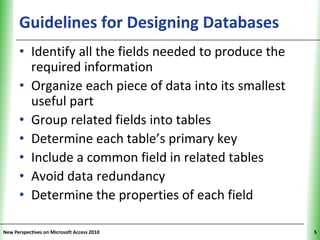
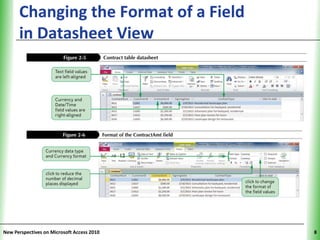
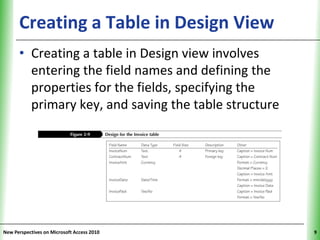
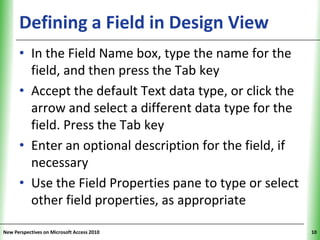
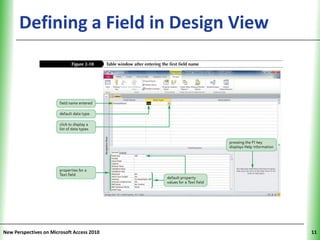
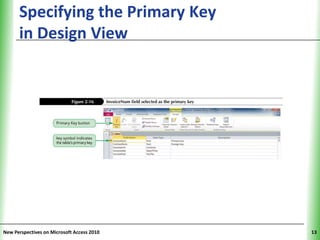
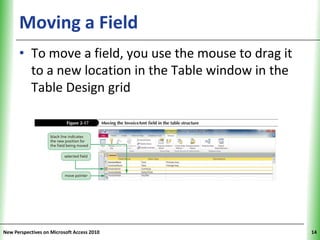
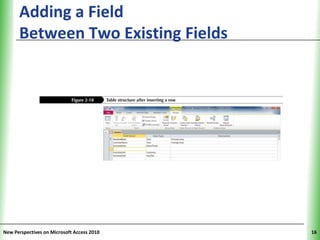
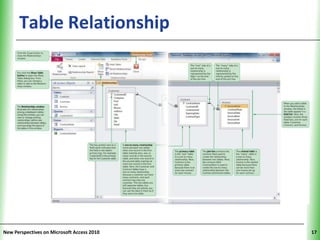
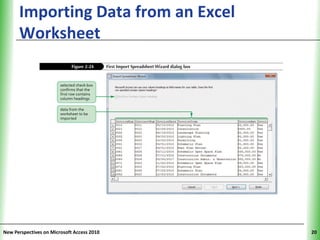
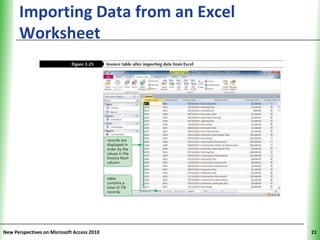
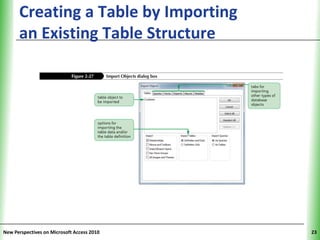
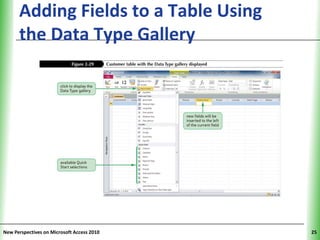
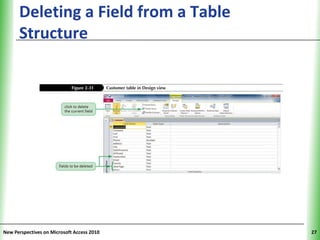
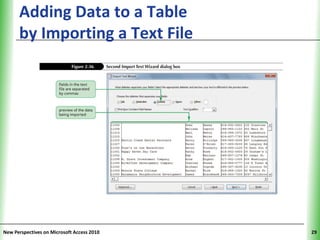
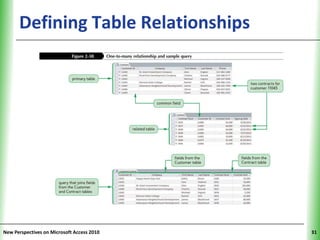
This document provides an overview of how to build a database in Microsoft Access, including guidelines for designing databases and defining table relationships. It discusses how to create and modify tables, define fields and primary keys, import data from Excel and text files, and set relationships between tables. The objectives are to learn how to design databases, create and modify tables and fields, import data, and define relationships between tables.