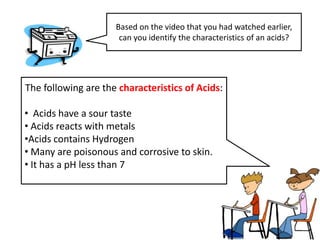
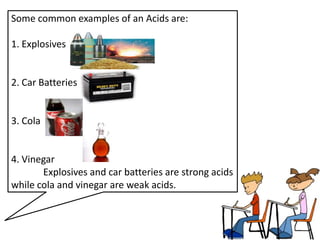
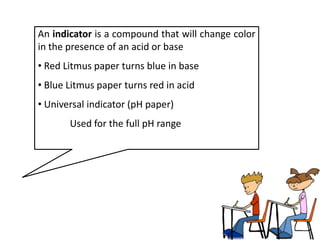
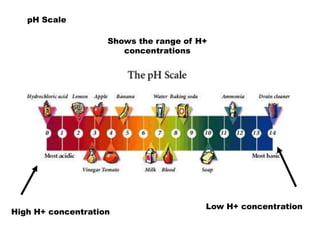
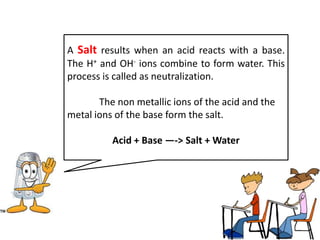
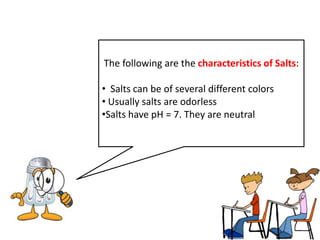
This document discusses acids, bases, and salts. It defines acids as substances that give H+ ions in water and have a sour taste, react with metals, and have a pH less than 7. Bases are defined as substances that give OH- ions in water, usually taste bitter, feel slippery, and have a pH greater than 7. Salts are formed when acids and bases react, combining H+ and OH- ions to form water. Common examples of acids include vinegar and cola, bases include drain cleaner and baking powder, and salts include table salt and toothpaste. The document provides characteristics, examples, and a brief activity to identify household substances as acids, bases or salts.