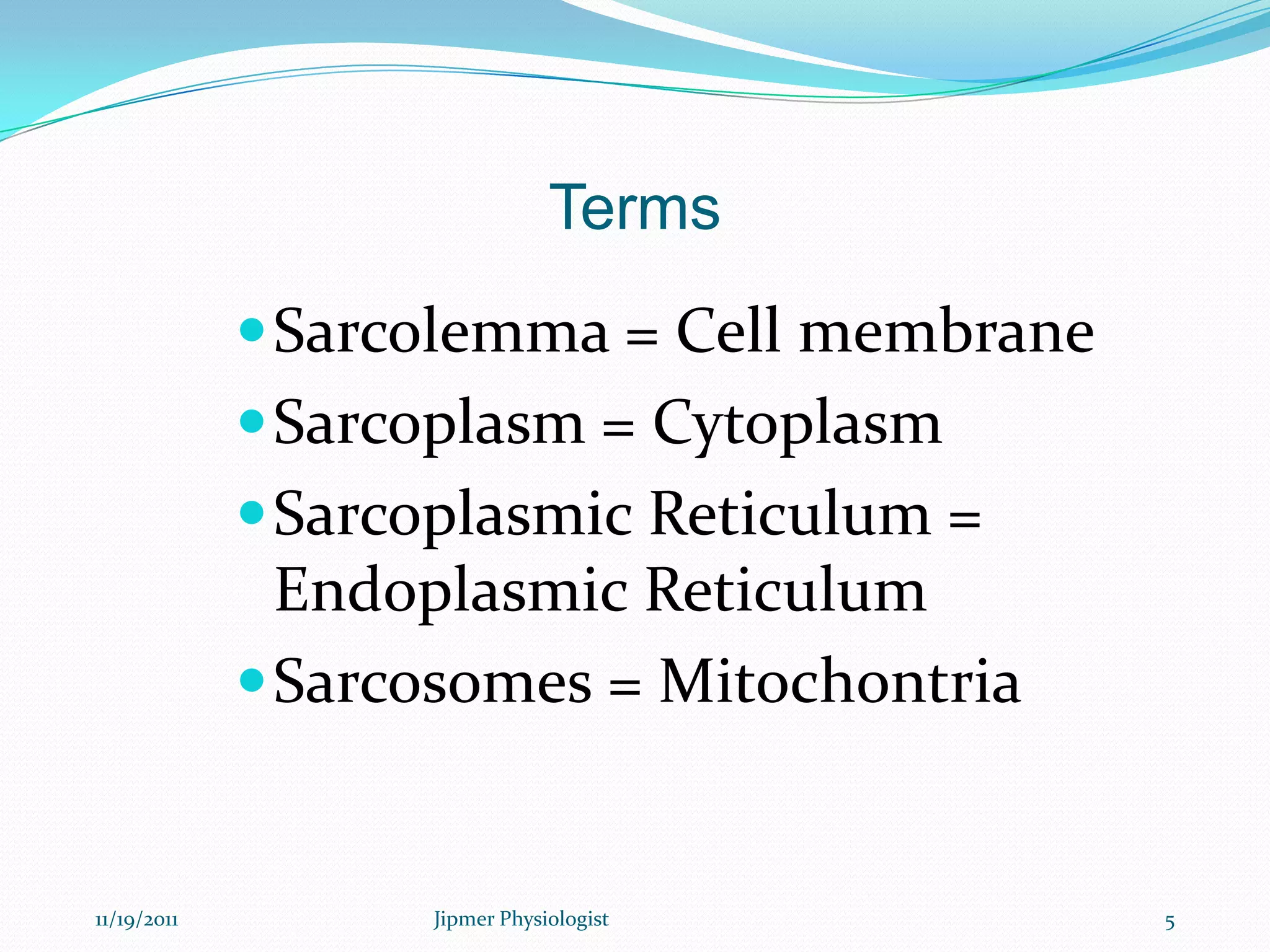
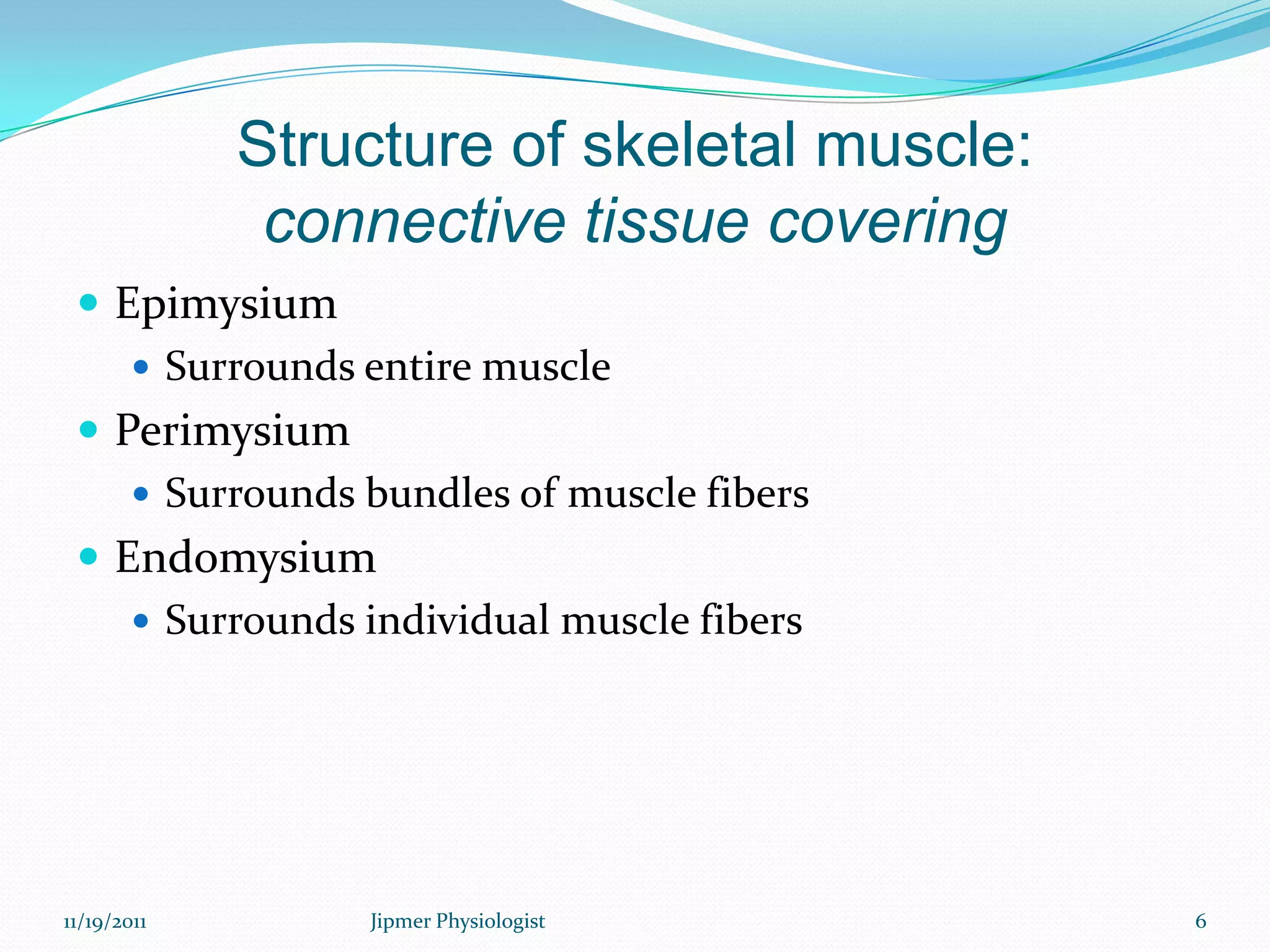
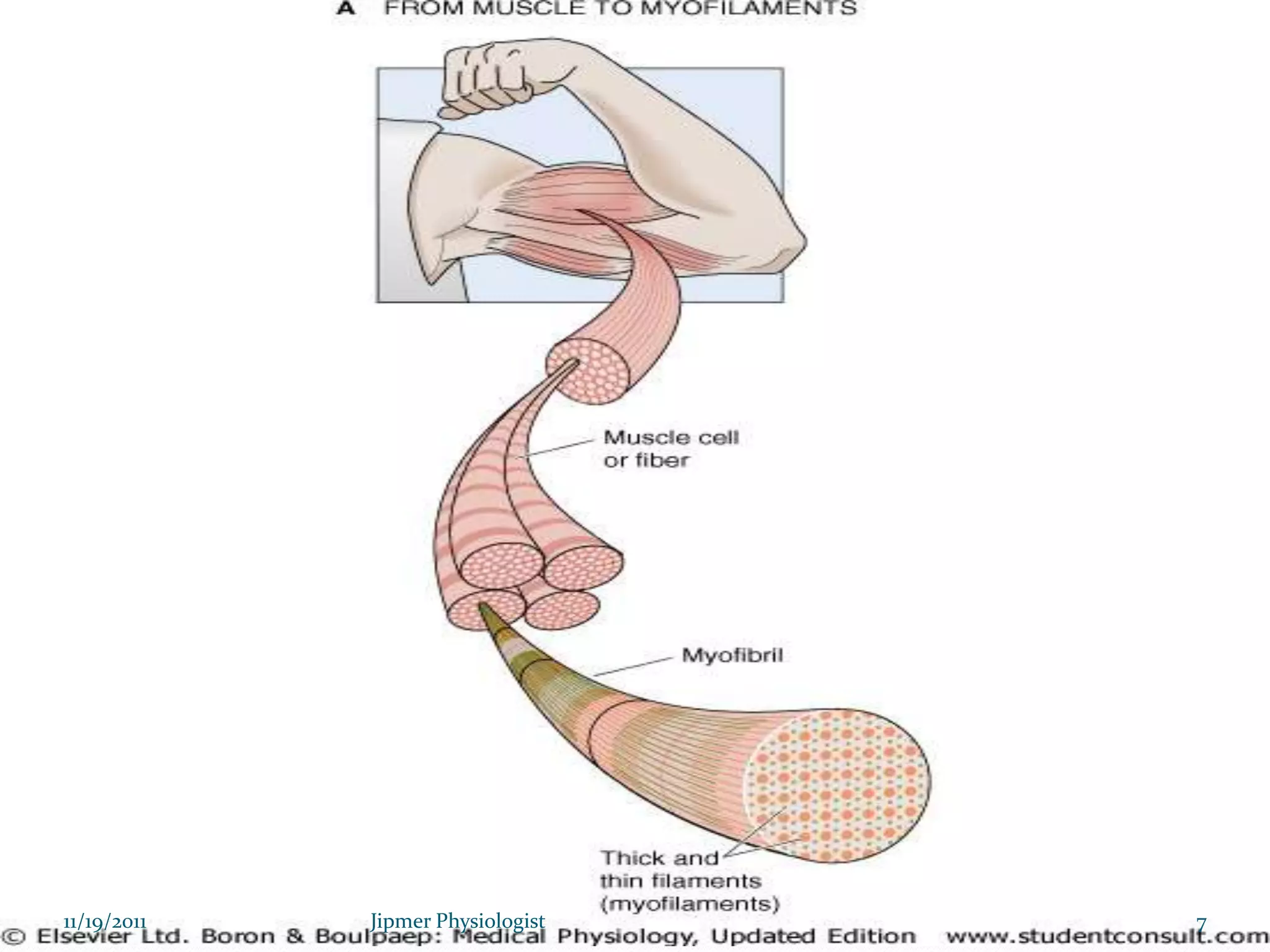
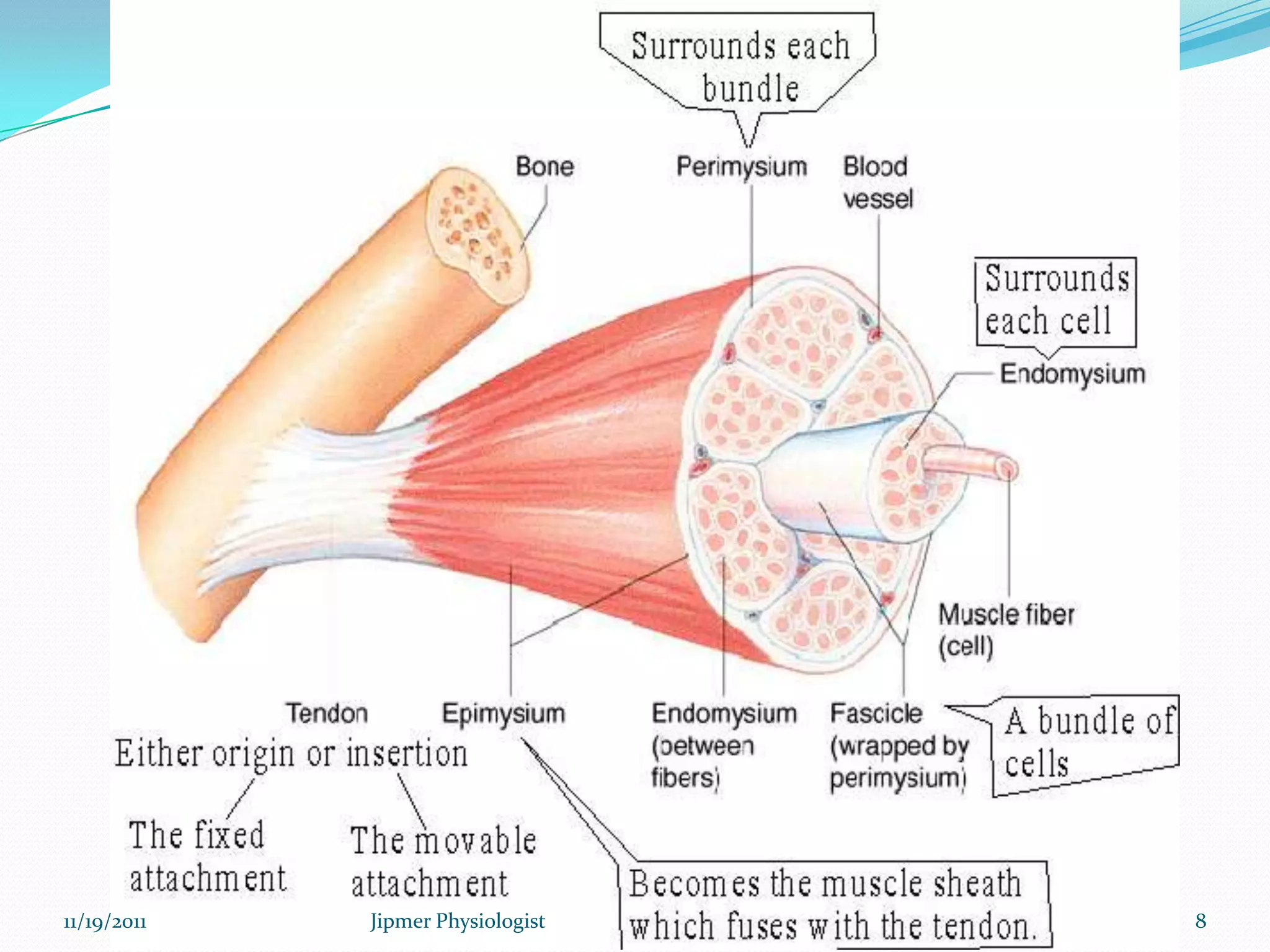
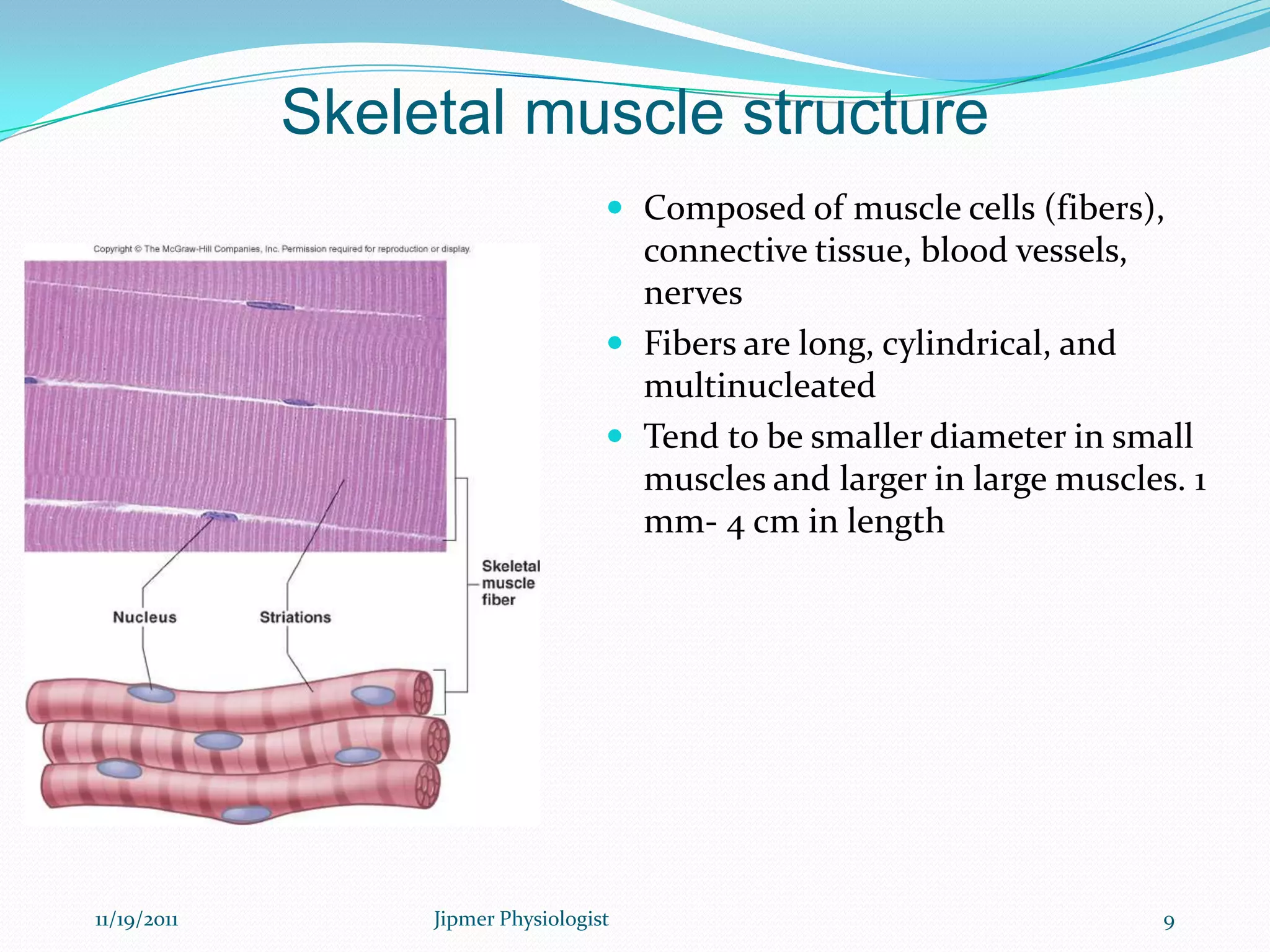
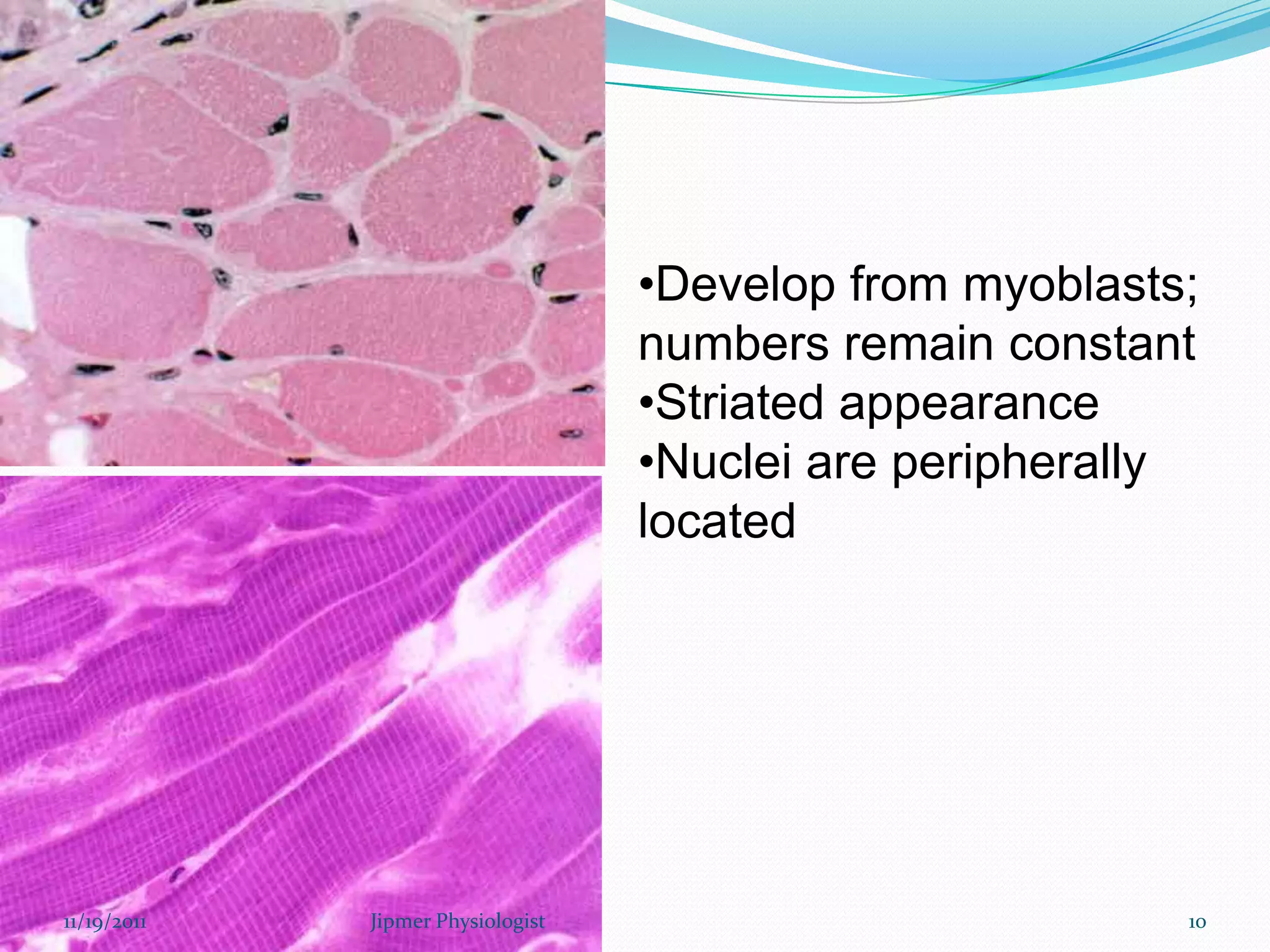
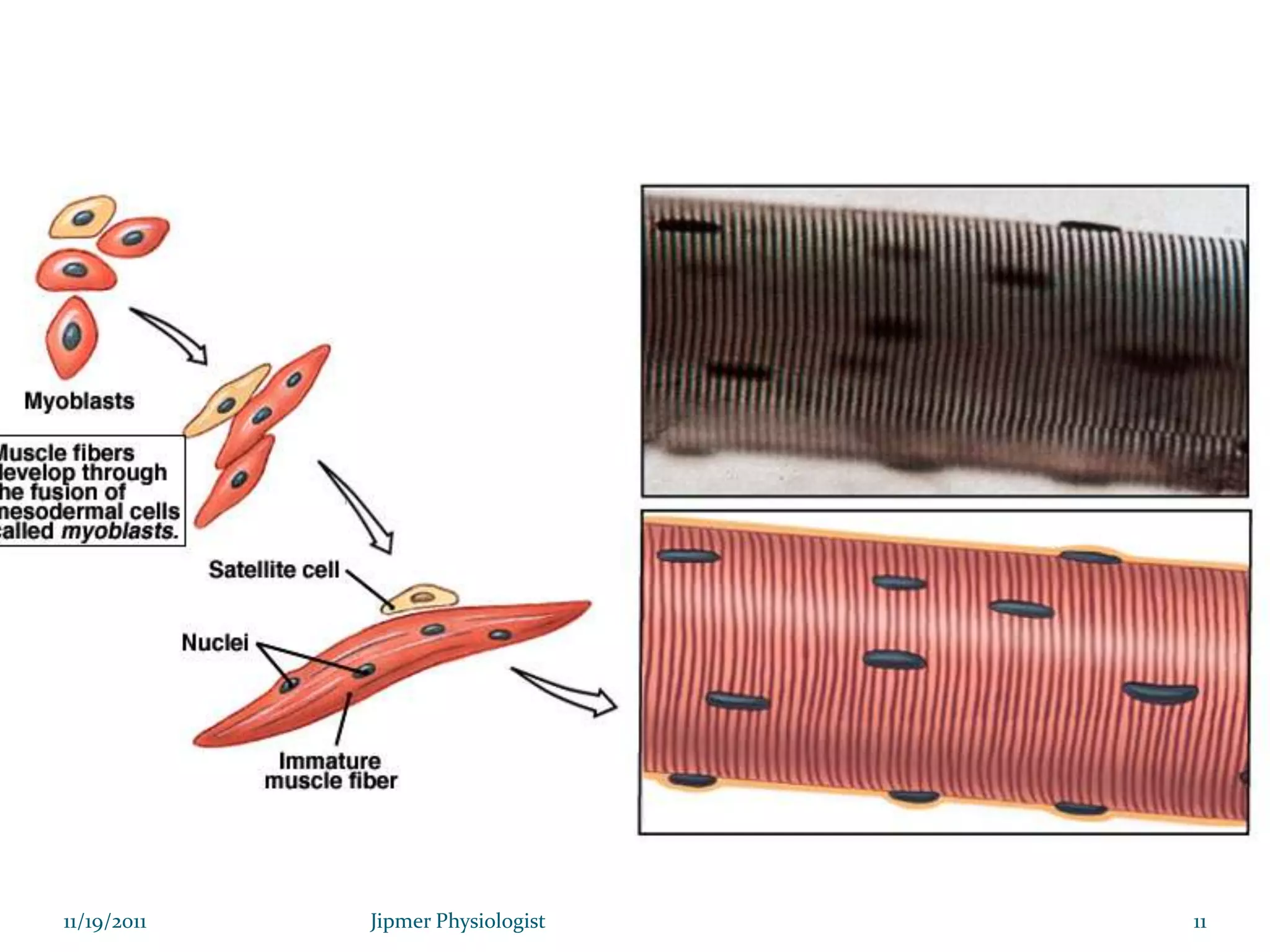
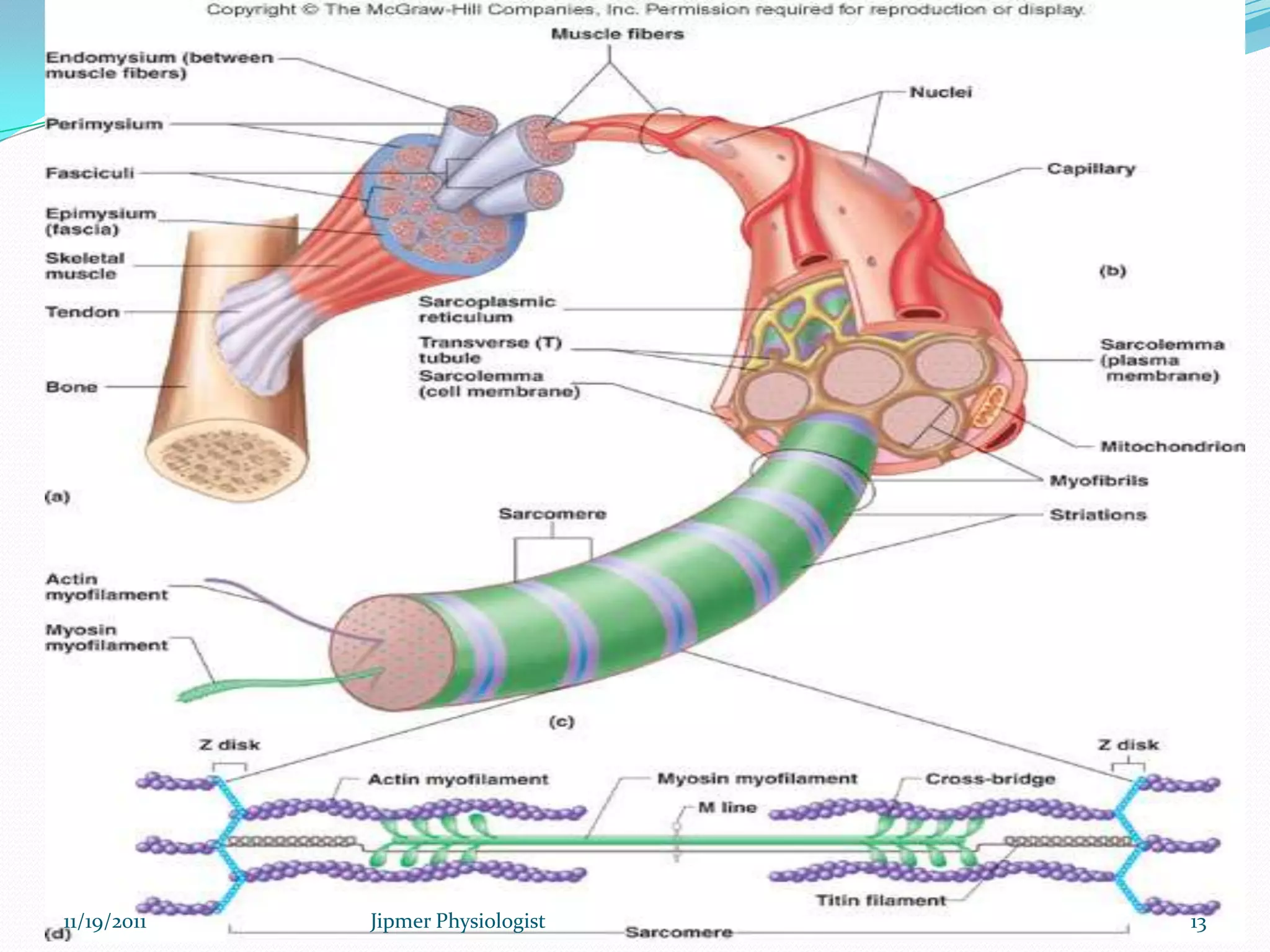
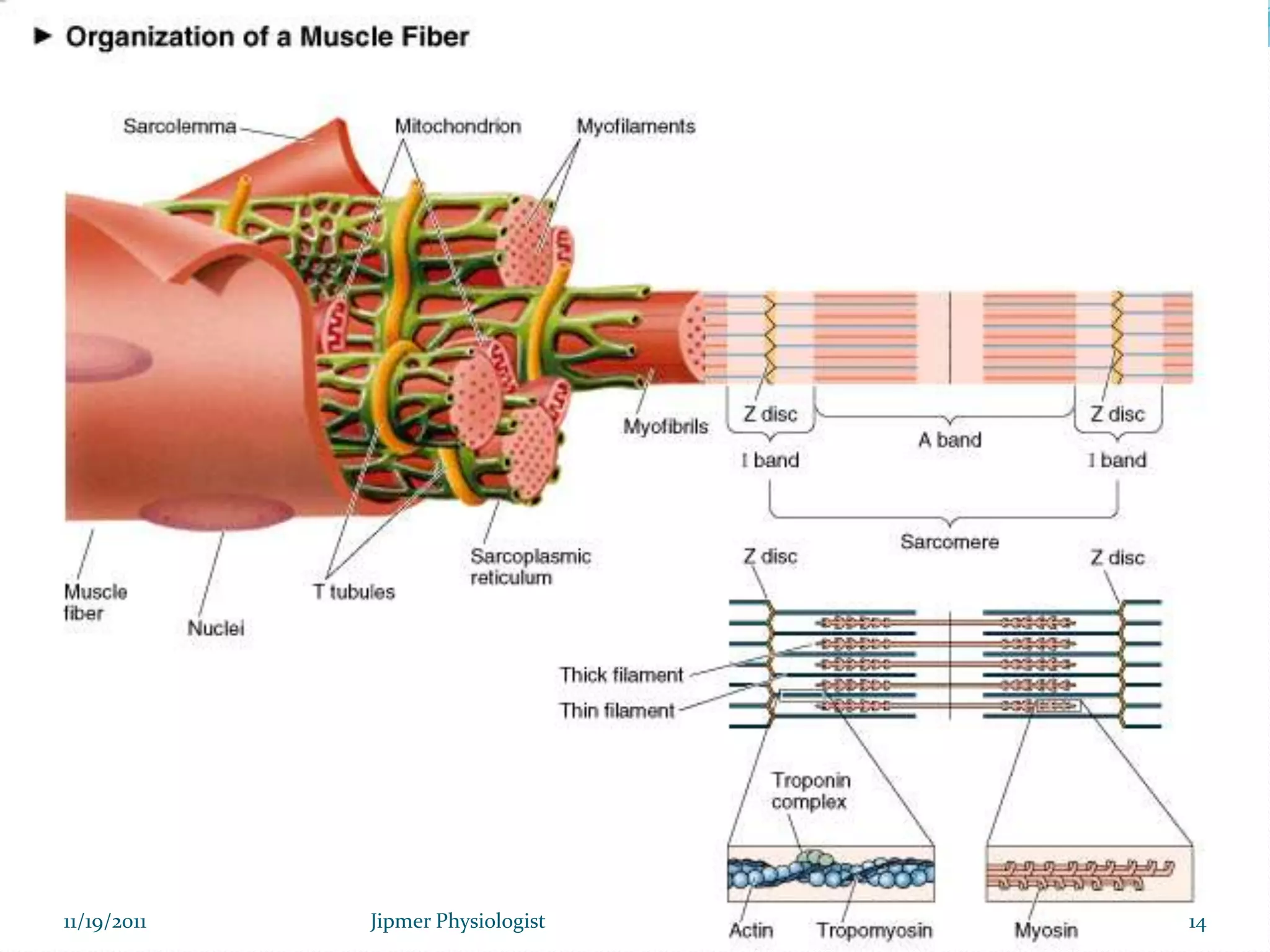
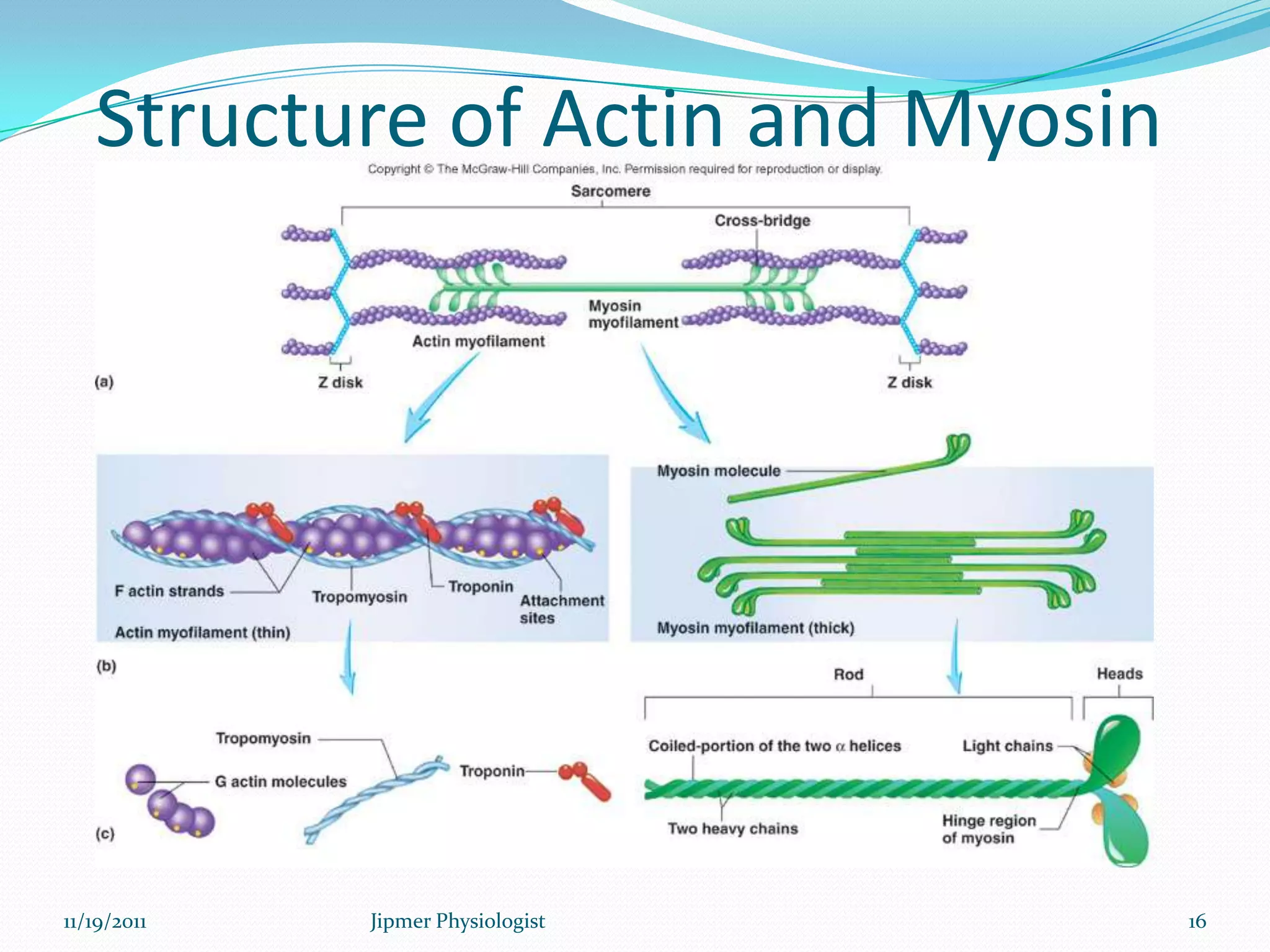
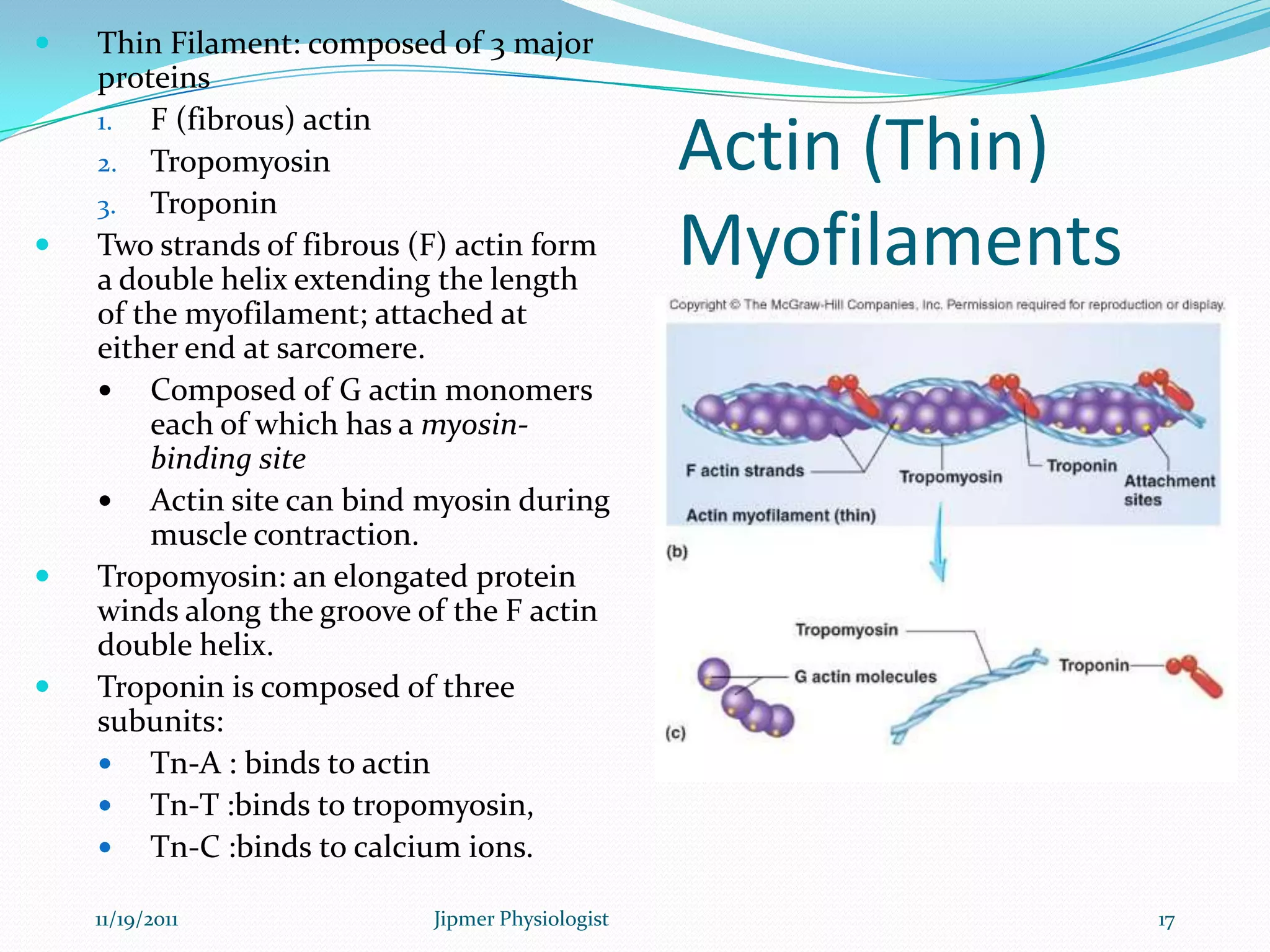
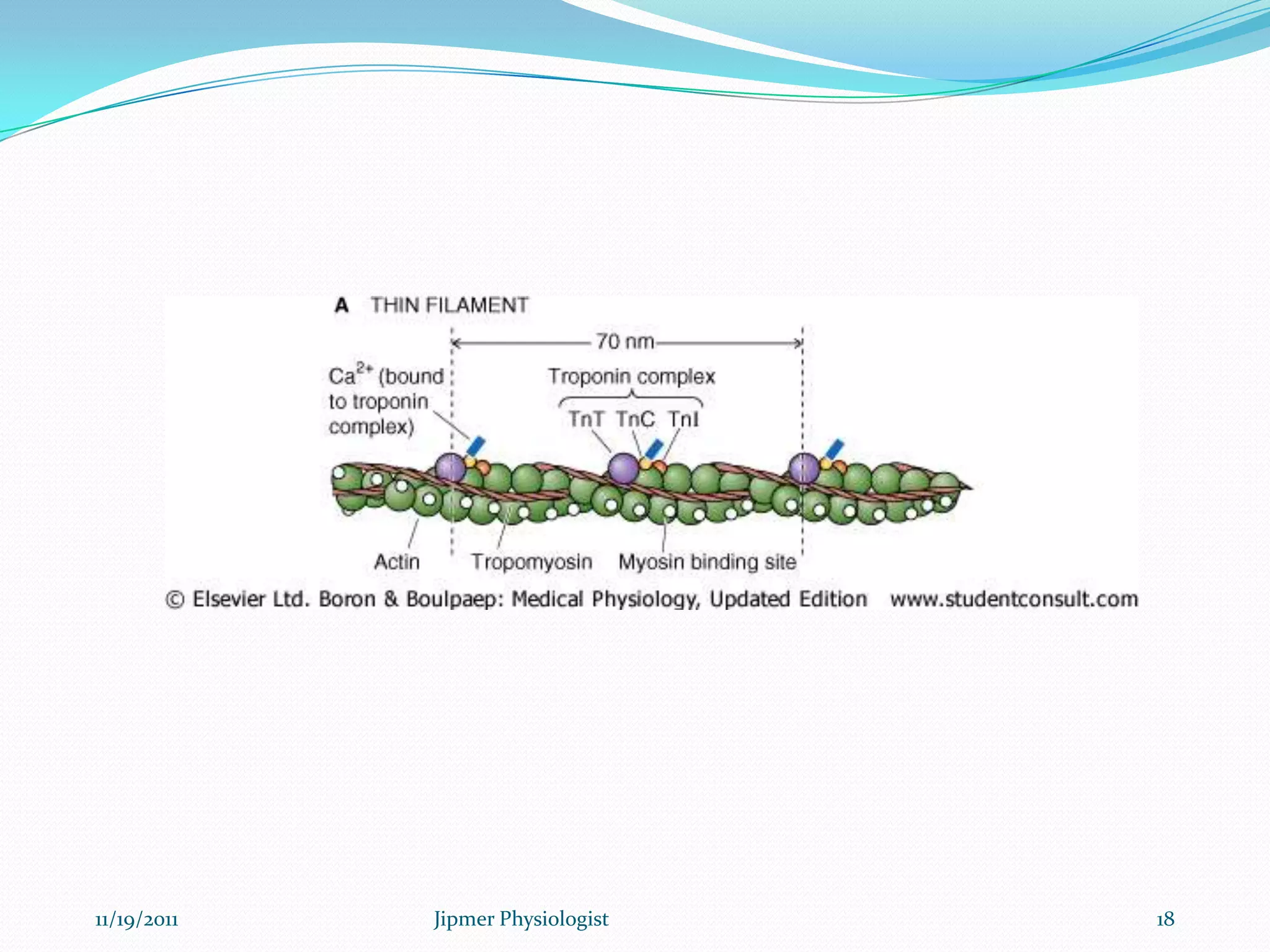
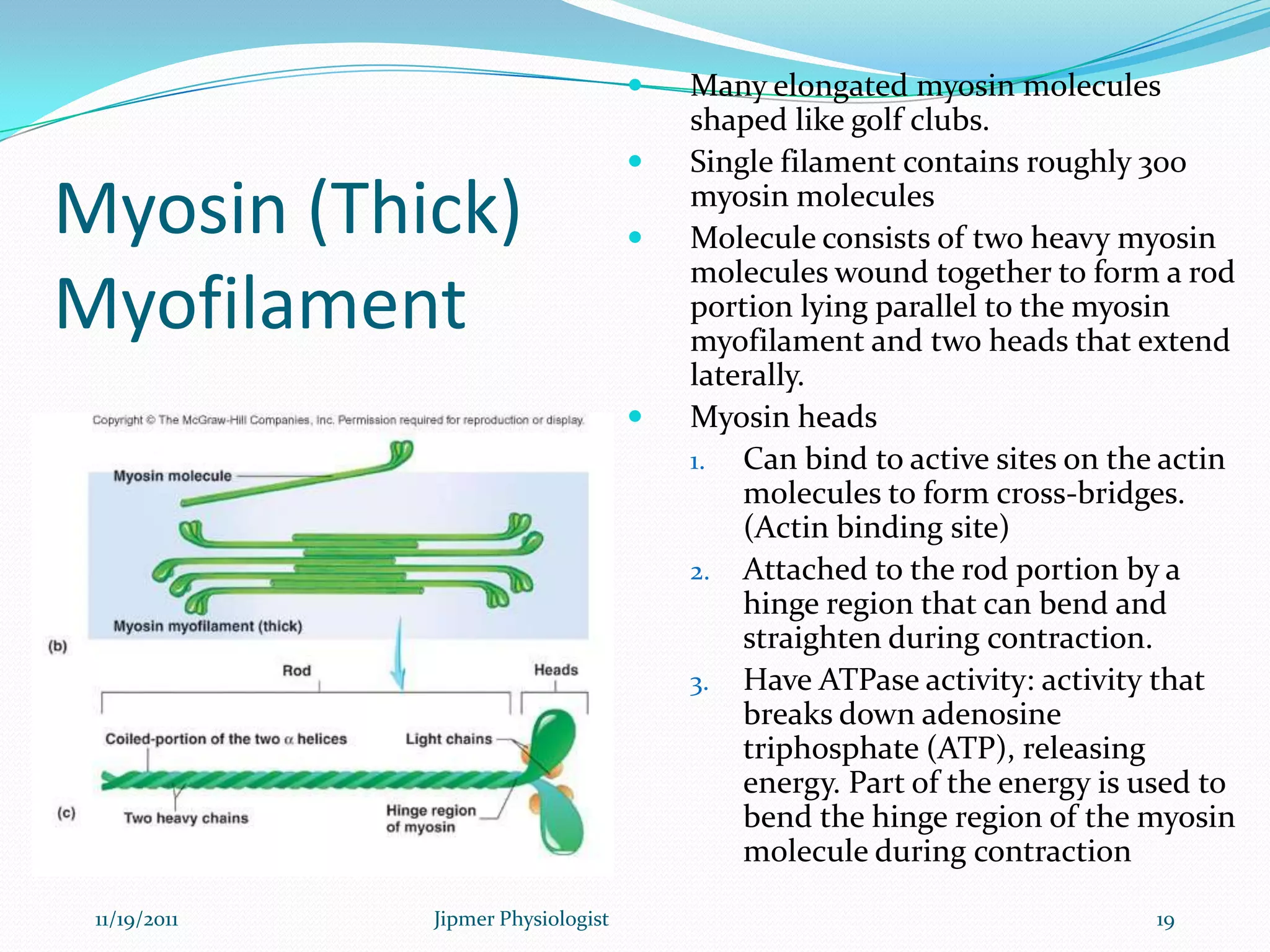
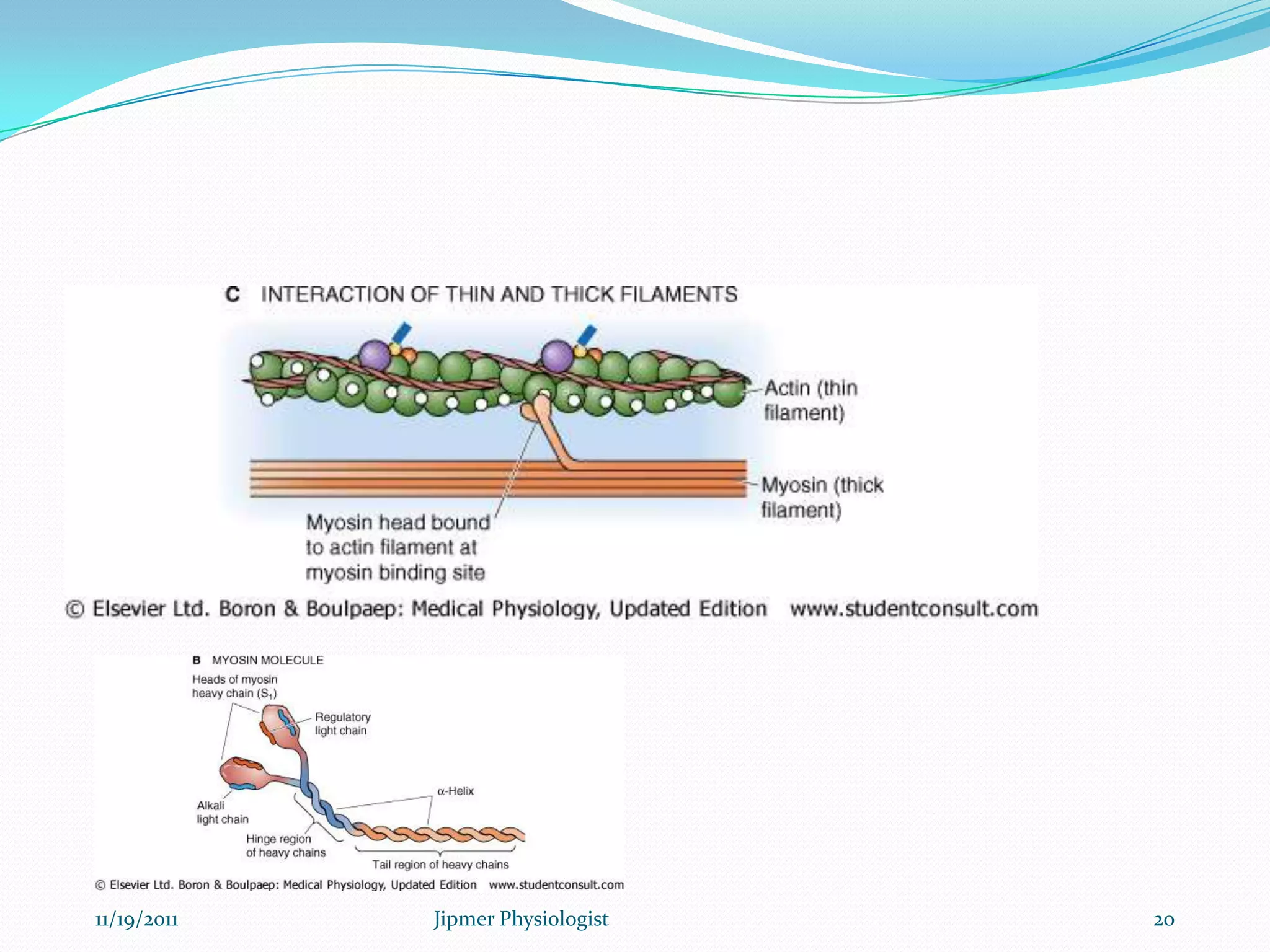
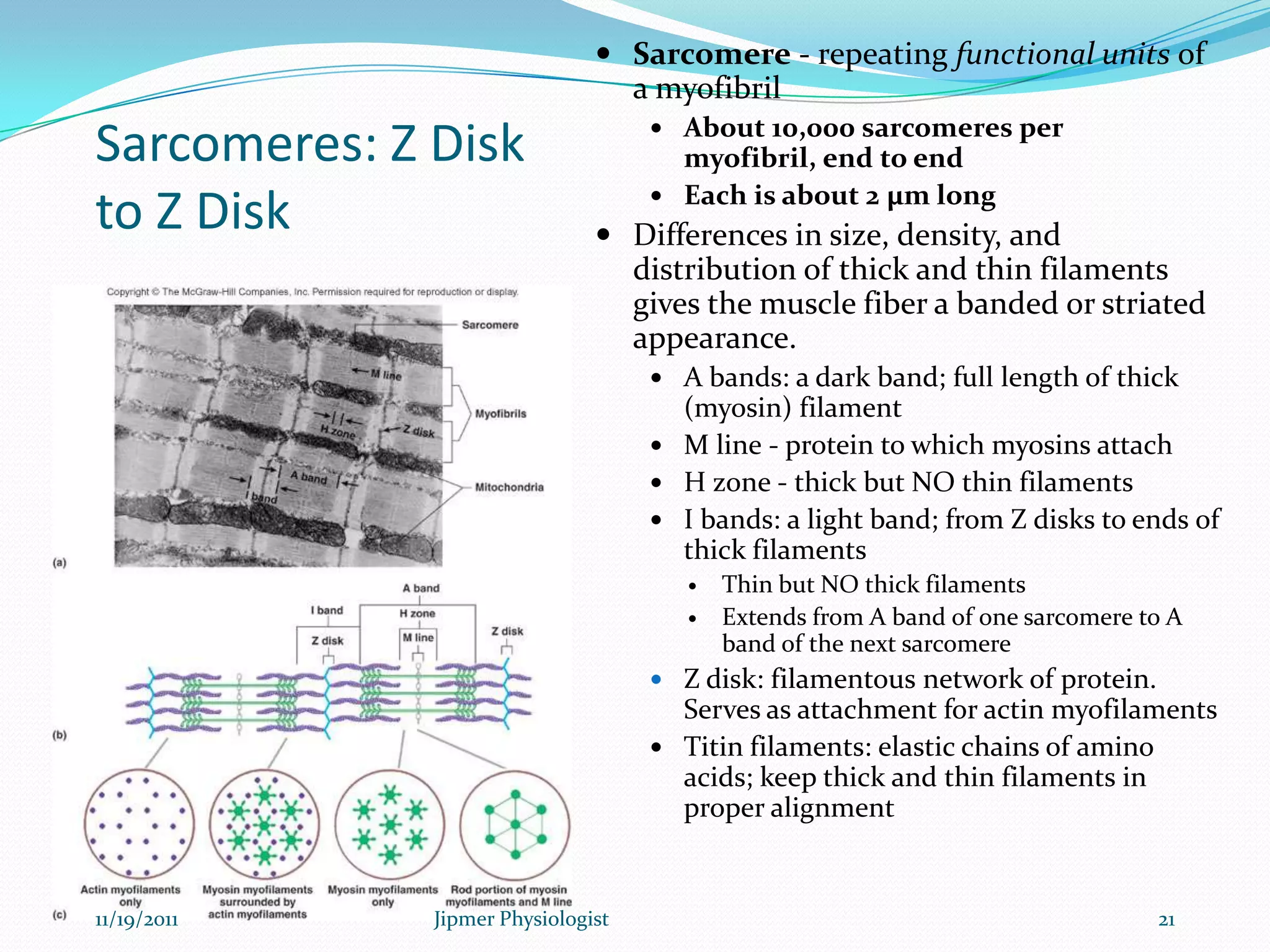
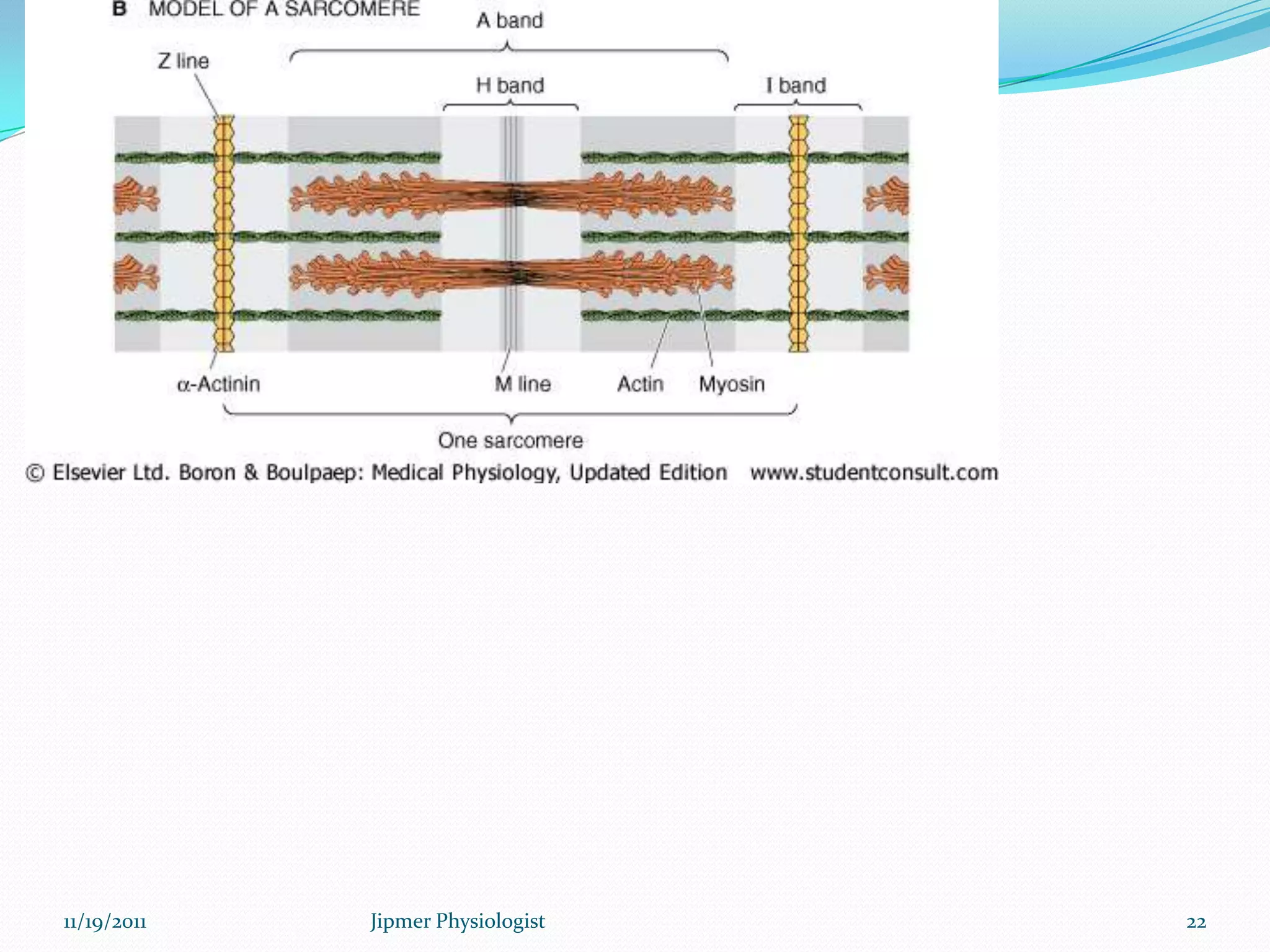
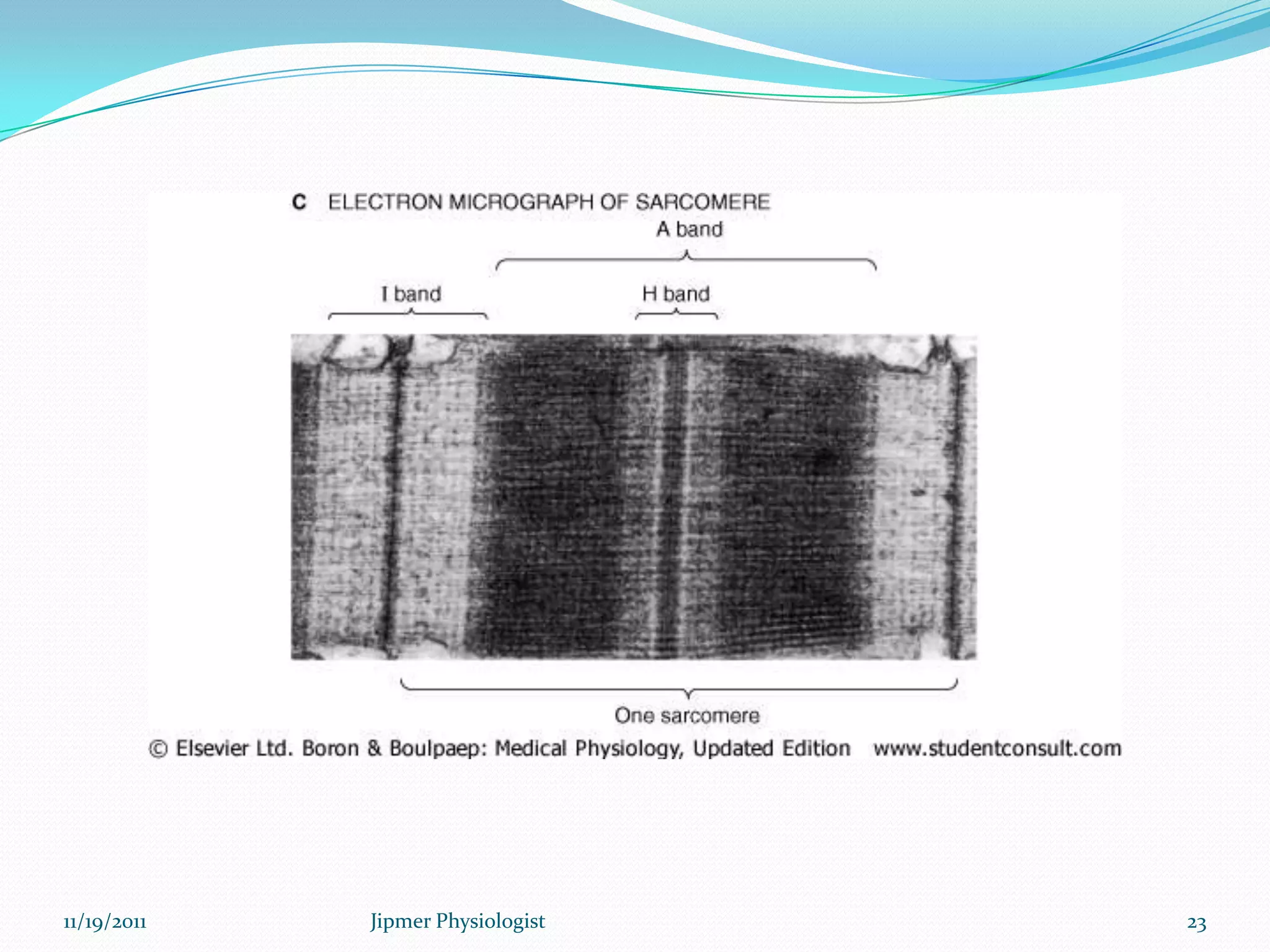
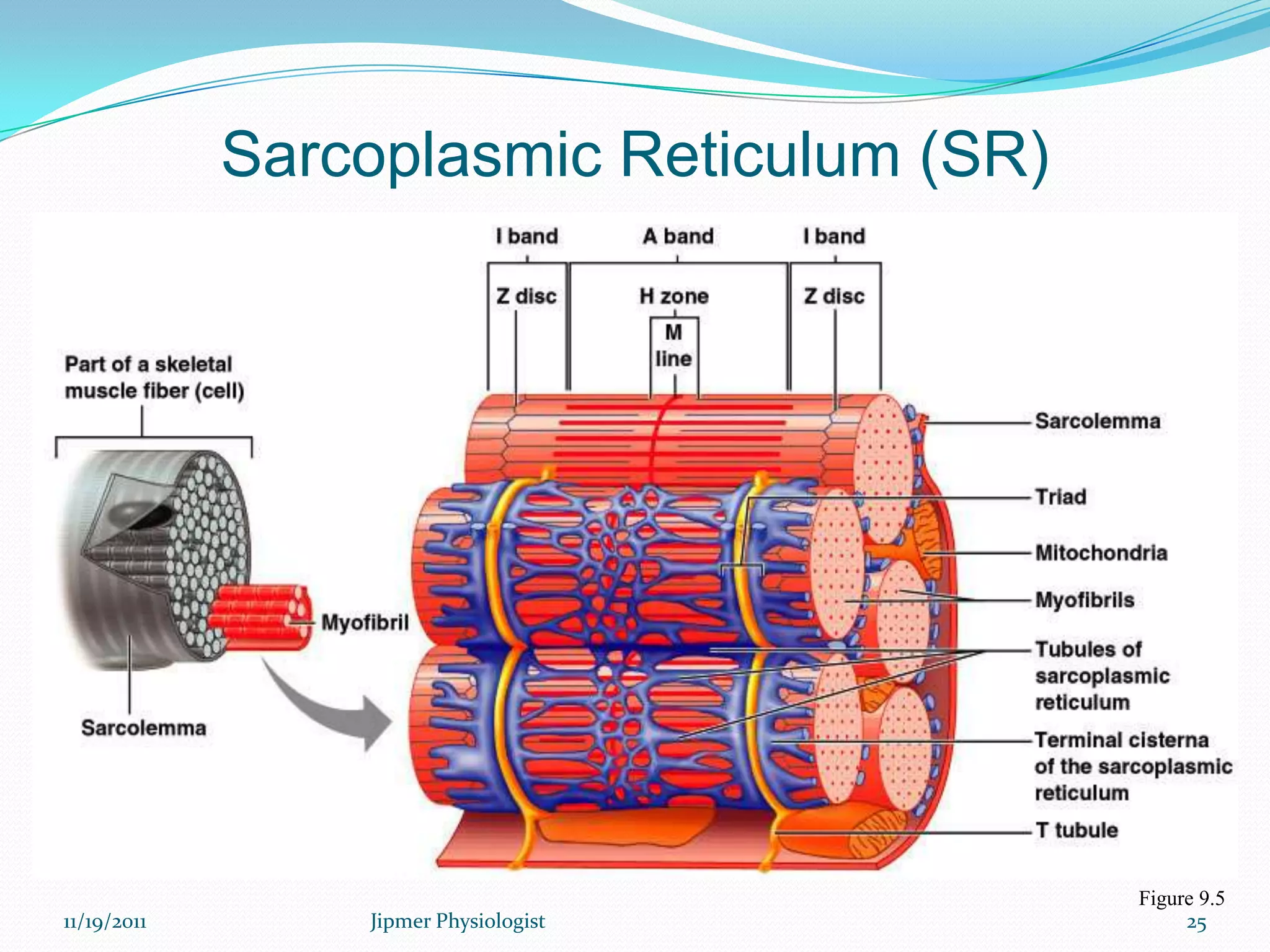
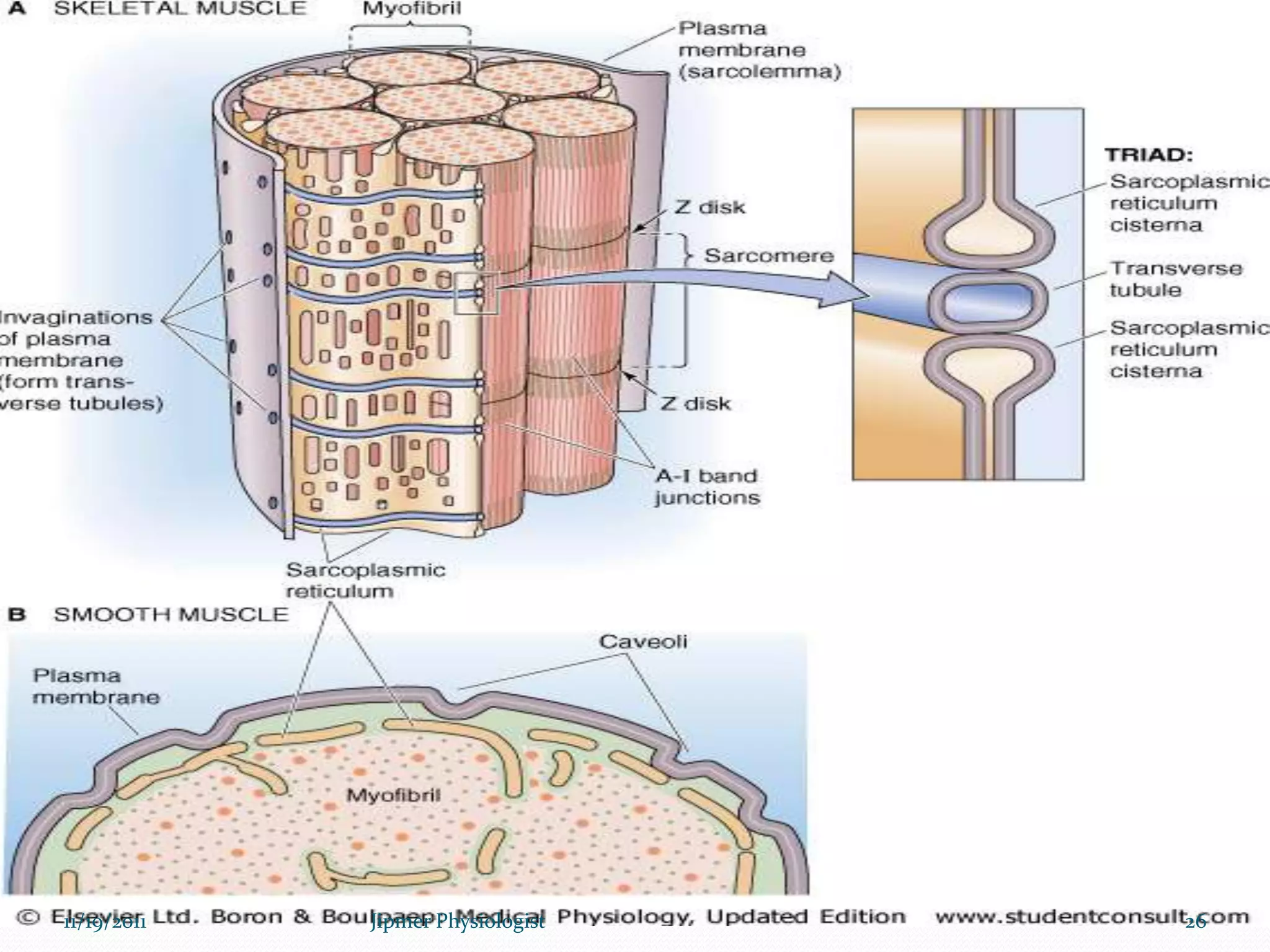
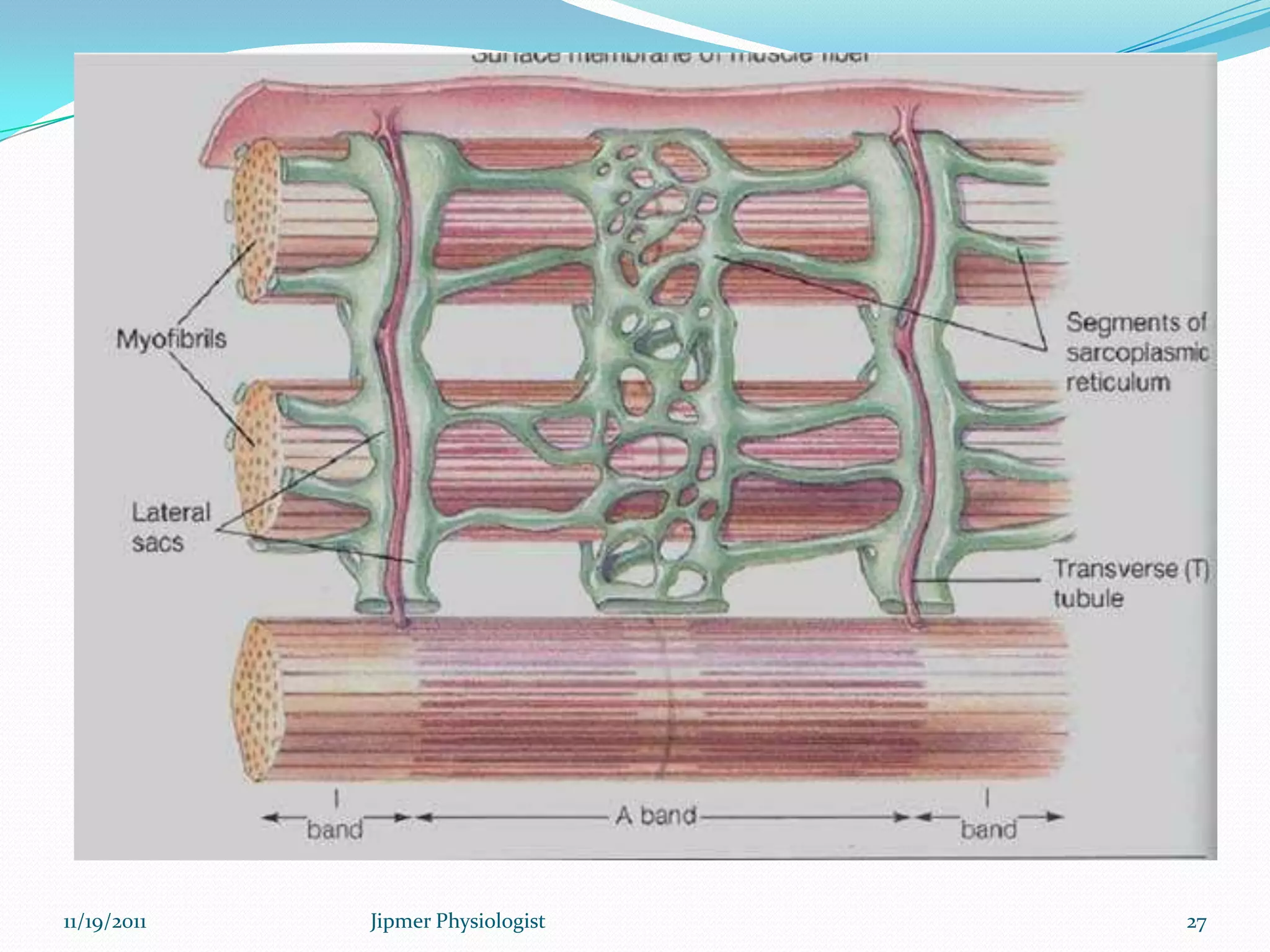
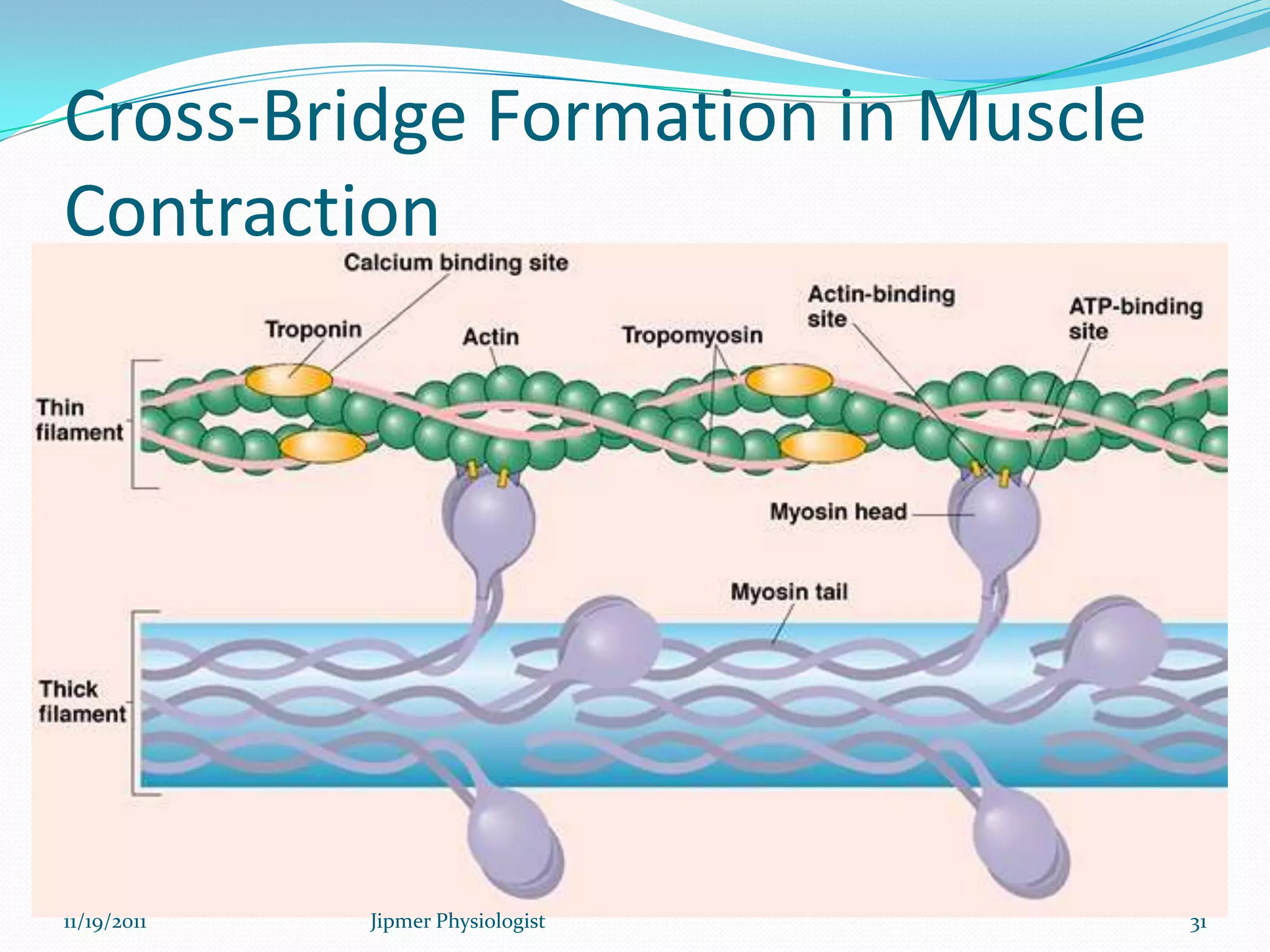
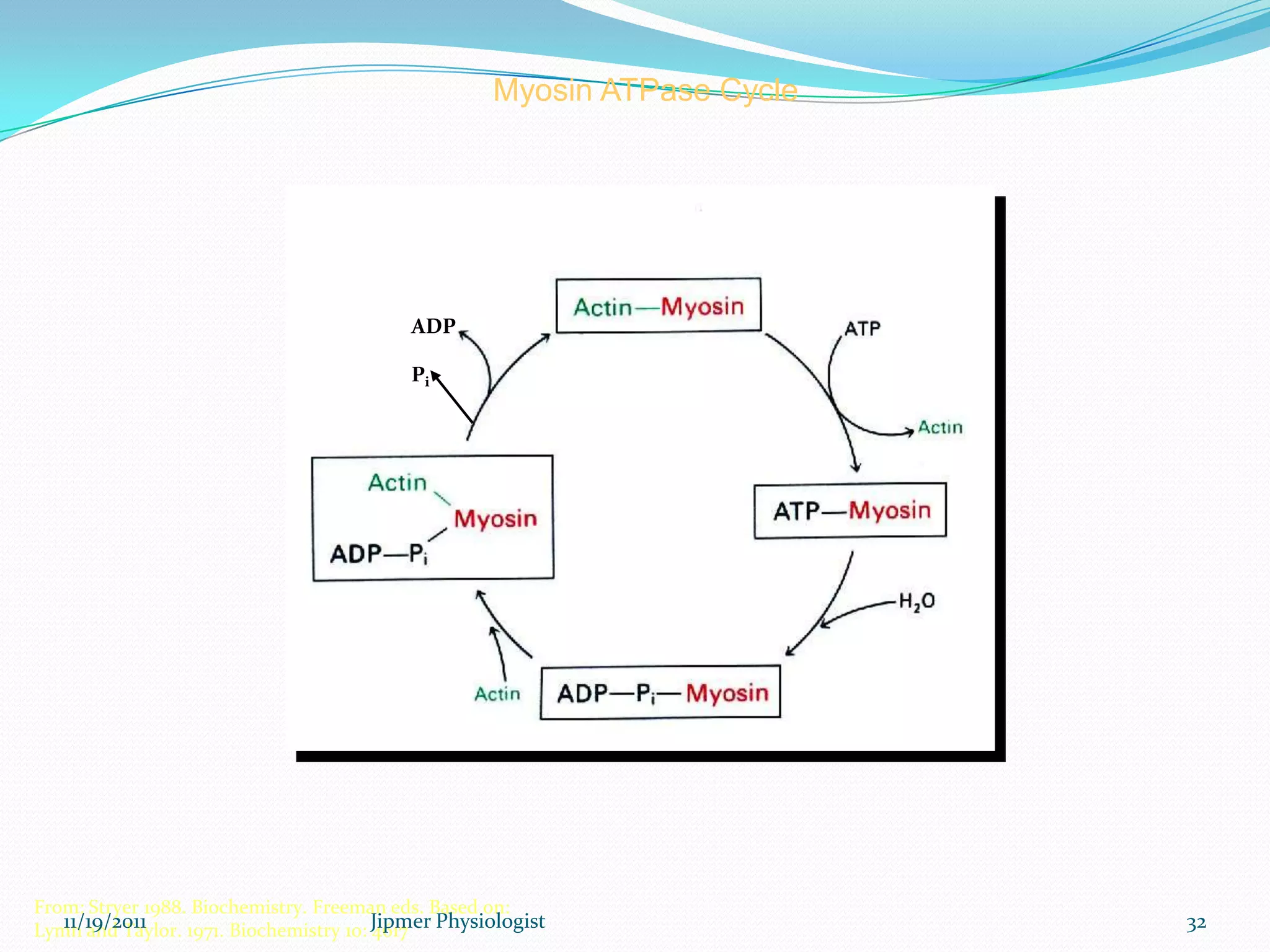
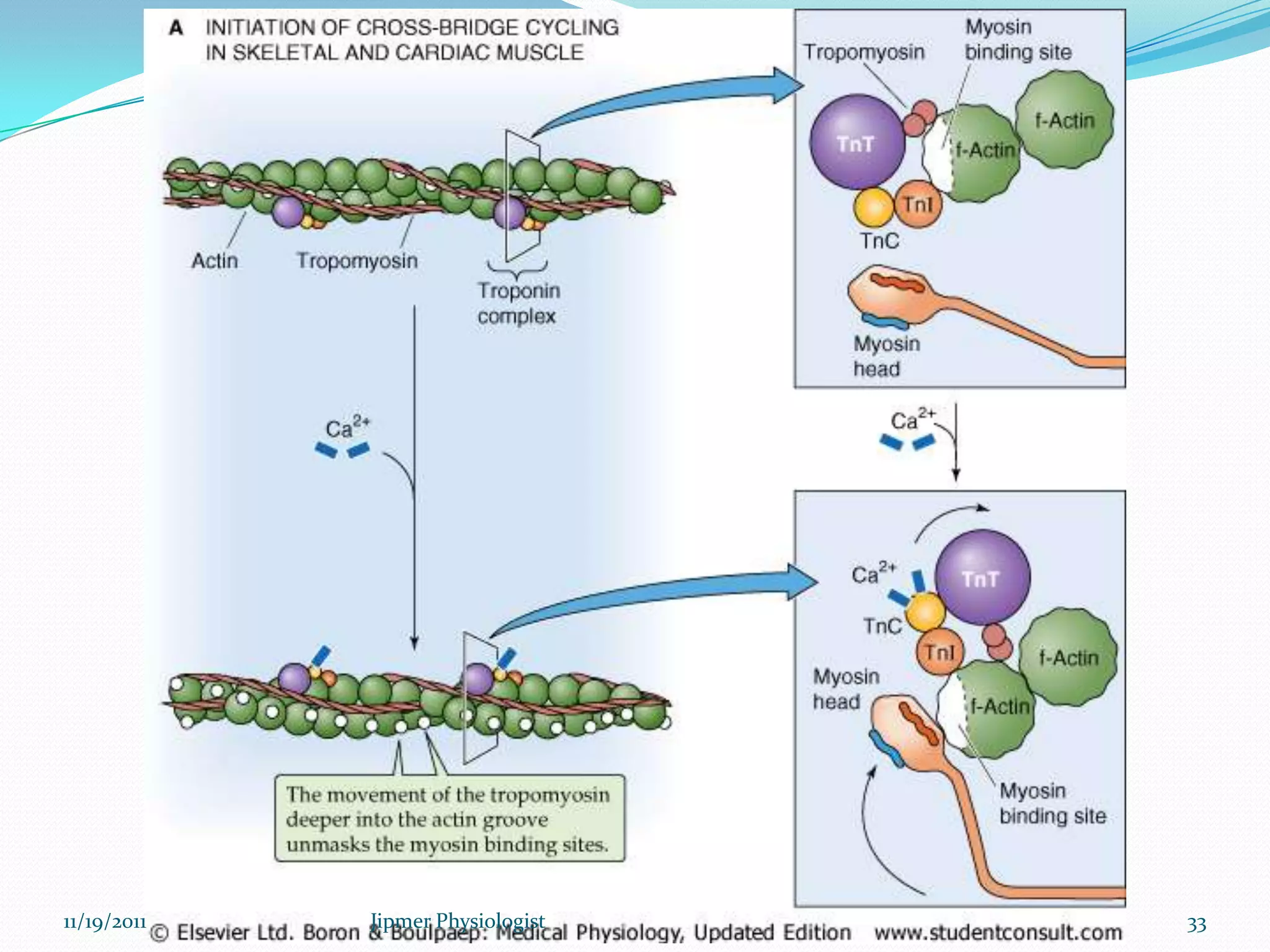
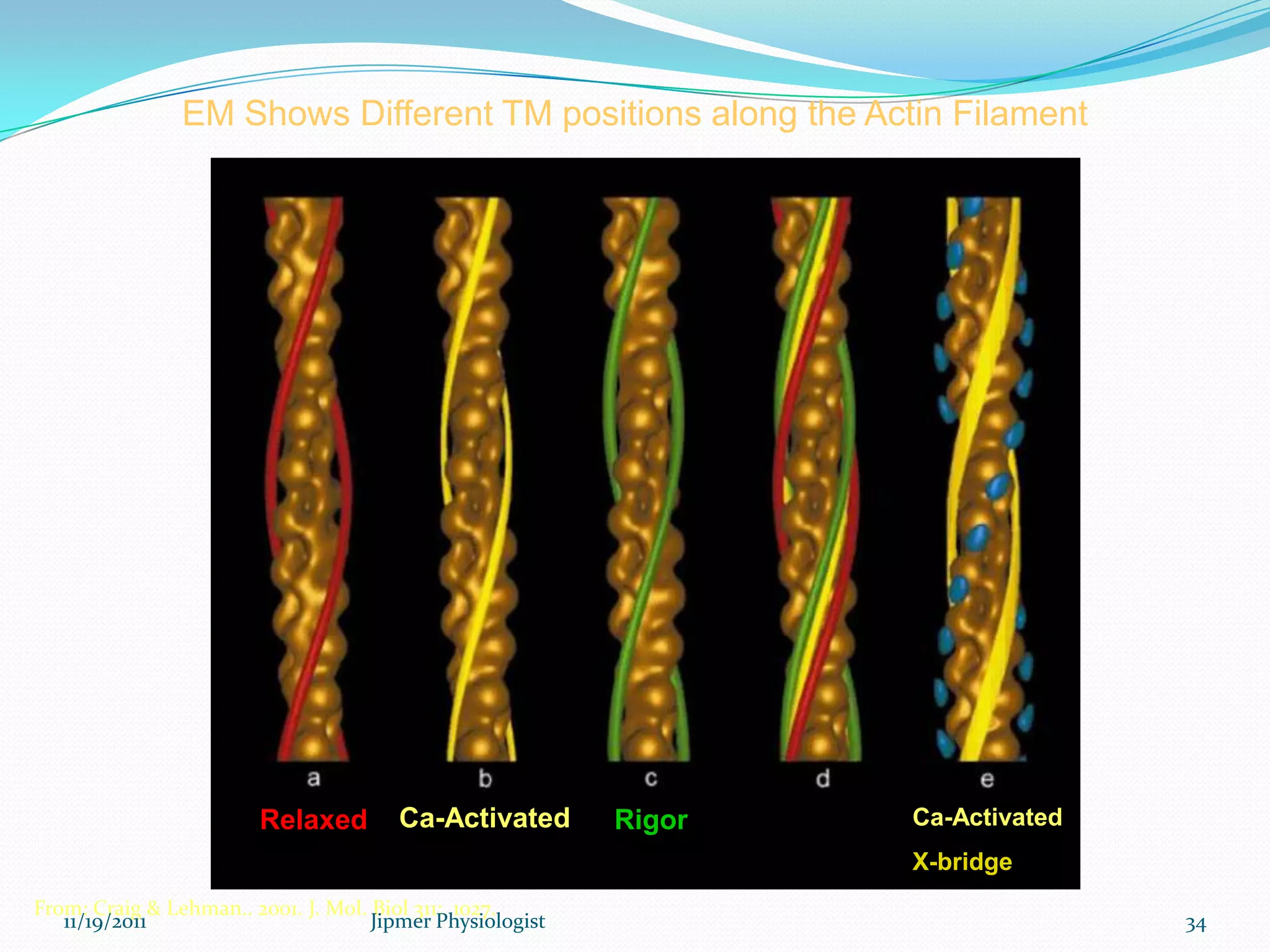
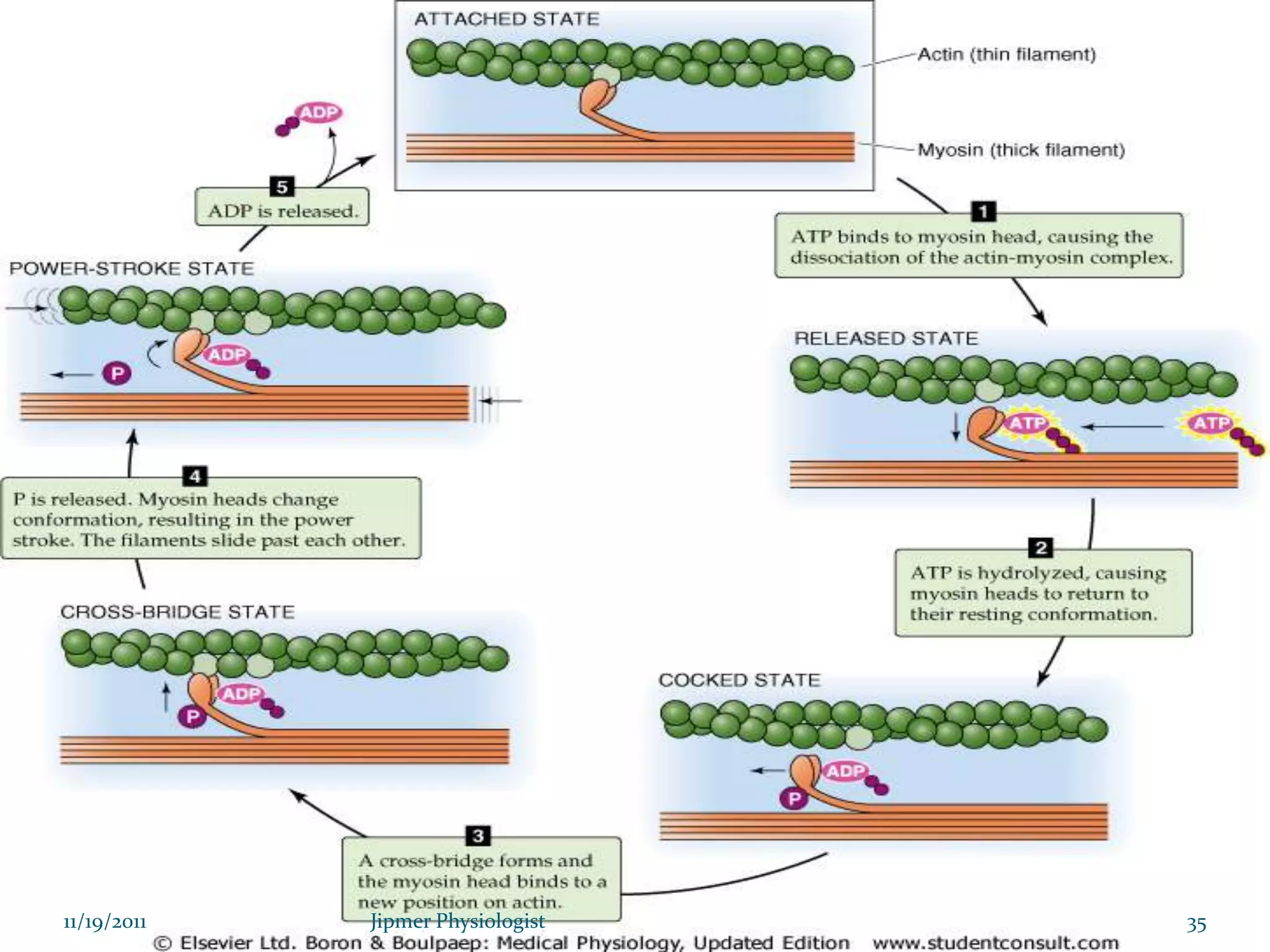
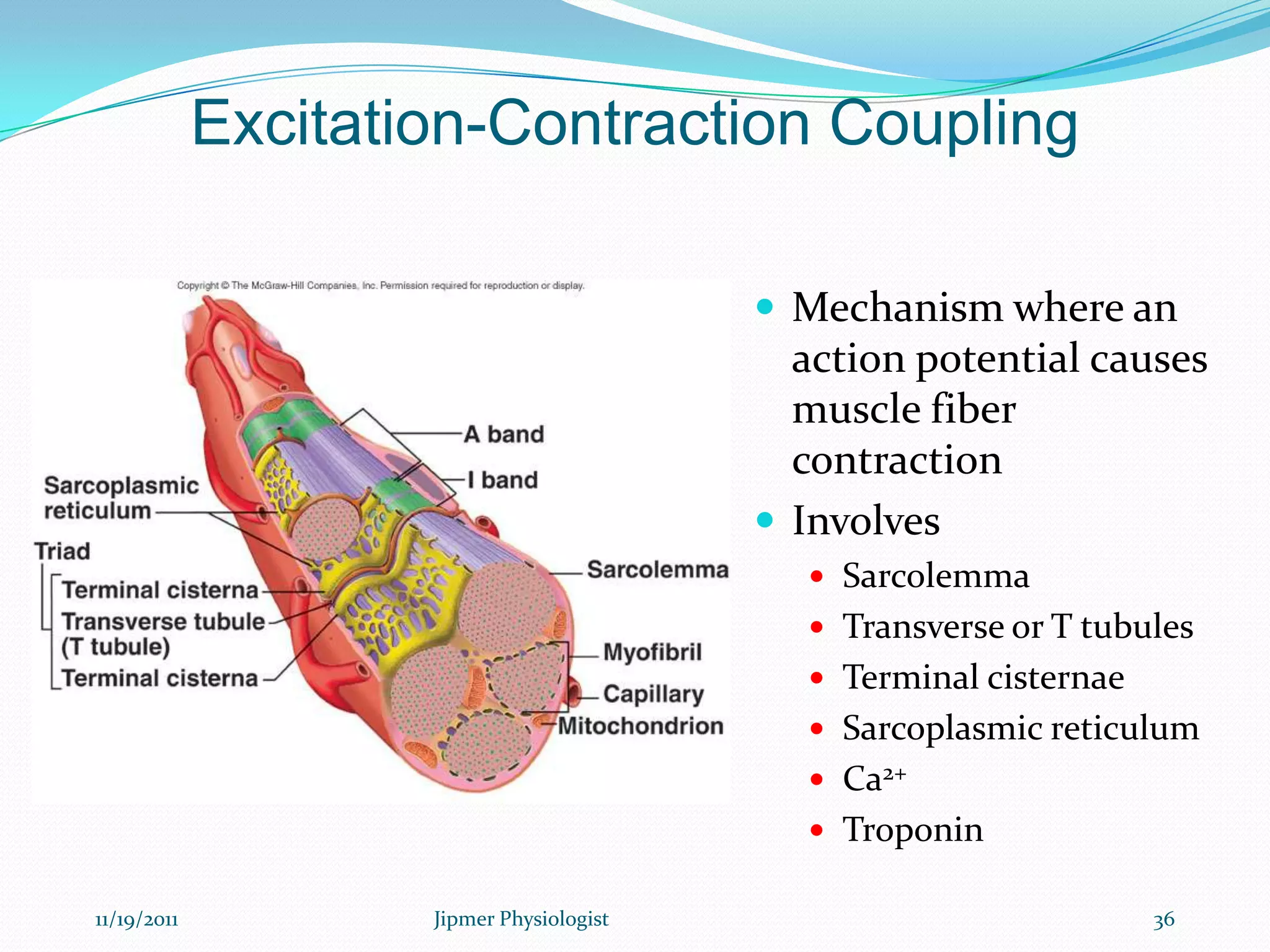
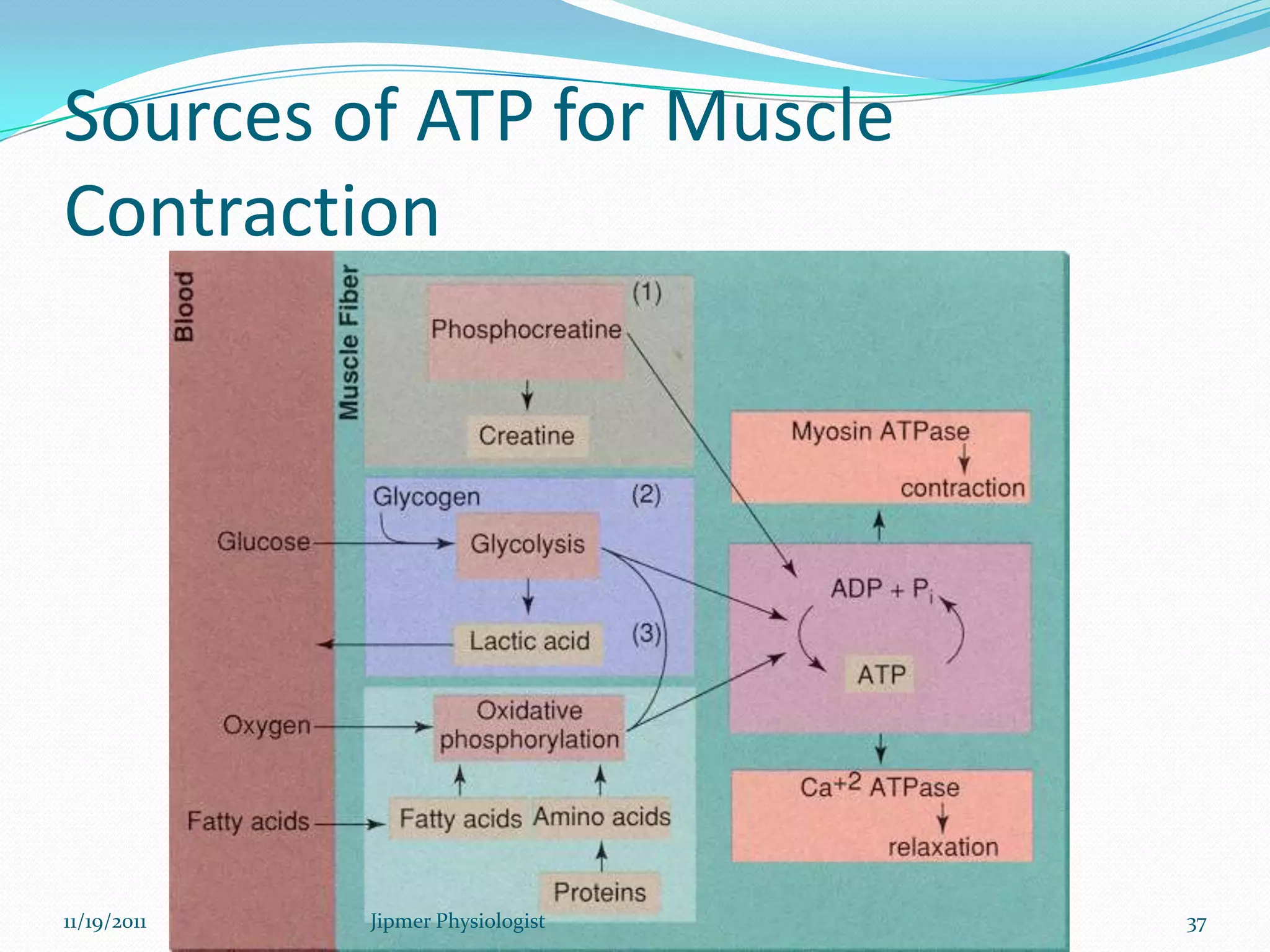
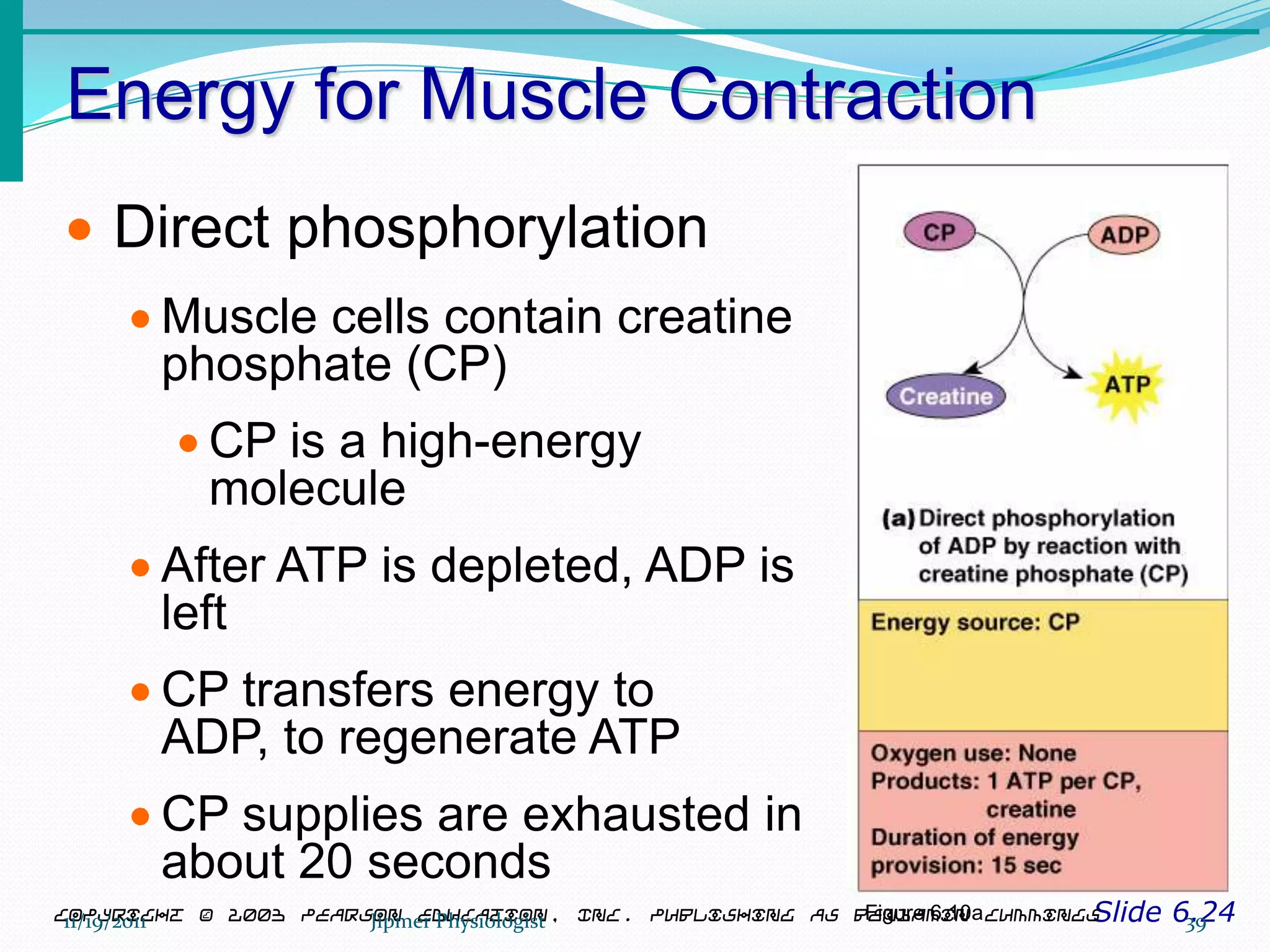
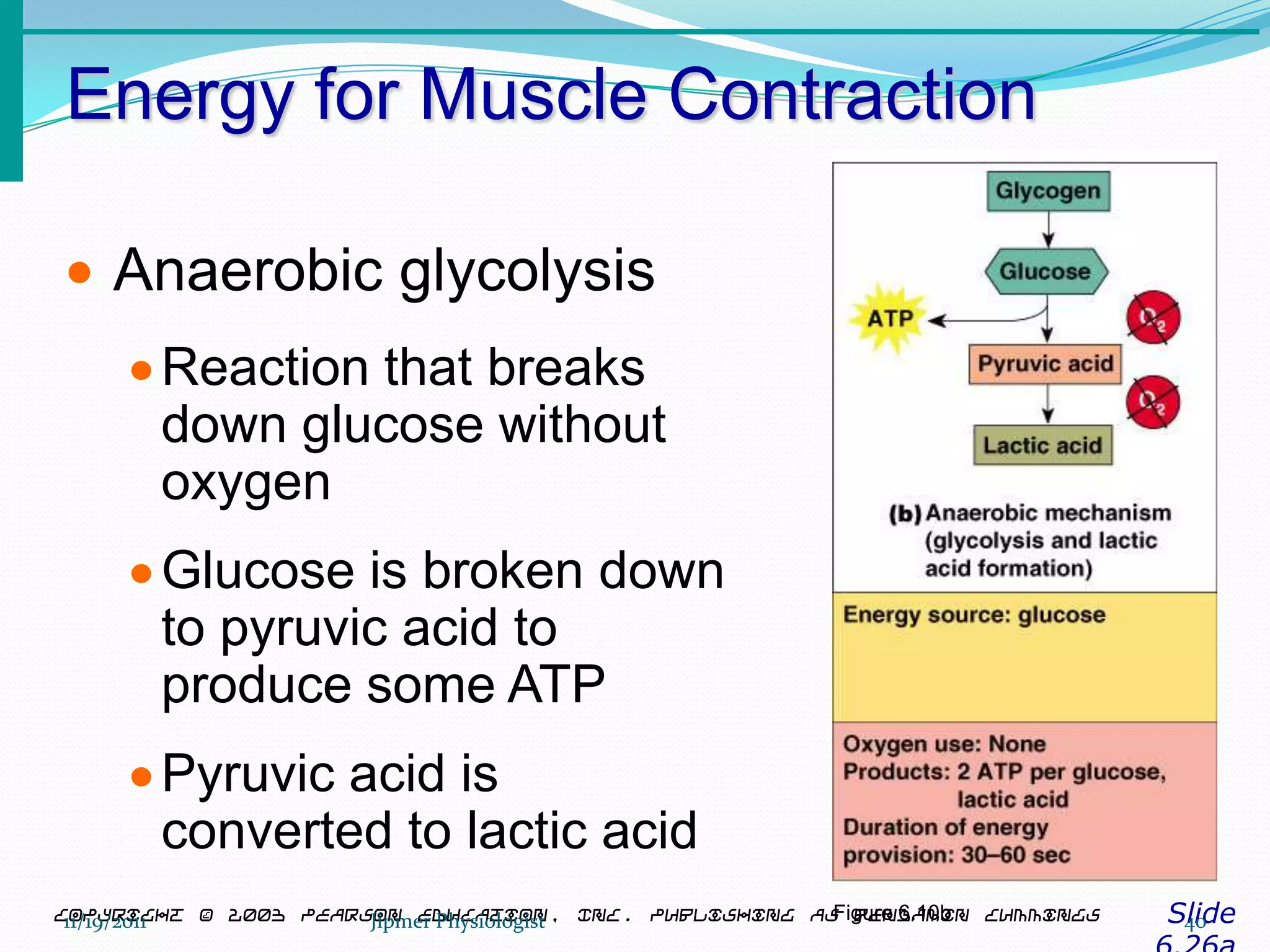
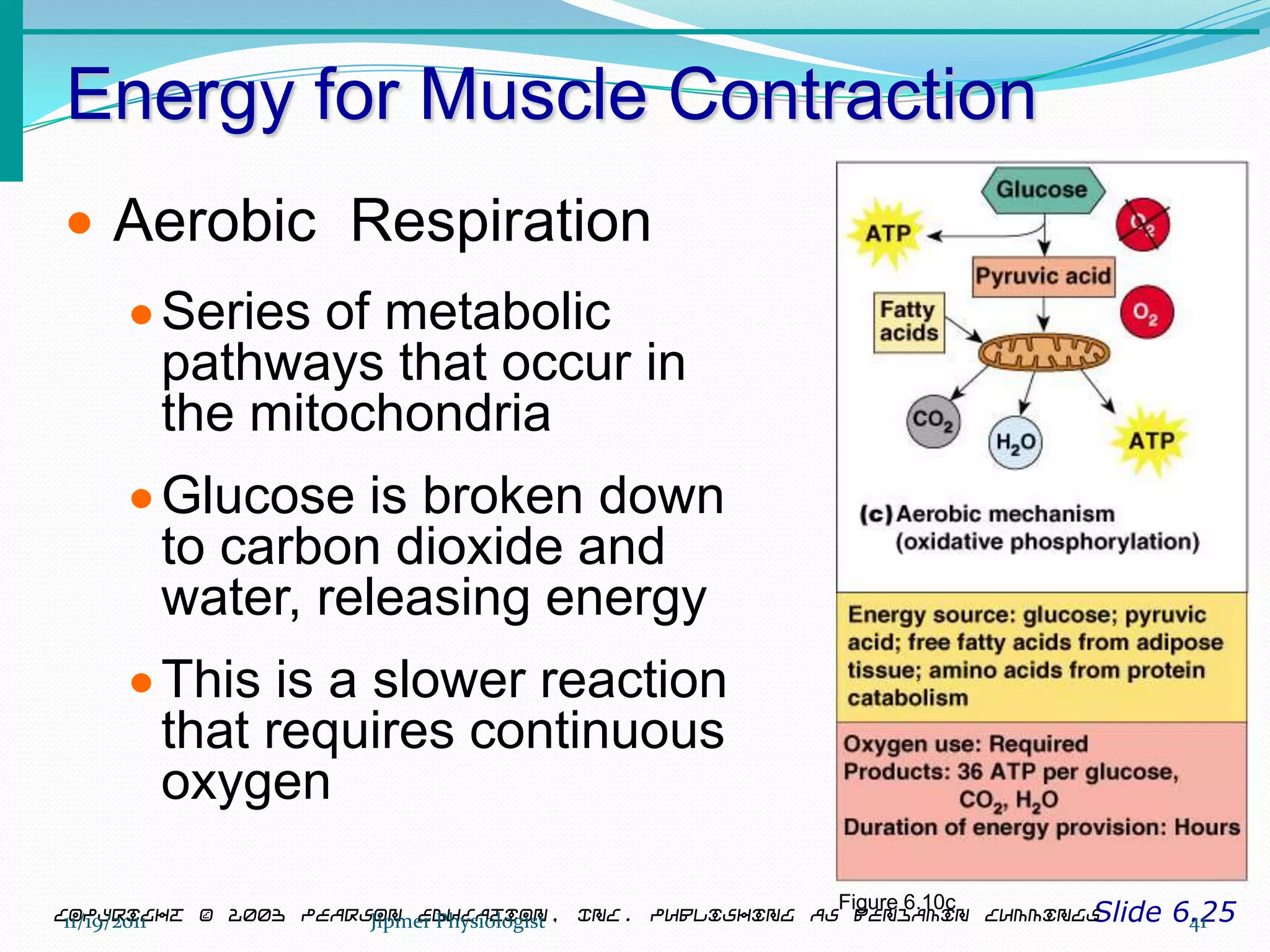
This document discusses the structure and function of skeletal muscle. It begins with an introduction to skeletal muscle and describes the characteristics of muscle fibers, including that they are multinucleated and striated. It then details the structure of the sarcomere, the basic contractile unit of skeletal muscle, including the thin actin filaments and thick myosin filaments. The document also describes excitation-contraction coupling and the sliding filament model of muscle contraction in which myosin cross-bridges attach to actin and generate force through an ATP-fueled cycling process.