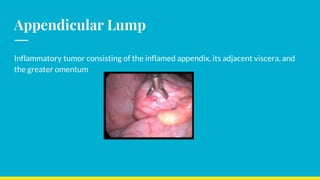
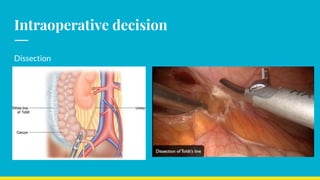
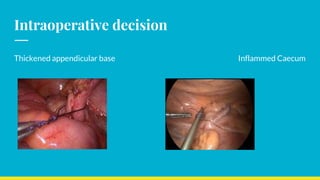
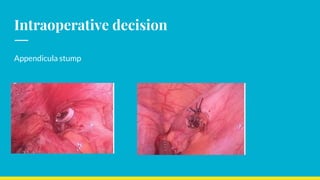
This document discusses the management of appendicular lumps. It notes that appendicular lumps are inflammatory tumors consisting of the inflamed appendix and surrounding tissues. Treatment options include emergency surgery, conservative management followed by interval surgery, or totally conservative management without interval surgery. Conservative treatment is associated with a risk of missing hidden pathologies. Emergency surgery carries a high risk of complications while interval surgery risks appendicular abscess or perforation during the waiting period. Randomized controlled trials have found that conservative treatment without interval surgery appears to be the best approach for appendicular masses and abscesses. The document examines factors to consider in decision making and presents cases studies from a tertiary care center.