This document discusses pulmonary embolism (PE), including its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment. Some key points:
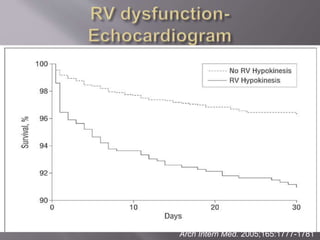
- PE is a common cause of preventable death, often occurring without warning signs. Prompt diagnosis and treatment are important.
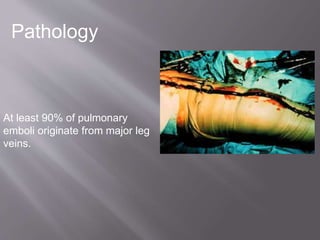
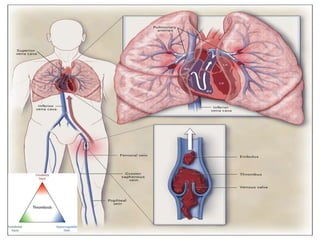
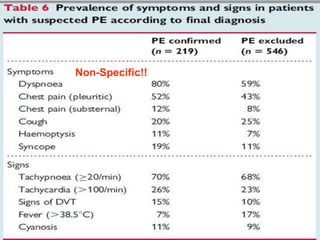
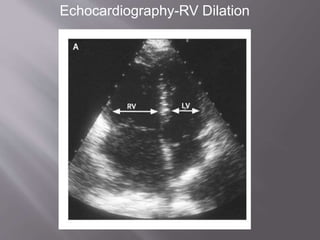
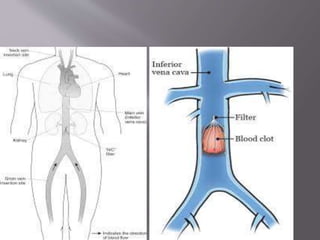
- PE usually originates from blood clots that form in the deep leg veins. Symptoms can include chest pain, difficulty breathing, and syncope.
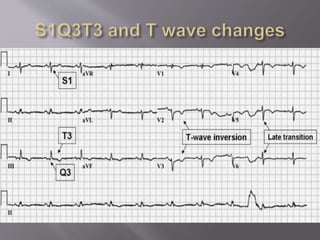
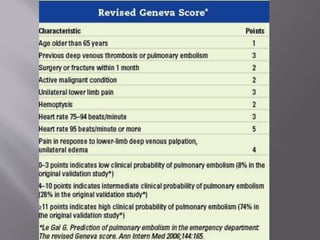
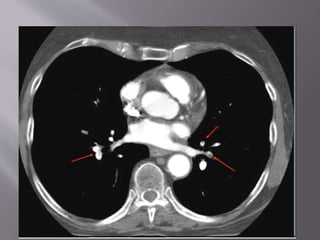
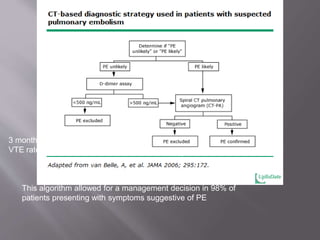
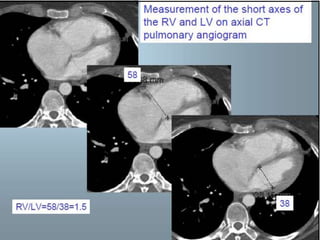
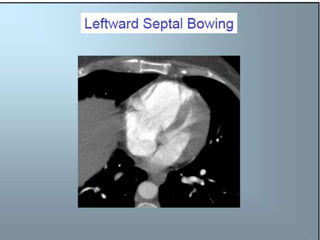
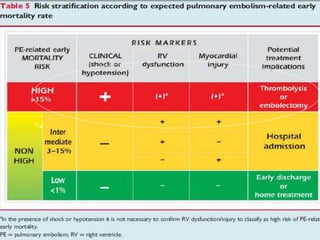
- Diagnosis is difficult as symptoms are non-specific. Imaging tests like CT scans are often needed along with blood tests like d-dimers.
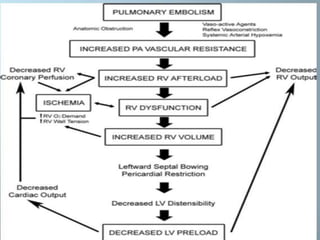
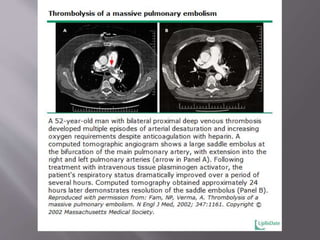
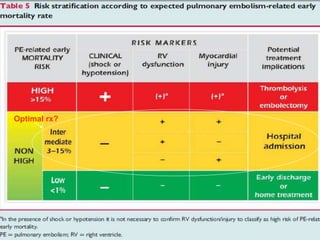
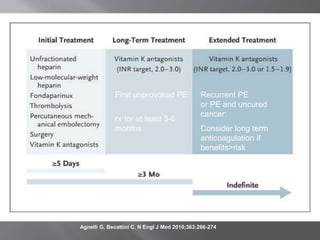
- Treatment involves blood thinners to prevent further clots. Thrombolysis may be used in high-risk cases but risks need to be weighed