Embed presentation
Downloaded 115 times



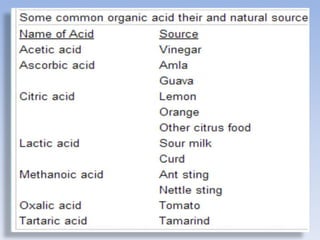


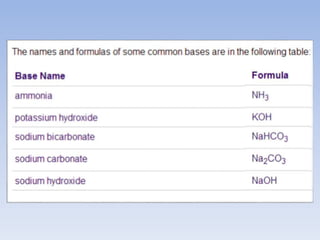





An acid is a substance that releases hydrogen ions (H+) in an aqueous solution. Acids have a sour taste, turn litmus paper red, and react with metals and bases. Common examples include hydrochloric acid, acetic acid, and sulfuric acid. Strong acids are corrosive. A base is a substance that releases hydroxide ions (OH-) in an aqueous solution and accepts protons. Bases usually taste bitter and feel slippery. Sodium hydroxide is an example of a base. Salts are ionic compounds formed through the neutralization reaction of an acid and a base. Salts can appear clear or colored, elicit various tastes, and do not conduct electricity as sol










