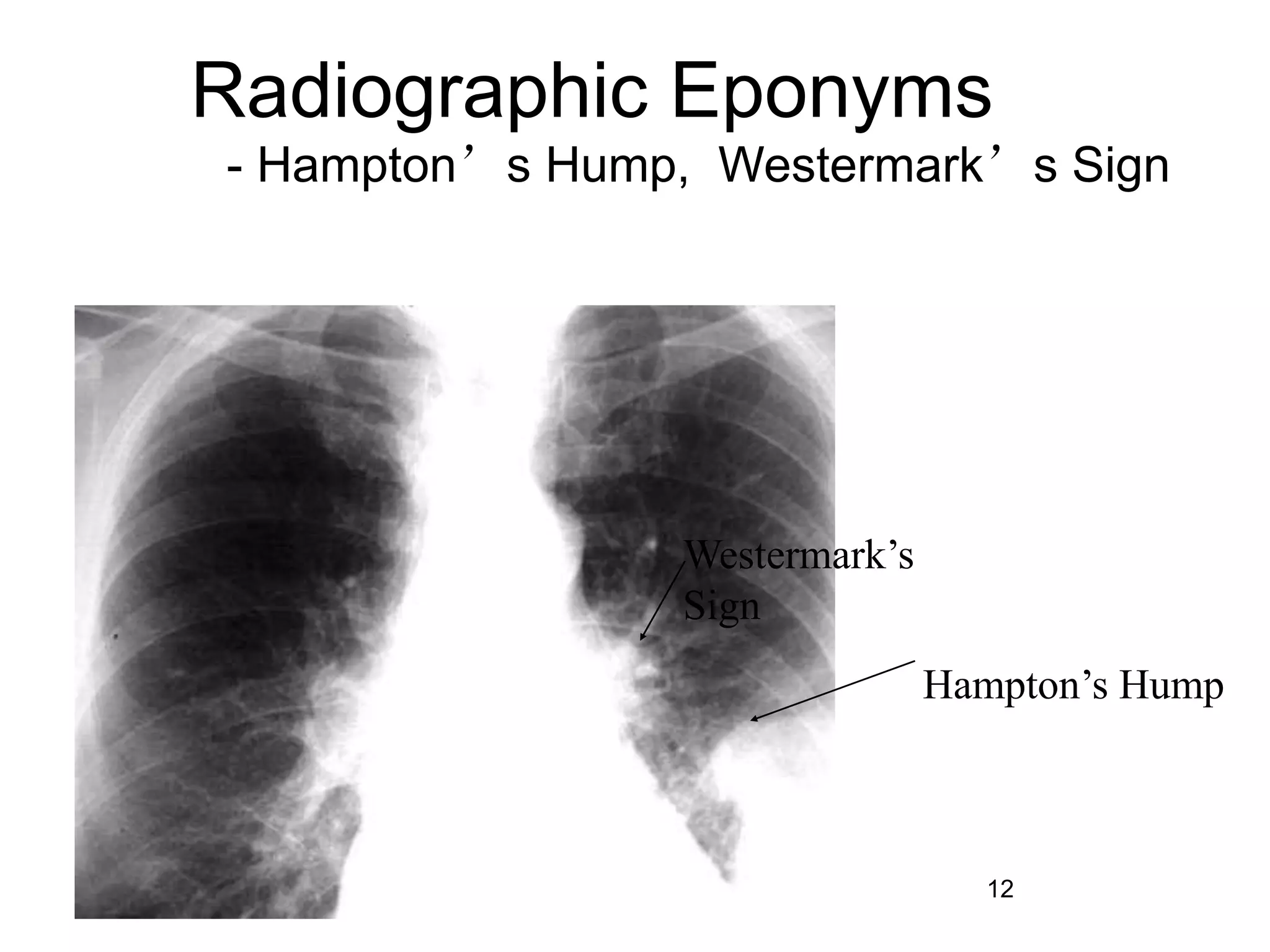
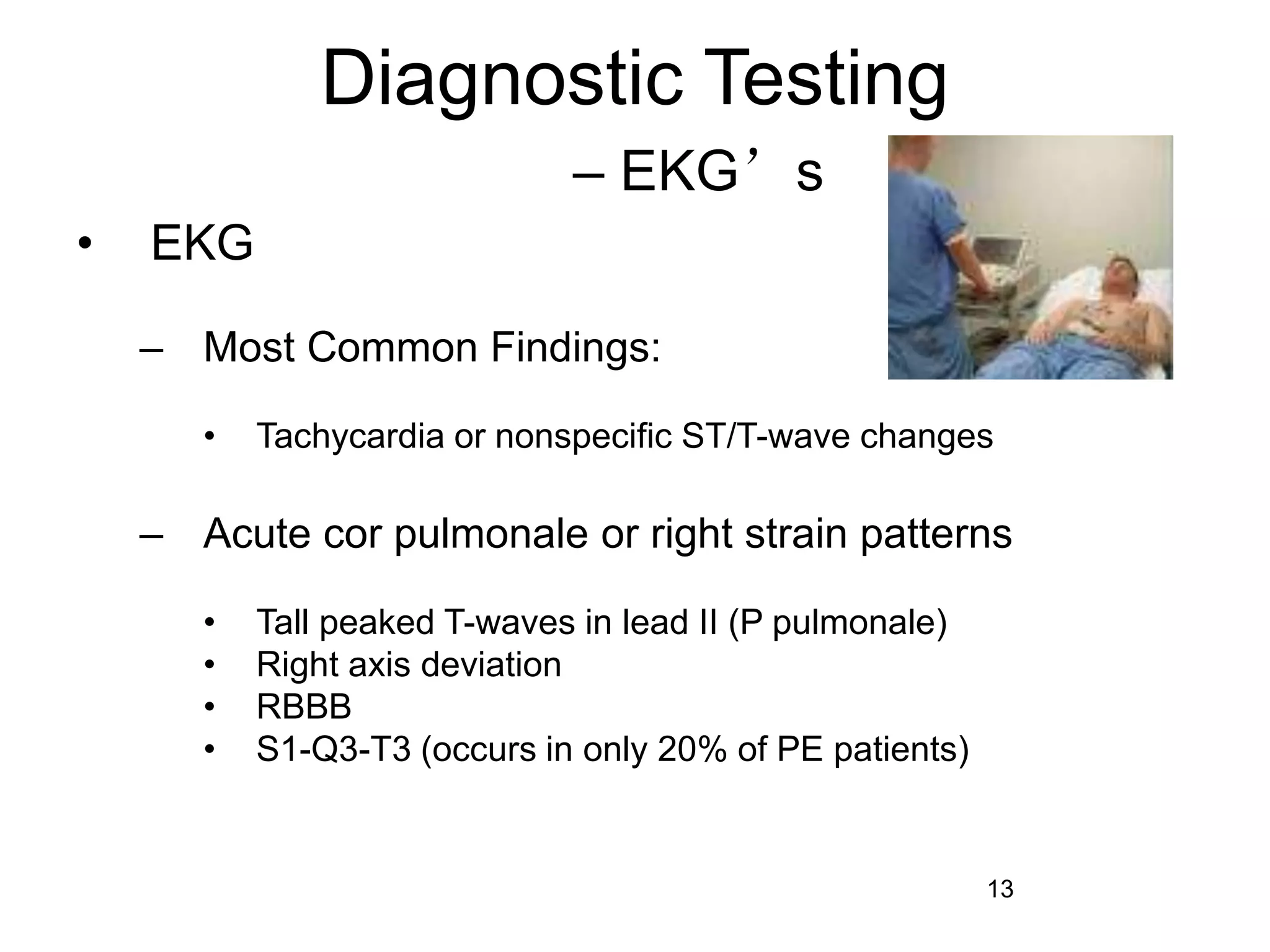
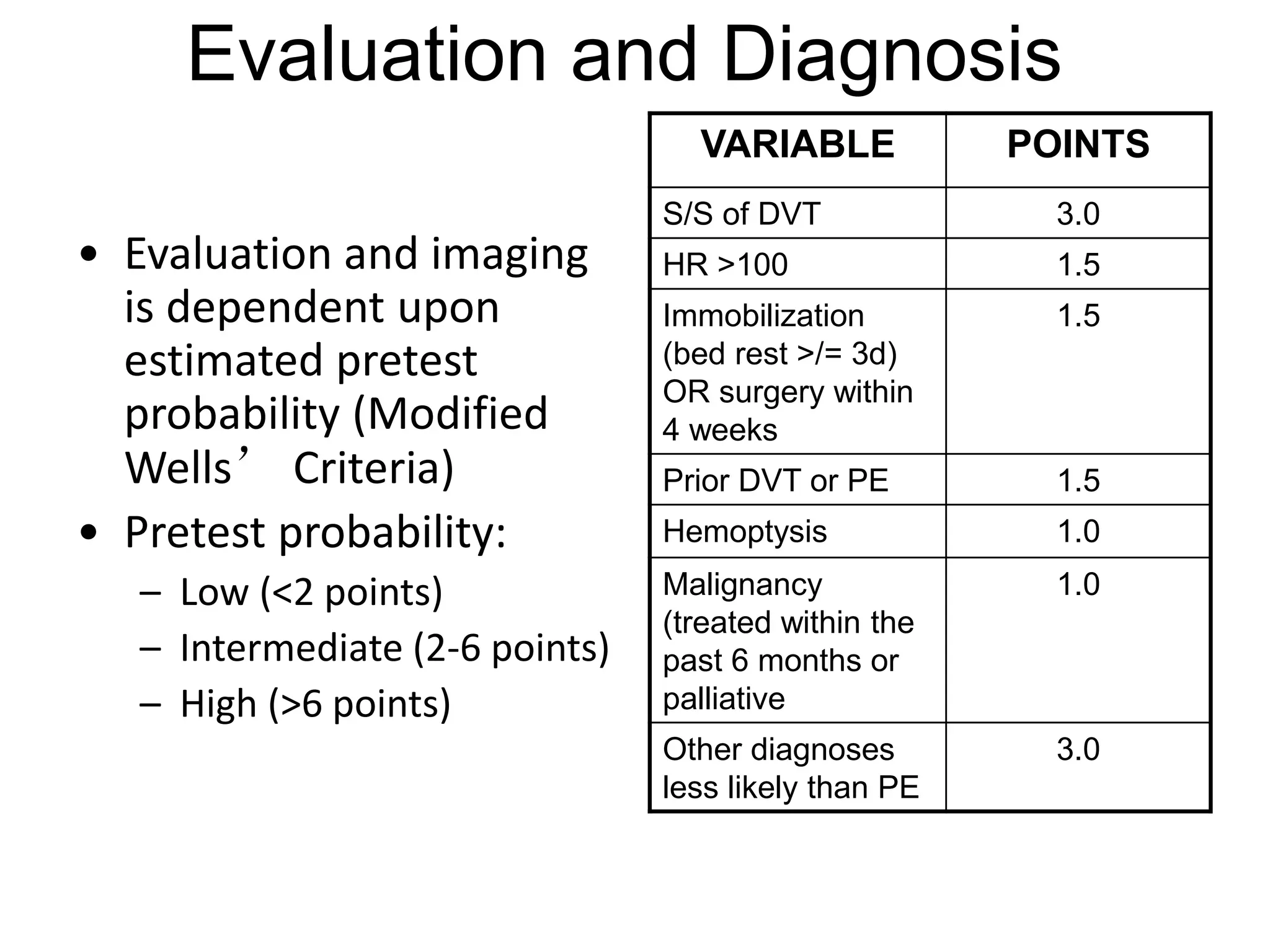
Pulmonary embolism is a blockage in the pulmonary arteries caused by blood clots that travel from deep veins. It has several risk factors and causes around 650,000 cases and 150,000-200,000 deaths annually in the US. Diagnosis involves assessing probability based on symptoms and risk factors, then tests like CT, VQ scan, ultrasound, or angiogram depending on probability. Treatment consists of blood thinners like heparin or warfarin to prevent further clots and long term anticoagulation to prevent recurrence based on the cause of clotting.