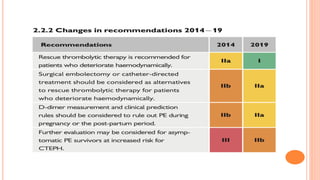
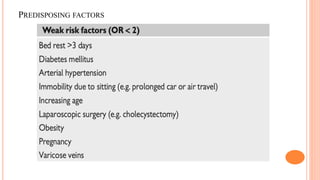
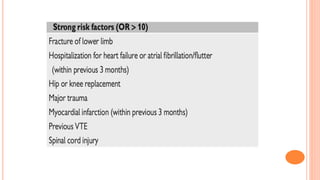
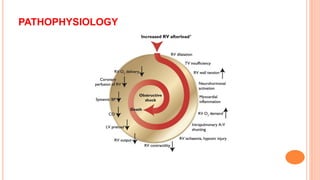
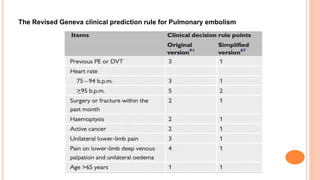
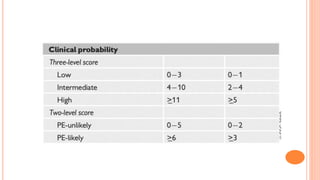
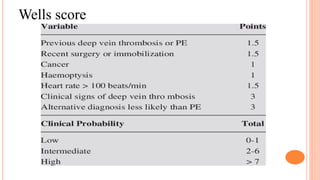
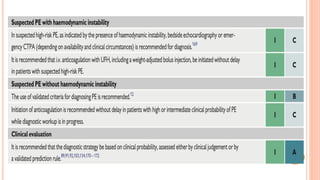
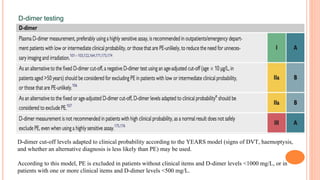
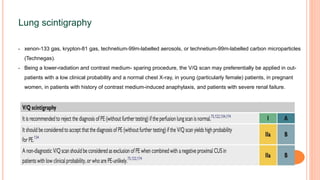
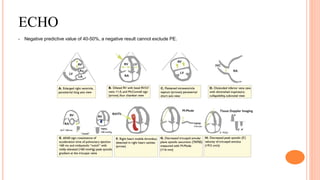
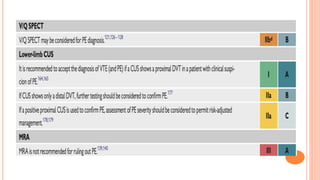
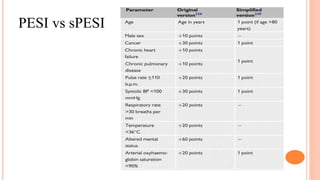
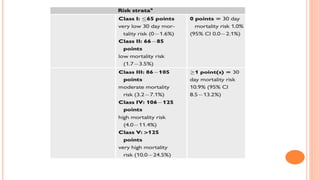
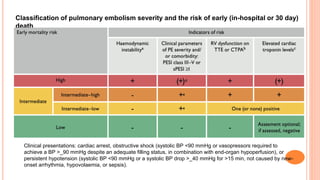
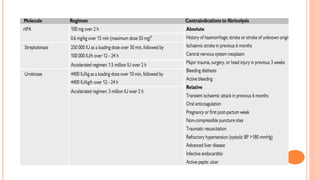
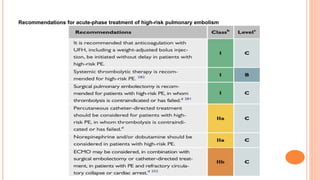
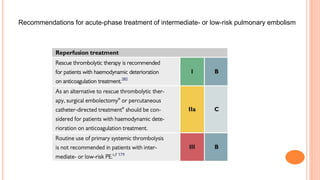
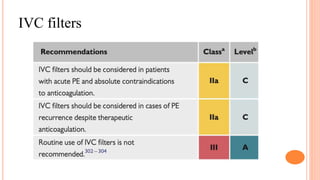
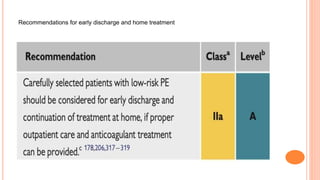
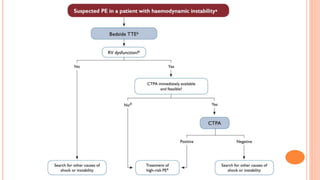
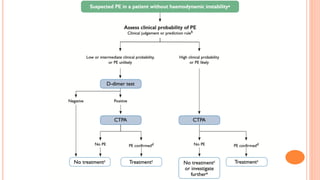
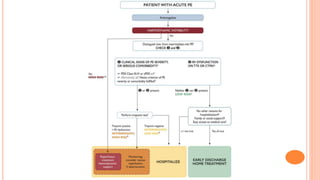
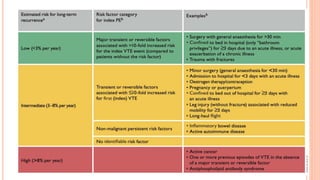
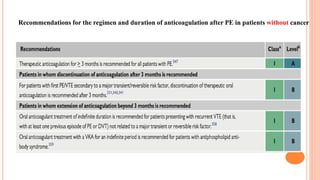
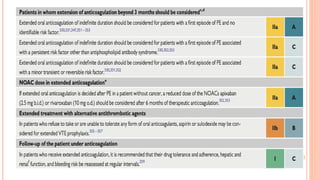
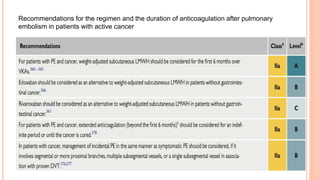
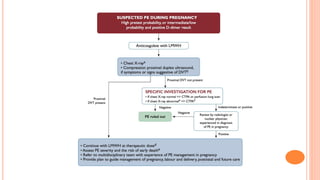
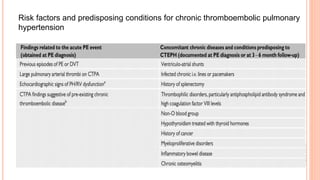
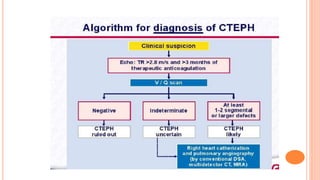
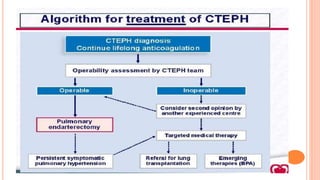
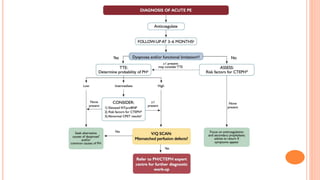
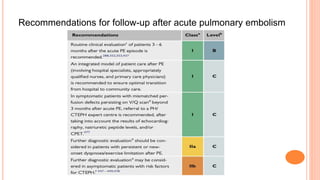
The document provides an overview of the updates in the 2019 guidelines for pulmonary embolism (PE) diagnosis and treatment. Key changes include adjusted D-dimer cut-off values based on age and probability; revised algorithms for diagnosing high-risk PE and assessing severity; recommending non-vitamin K antagonist oral anticoagulants as first-line treatment for eligible patients; classifying recurrence risk factors and extending treatment duration indications; and proposing a comprehensive post-PE patient follow-up algorithm. The guidelines aim to improve PE risk stratification, optimize acute care, determine chronic anticoagulation regimens, and ensure long-term management and surveillance for complications.