This document provides information on acute pancreatitis including:
1. The epidemiology, causes, pathophysiology, clinical presentation, investigations, management, and complications of acute pancreatitis are summarized. Gallstones and alcohol are the most common causes.
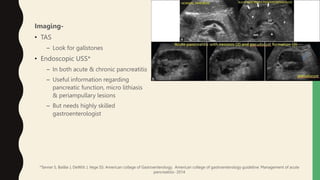
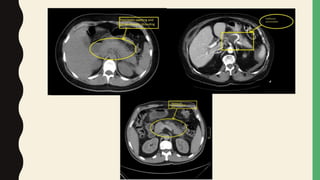
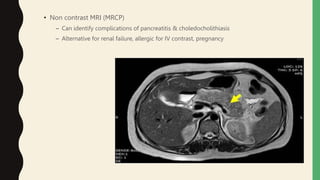
2. Laboratory markers like lipase and amylase are used to diagnose, while CT, MRI, and ultrasound can identify complications like fluid collections and necrosis. Treatment involves fluid resuscitation, pain management, and treating any organ dysfunction.
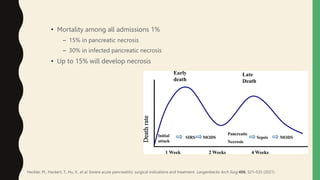
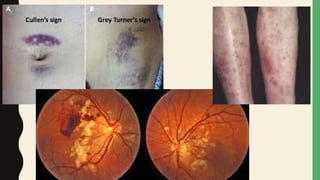
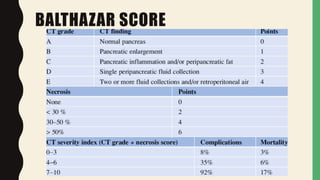
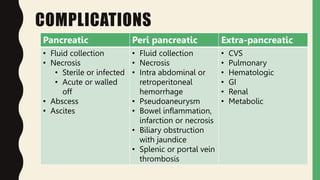
3. Complications include pancreatic and extra-pancreatic complications like fluid collections, necrosis, infection, and vascular or bowel issues. Infected necrosis requires antibiotics while severe cases may require drainage procedures or surgery.