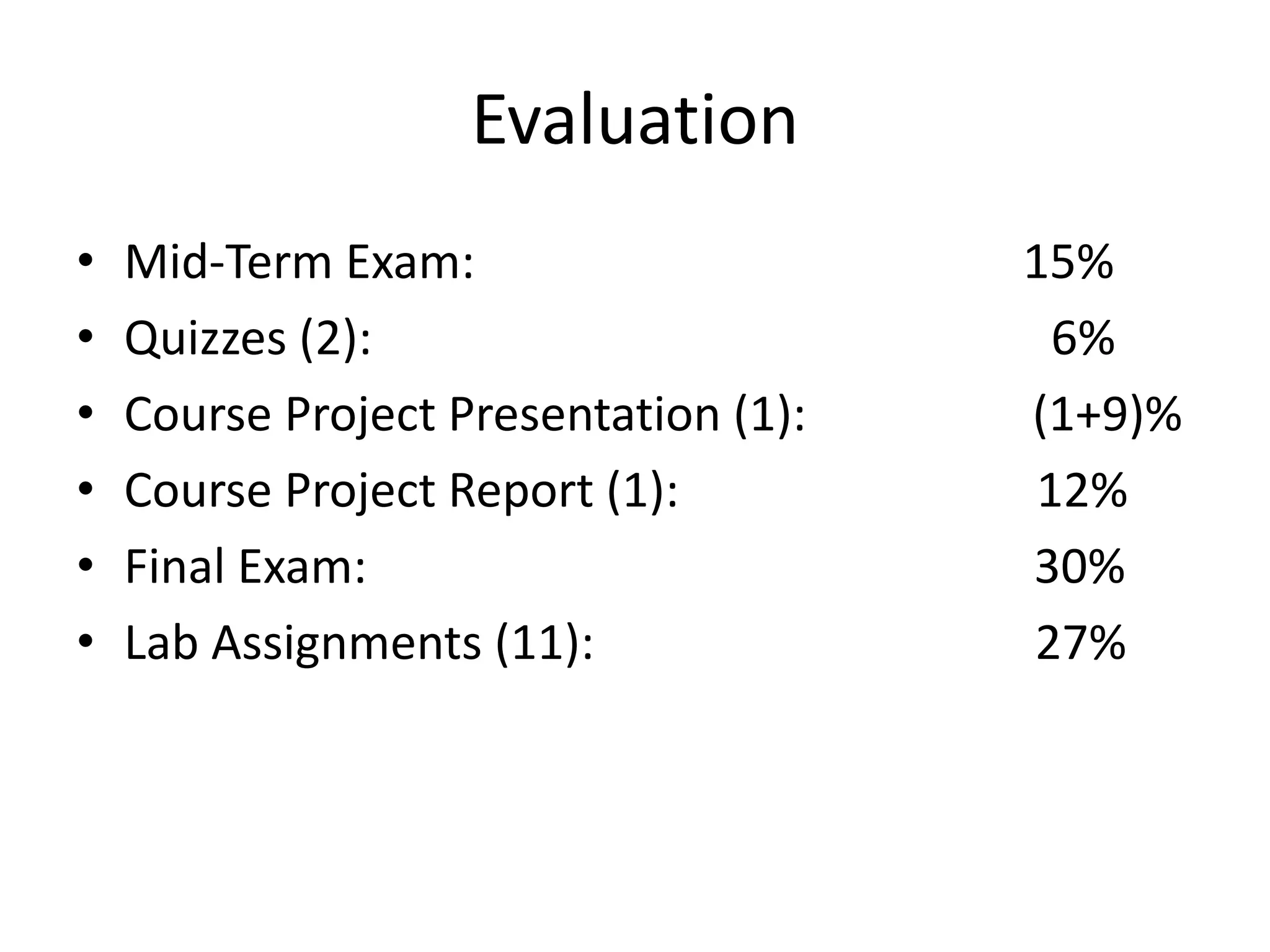
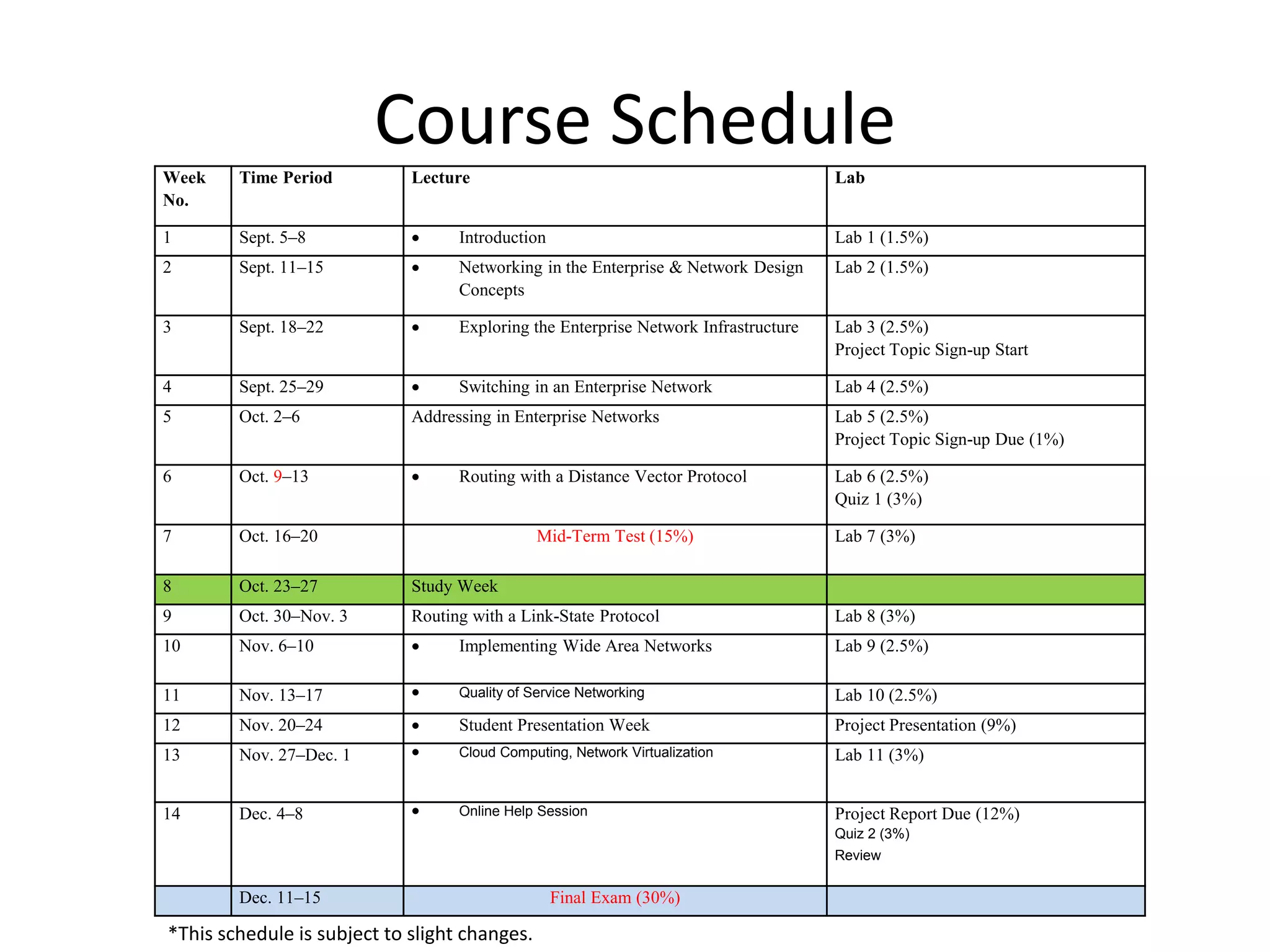
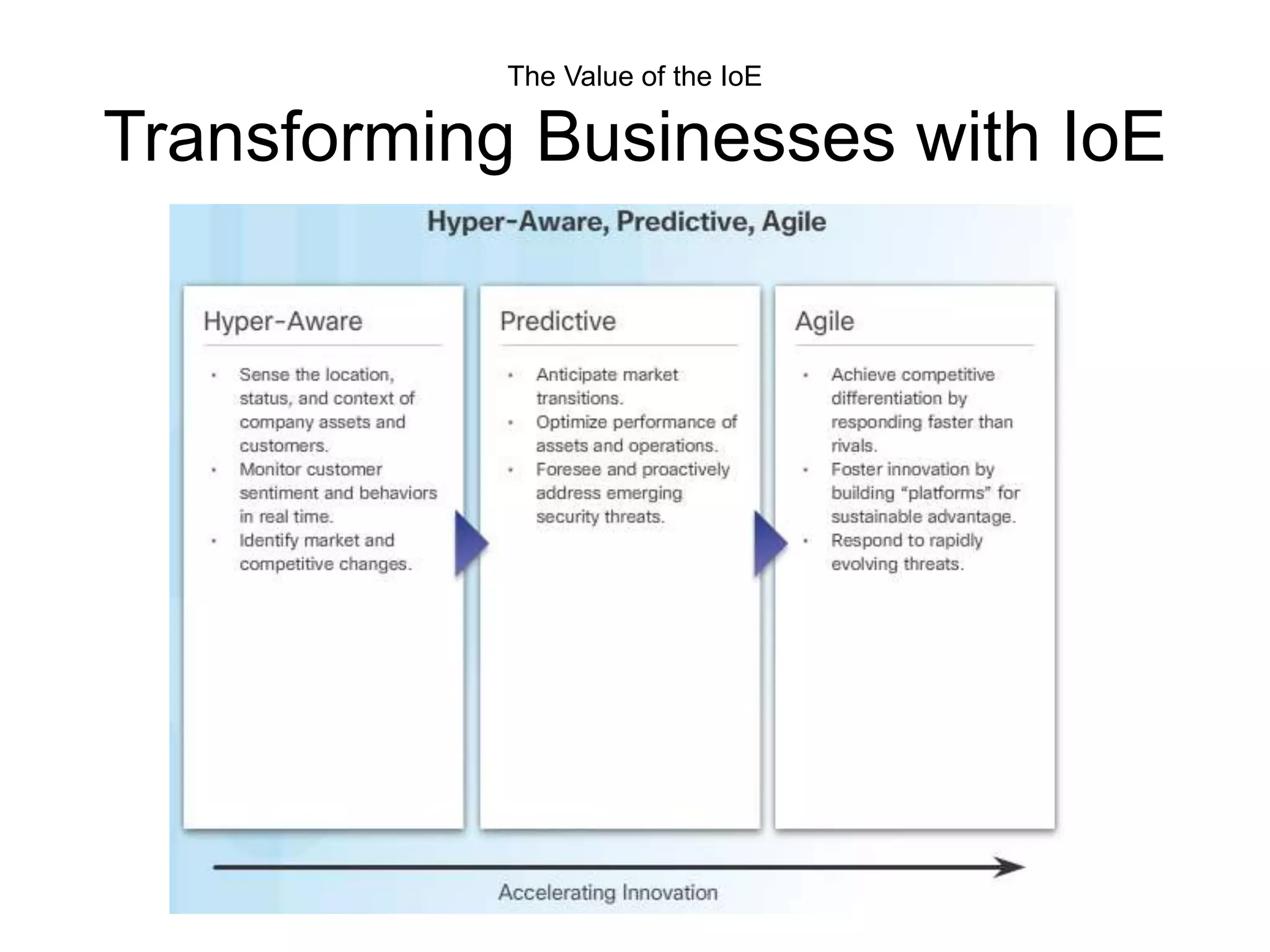
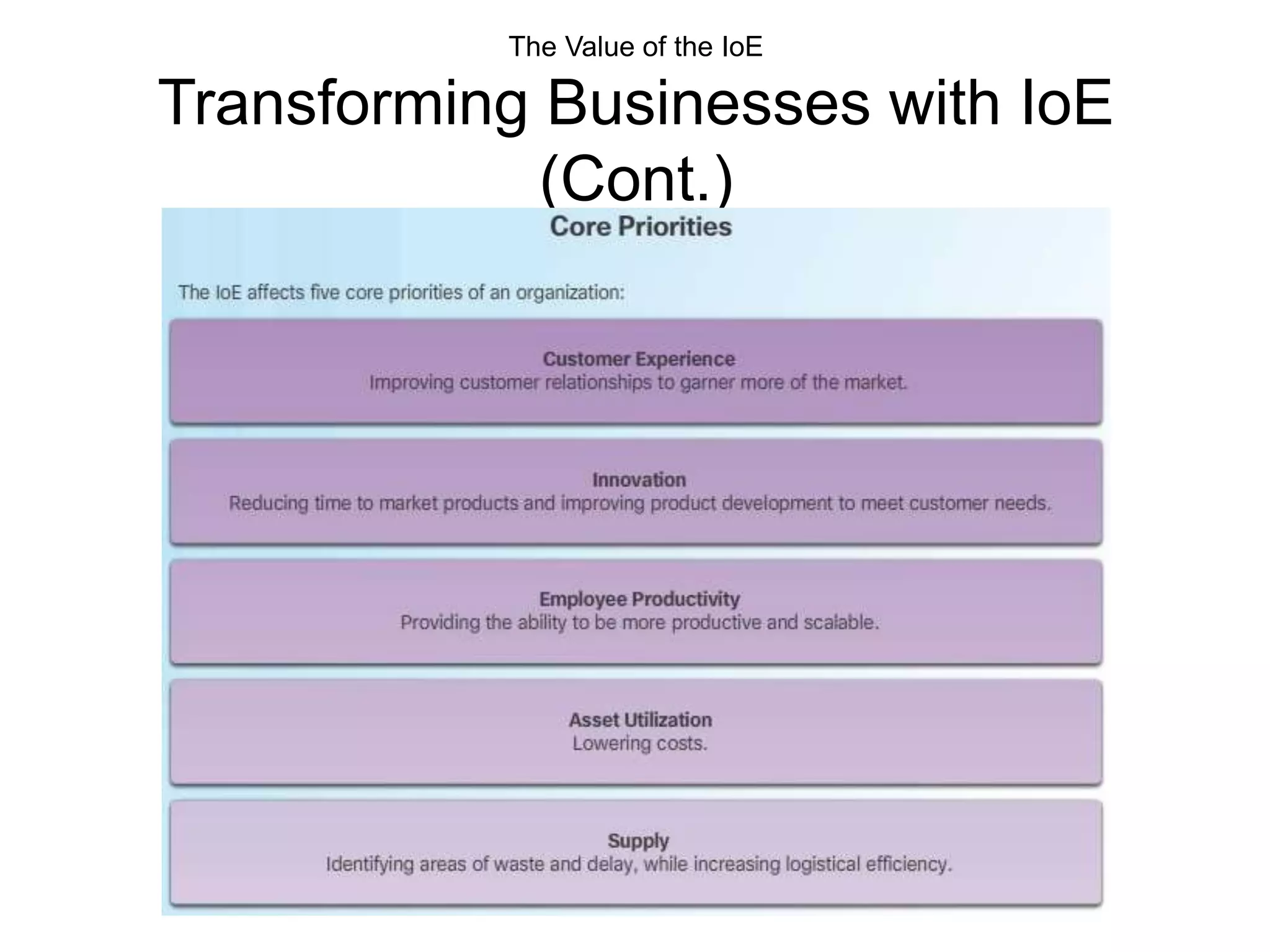
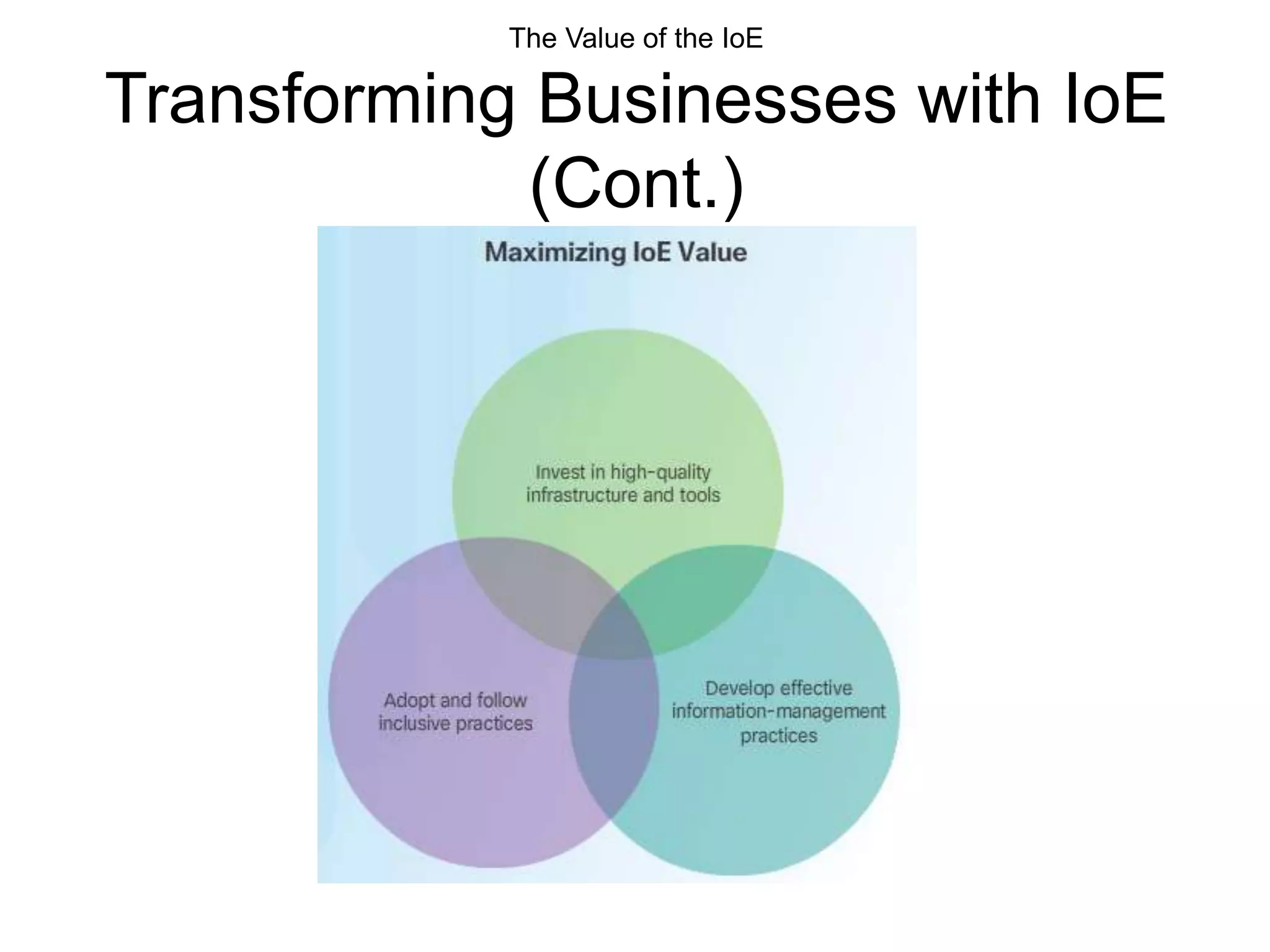
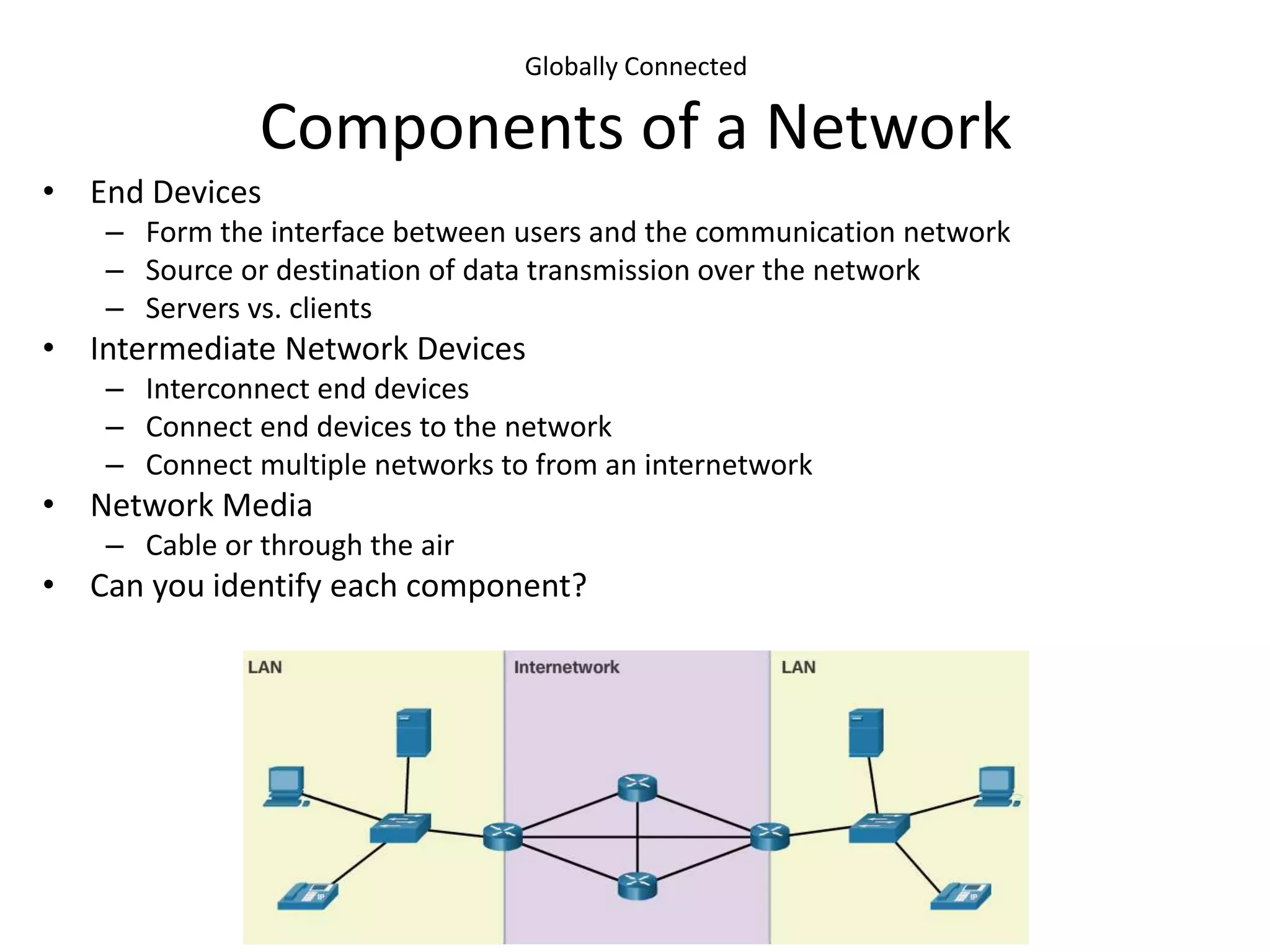
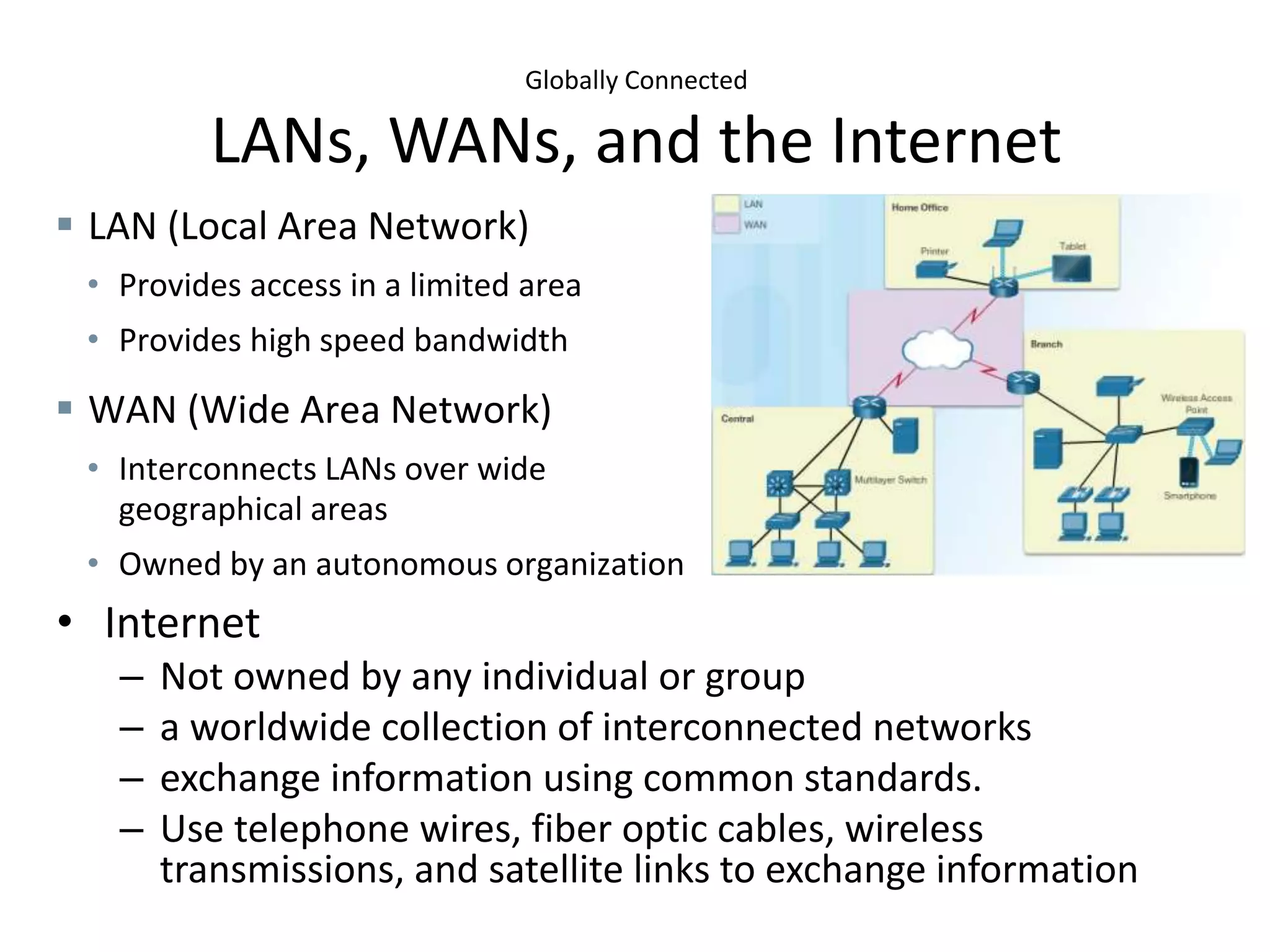
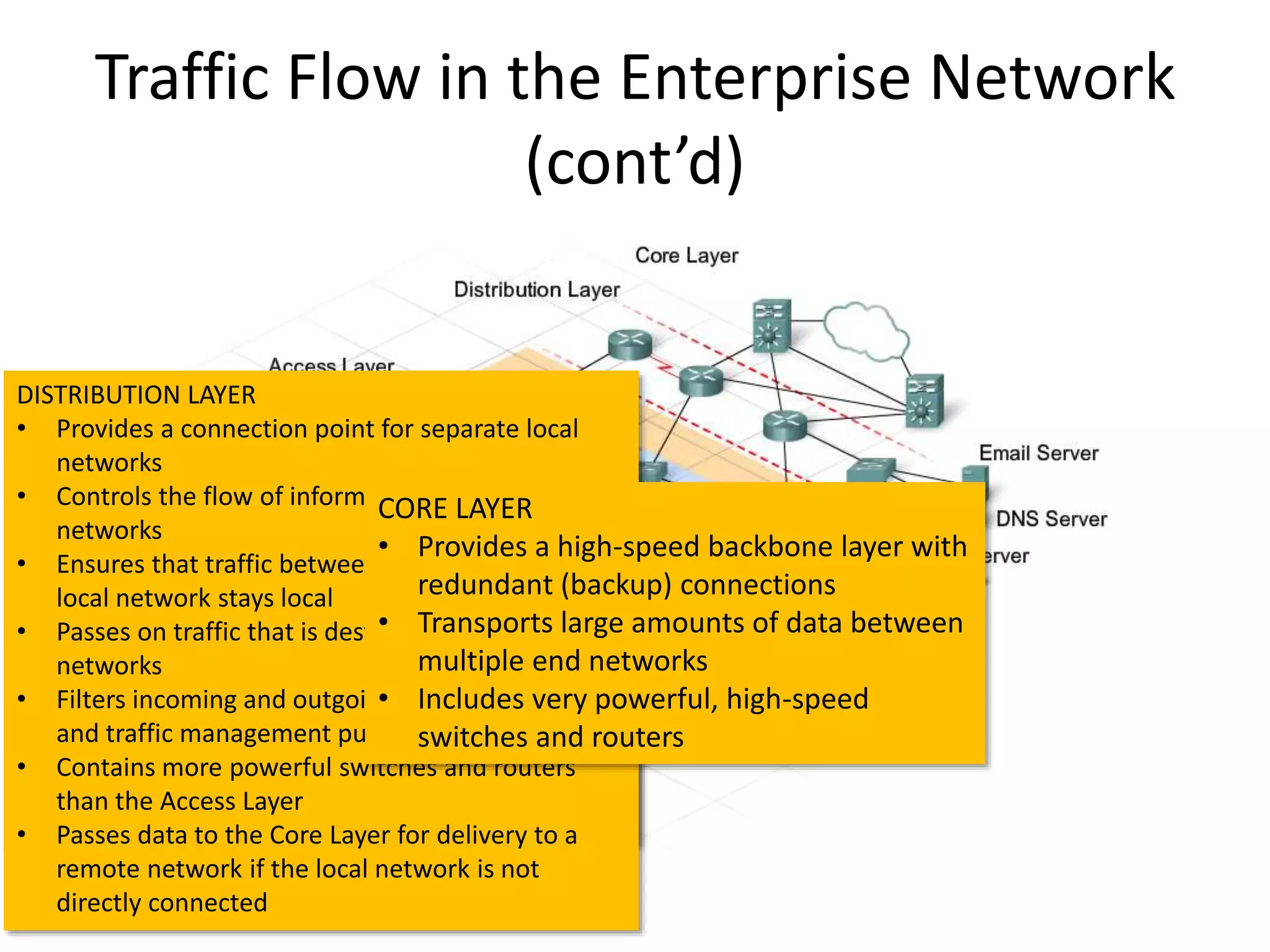
This document outlines the course DCN 330 which covers data communication and network interconnectivity, including distinguishing network devices, analyzing network designs, quality of service, cloud computing, and gaining hands-on experience through lectures, labs, and a course project using tools like Cisco Packet Tracer and lab equipment. Students will be evaluated through exams, quizzes, lab assignments, and a course project presentation and report.