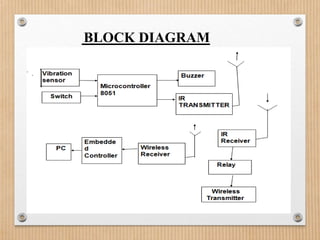
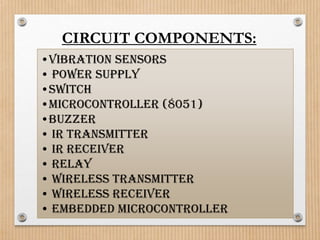
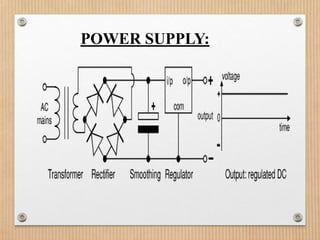
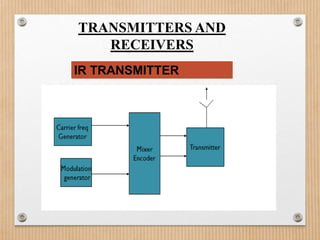
This document proposes a system to automatically identify road accidents using wireless technology. The system has three modules: a vehicle side module, road side module, and control room module. When an accident occurs, vibration sensors on the vehicle trigger a microcontroller to send an IR signal to a roadside transmitter informing the control room of the accident location. This allows emergency services to quickly locate and assist victims, increasing survival chances. The system aims to address India's high road accident rates by expediting emergency response times.