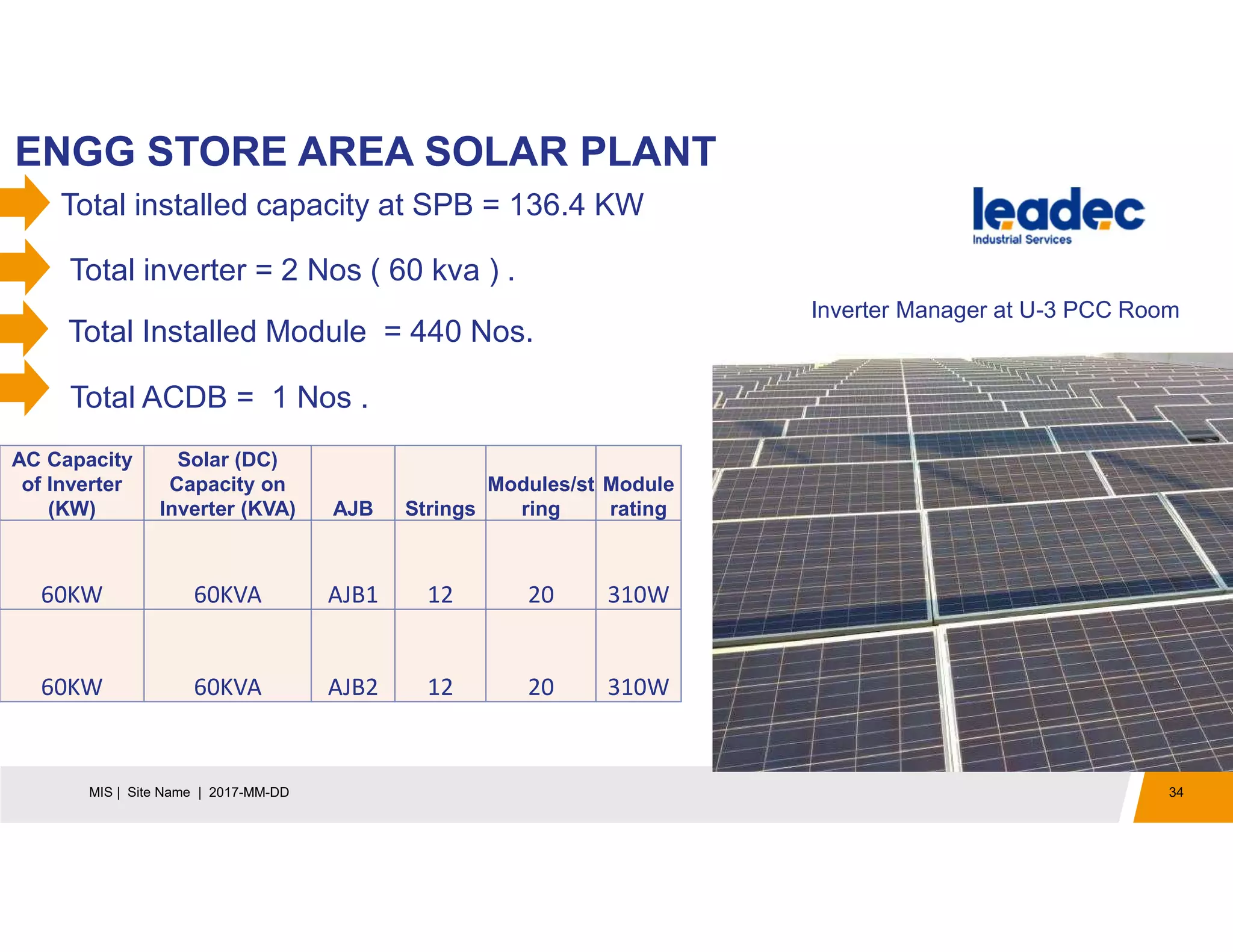
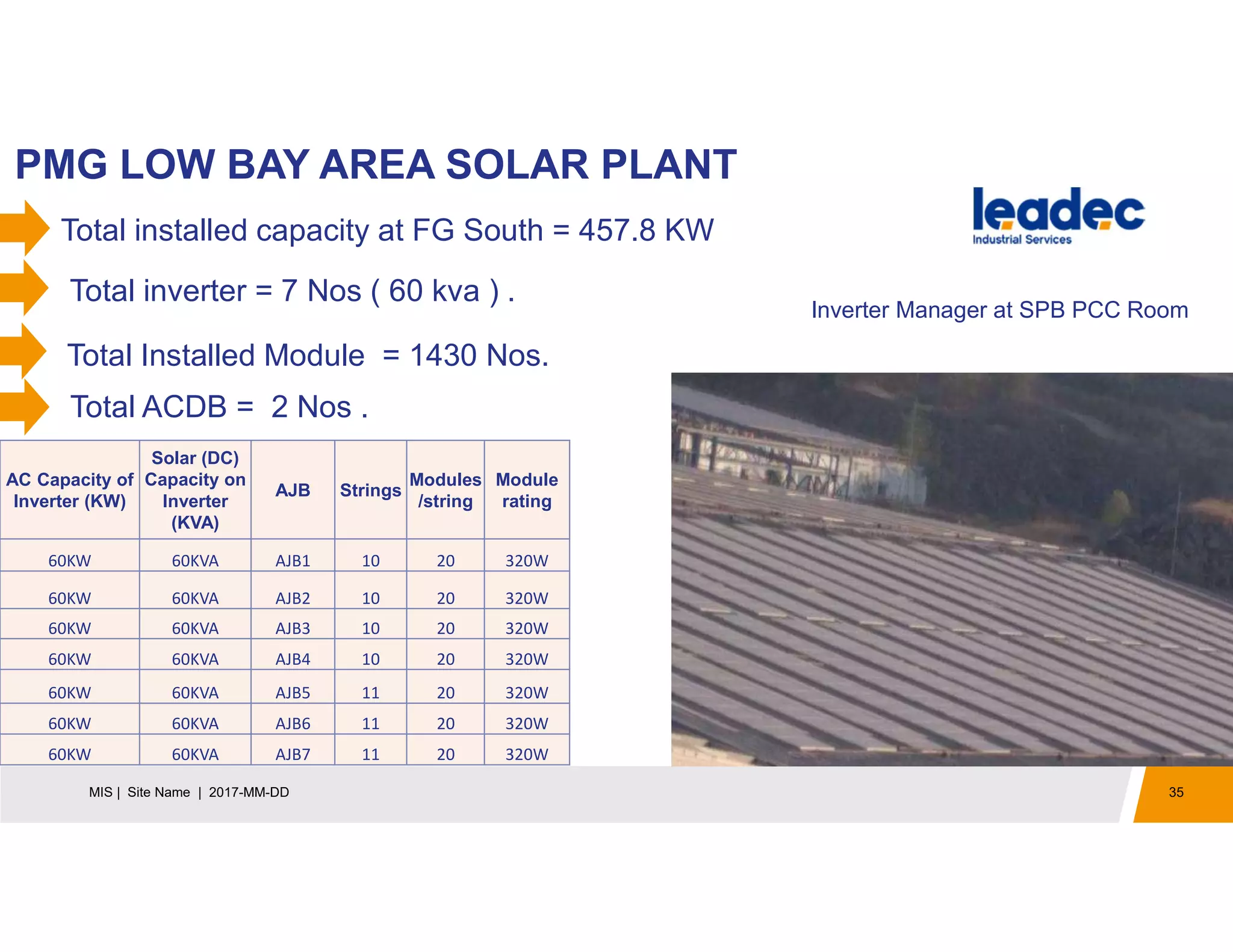
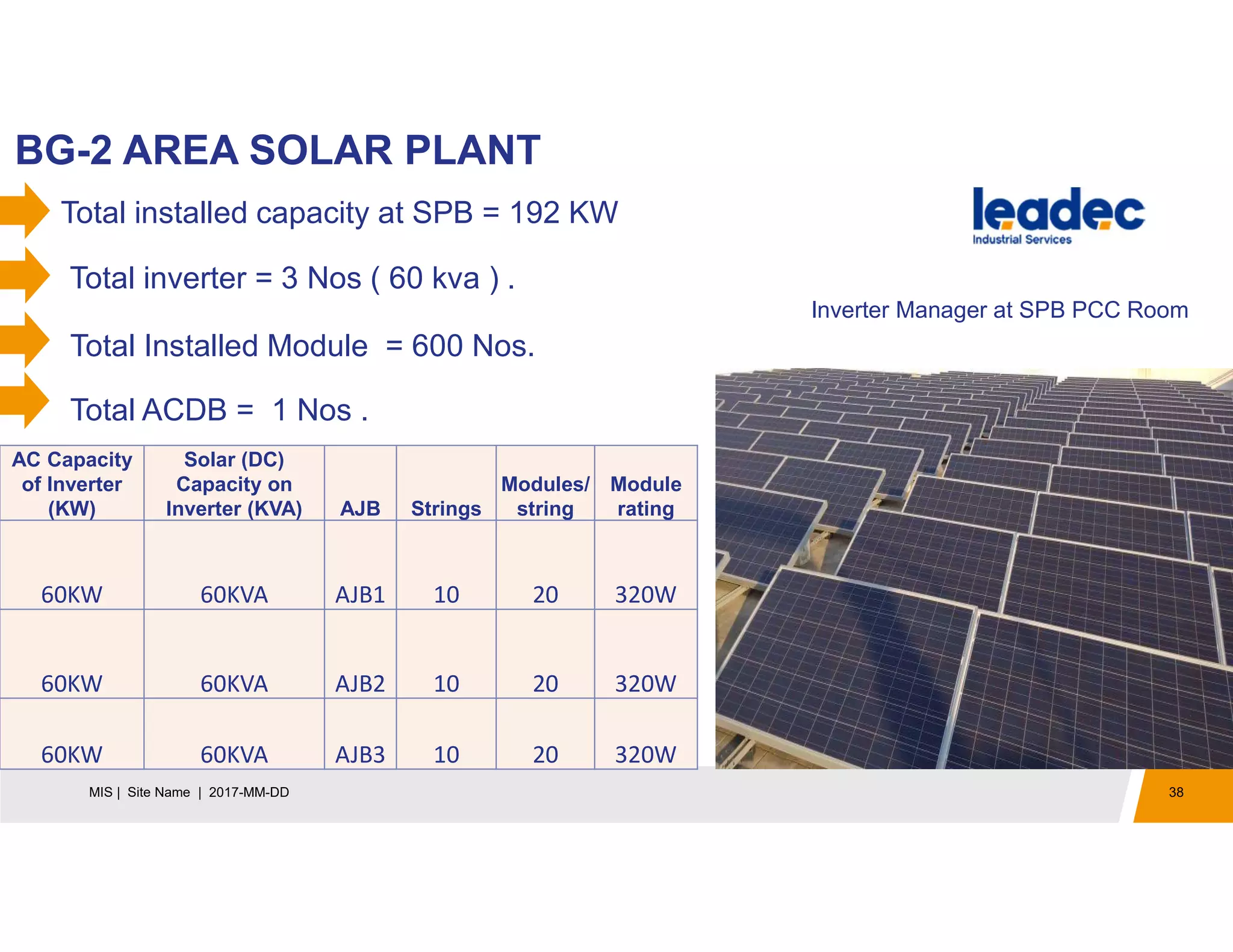
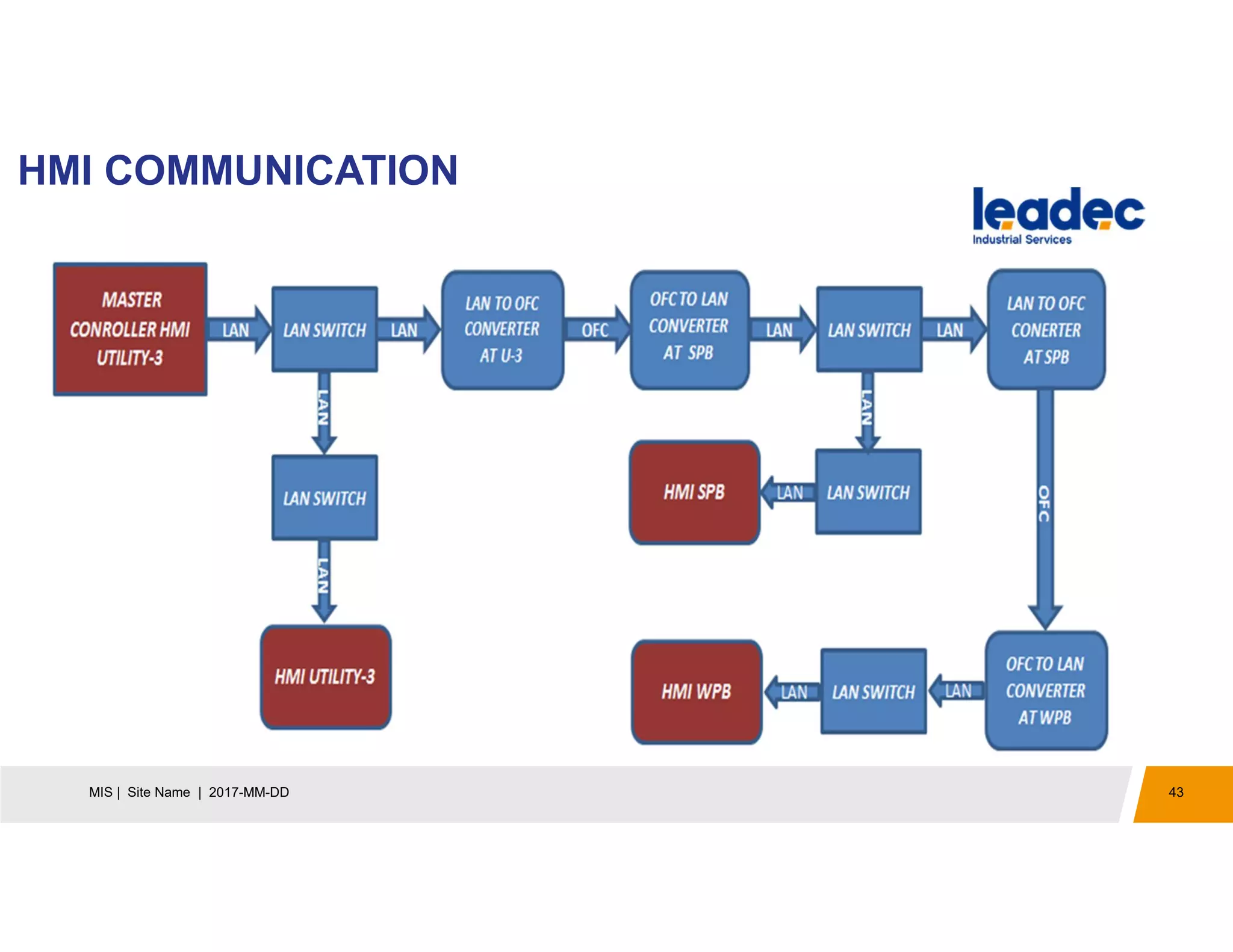
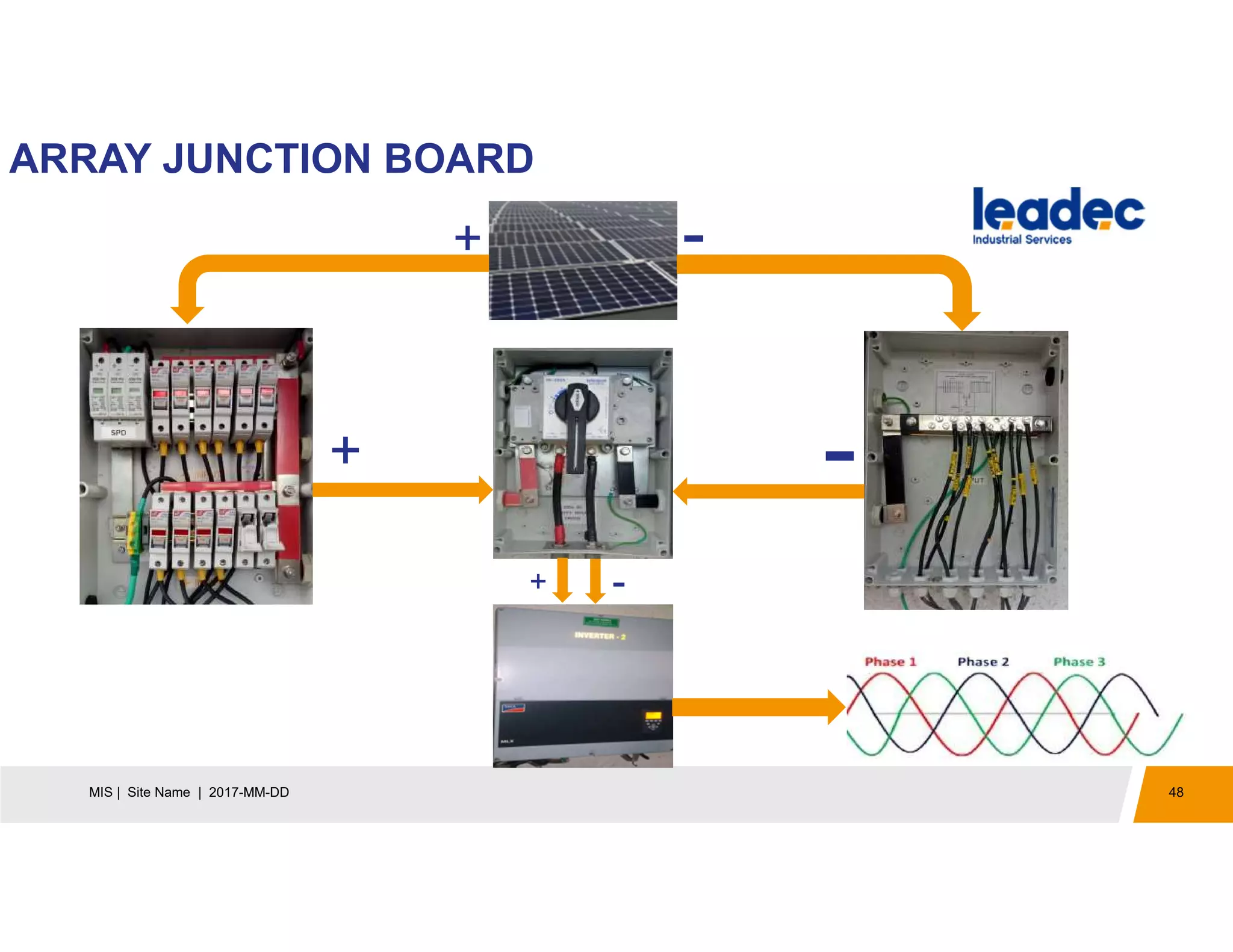
The document discusses solar power plants and photovoltaic cells. It describes how solar power plants convert sunlight into electricity using photovoltaic cells or solar panels. The cells are made of semiconductors, usually silicon, that produce a current when light hits the cell. Large solar power plants use arrays of many cells and mirrors or lenses to direct sunlight and produce electricity on a large scale to supply energy. They provide a clean, renewable source of energy.