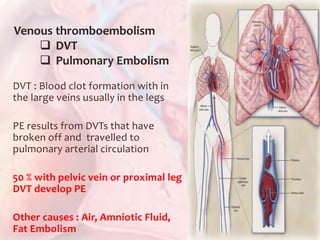
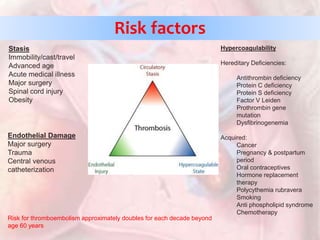
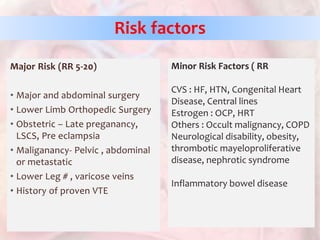
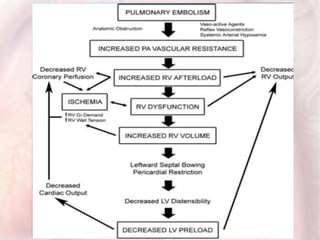
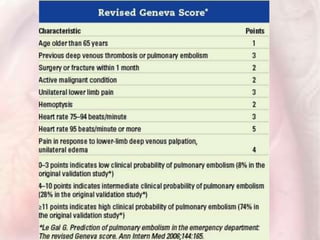
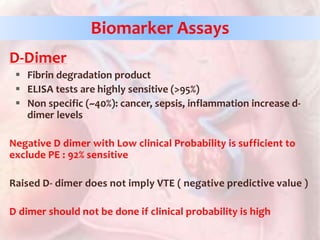
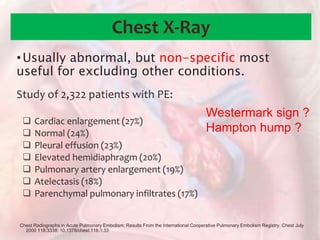
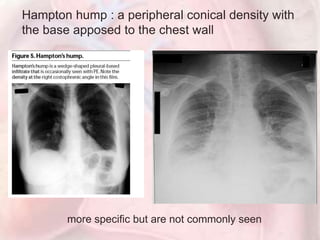
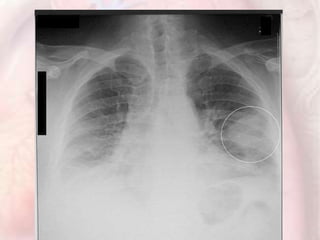
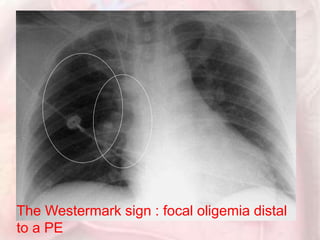
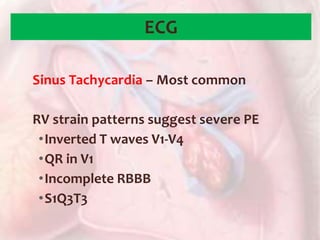
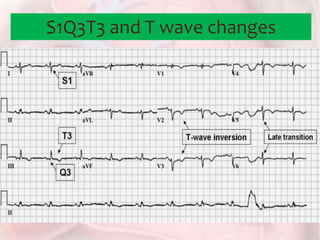
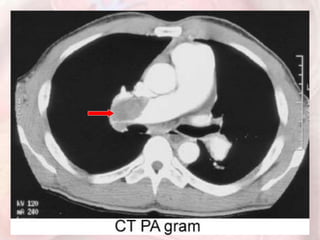
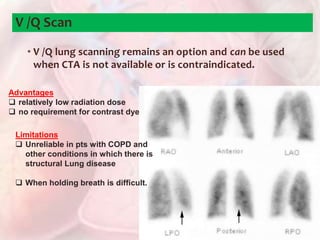
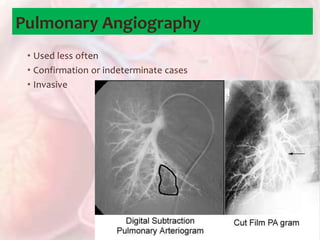
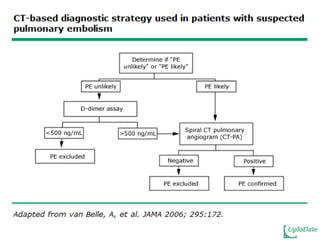
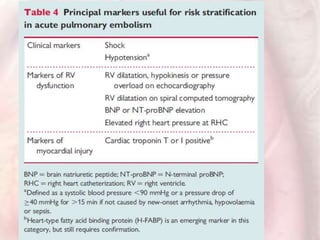
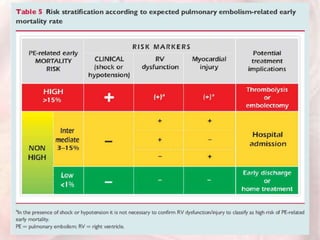
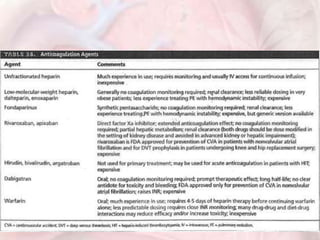
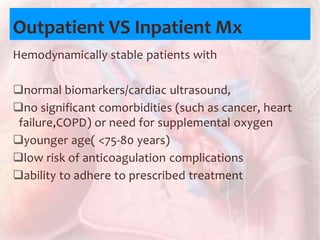
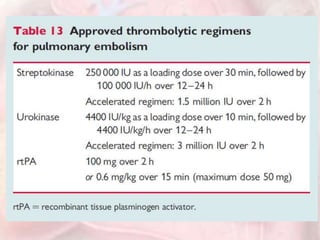
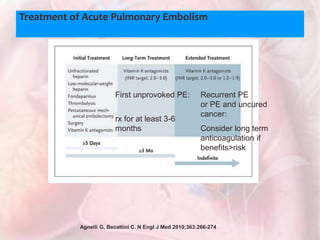
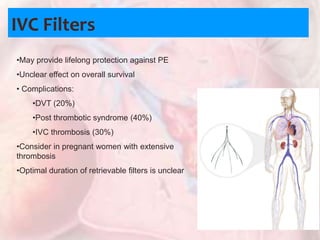
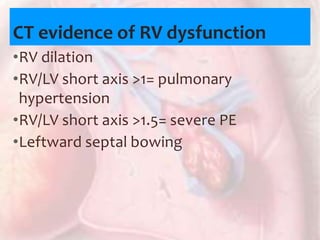
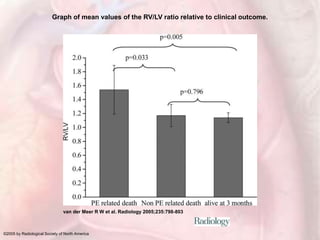
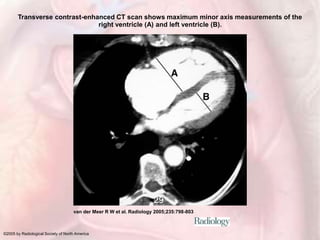
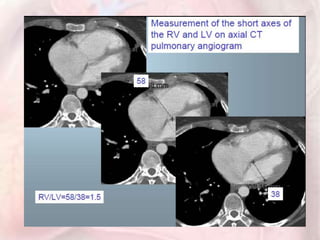
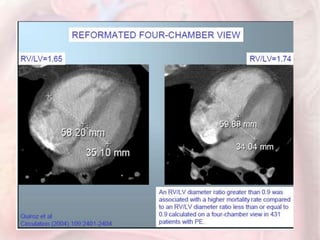
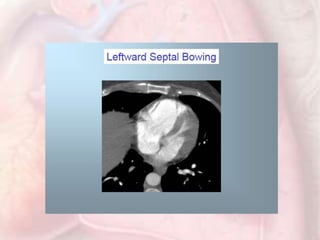
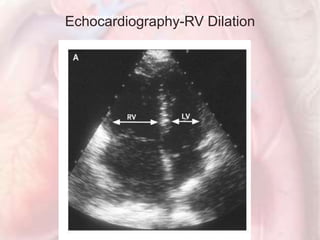
This document discusses acute pulmonary embolism (PE), which results from blood clots (deep vein thromboses or DVTs) breaking off and traveling to the lungs. PE is a leading cause of preventable hospital death. The document covers risk factors for PE like immobility, surgery, cancer, and inherited conditions. It also discusses methods for diagnosing PE like the Wells criteria, D-dimer testing, chest imaging like CT scans, and treatment including anticoagulation and thrombolysis for hemodynamically unstable patients. Poor prognostic signs of PE include hypotension, cardiac biomarkers indicating injury, and imaging findings of right ventricular dysfunction. Prevention through appropriate DVT prophylaxis is emphasized.