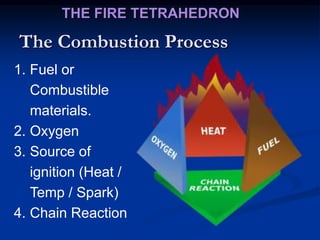
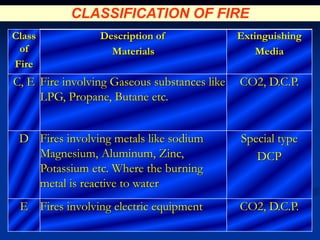
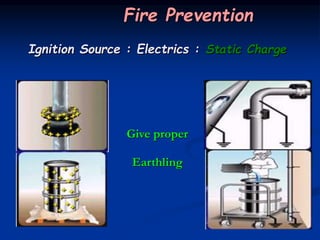
This document provides an overview of fire fighting training. It discusses understanding the combustion process and different fire classes. It also covers understanding different types of fire extinguishers, their operating procedures, capabilities and limitations. Finally, it addresses basic fire fighting concepts such as objectives, the chemistry of fire, how fire works using the fire tetrahedron model, different materials used to extinguish fires, classification of fires by class, causes of fires and methods of prevention, ignition sources and prevention, and fire control and protection systems including detection/alarm systems, mobile and portable equipment, and fixed systems like sprinklers, hydrants, and specialized suppression systems.