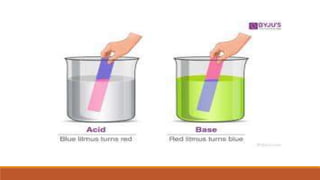
This document discusses acids and bases according to the Arrhenius concept. It defines acids as substances that dissociate in water to produce hydrogen ions and bases as those that dissociate to produce hydroxide ions. Examples of common Arrhenius acids include hydrochloric acid, nitric acid, and sulfuric acid. Examples of common Arrhenius bases include sodium hydroxide, potassium hydroxide, and calcium hydroxide. The document notes limitations of the Arrhenius concept, including that it only applies to aqueous solutions and cannot explain the behavior of compounds like carbon dioxide and ammonia that act as acids and bases yet do not contain hydrogen or hydroxide ions.