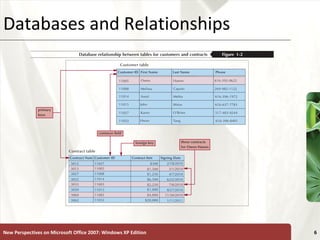
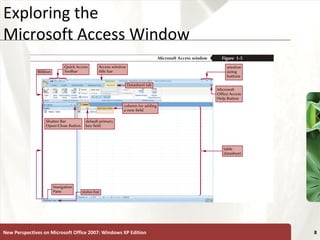
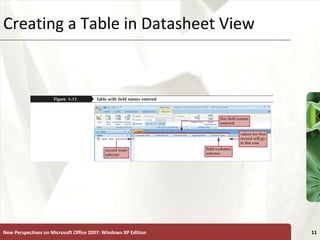
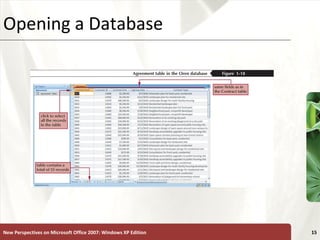
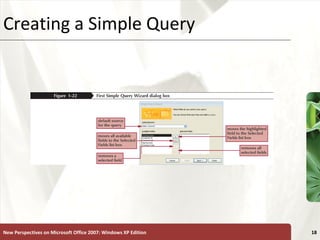
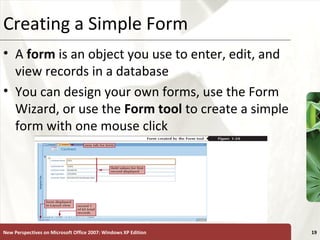
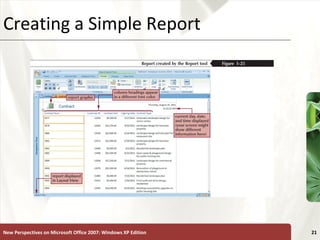
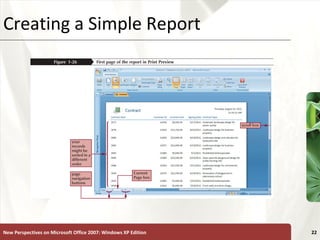
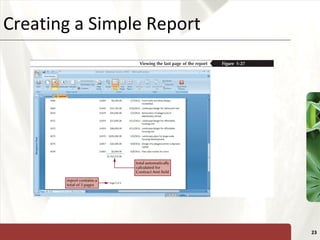
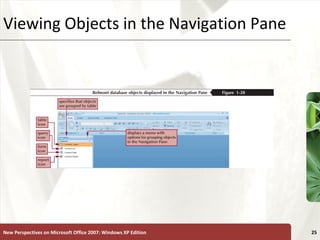
The document provides a tutorial on how to create and manage a database using Microsoft Access 2007, covering key concepts such as fields, records, tables, and relational databases. It instructs on creating and saving tables, entering records, navigating databases, and utilizing features like queries, forms, and reports. Additionally, the tutorial explains how to compact, back up, and restore a database to maintain its integrity.