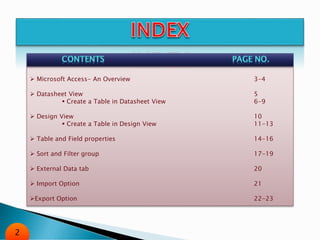
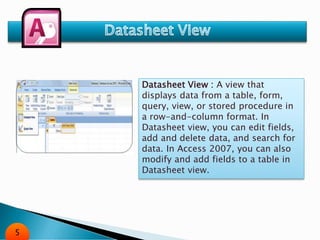
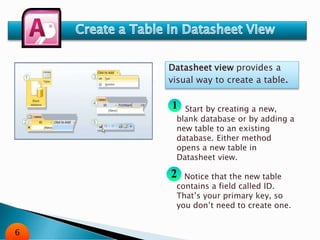
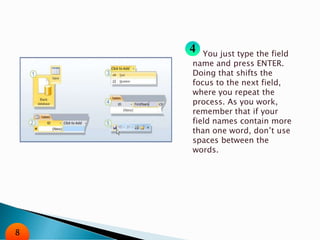
The document is an overview of Microsoft Access, a database management system that helps organize and manage data. It covers various features such as datasheet and design views, table and field properties, sorting and filtering techniques, and external data import/export options. Guides are provided for creating and modifying tables, as well as utilizing Access for managing and sharing data.













![Siddikulla_MS_Access[1].pdf ROLL - 220711130077](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/siddikullamsaccess1-240713073829-6af27082/85/Siddikulla_MS_Access-1-pdf-ROLL-220711130077-24-320.jpg)