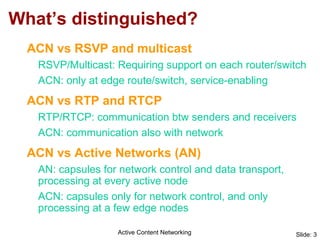
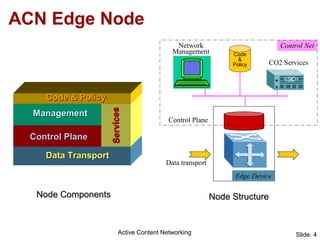
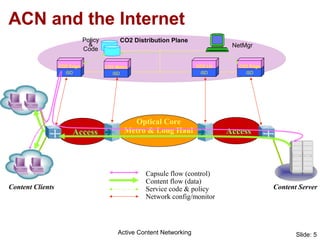
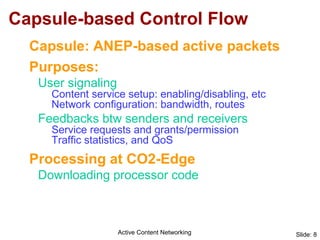
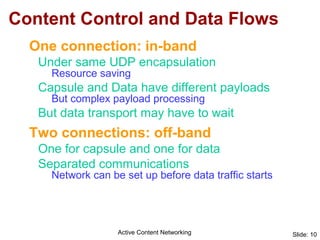
Active Content Networking (ACN) uses capsules for network control and service setup that are processed only at edge nodes, while content is transported via normal IP. This allows on-the-fly setup of content services with minimal interference to data traffic. The ACN edge node processes capsules to configure the network and duplicate content for multiple receivers. ACN integrates technologies for signaling, transport, and feedback while enabling content services through capsule-based communication with the network.