The document discusses acceleration and related concepts:
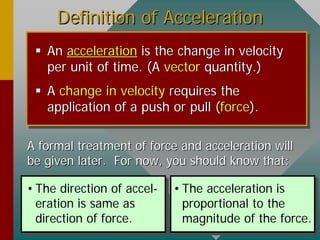
- Acceleration is the change in velocity per unit of time and is a vector quantity. It results from an applied force and is proportional to the force's magnitude.
- Velocity is speed in a given direction, while speed is the distance traveled per time and does not consider direction.
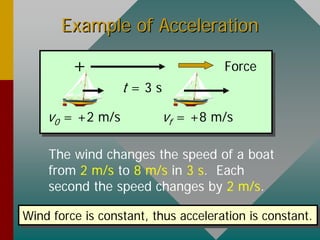
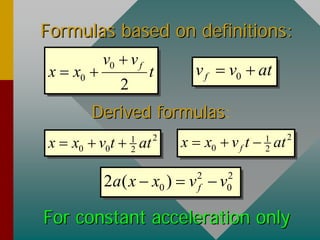
- Average acceleration is calculated as the change in velocity divided by the time interval. Instantaneous acceleration is the slope of the velocity-time graph at an instant.
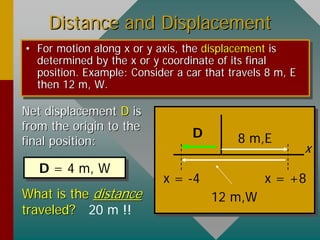
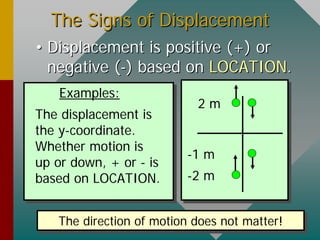
- Examples demonstrate calculating average speed and acceleration from initial and final velocities and time intervals. Direction and signs of displacement, velocity, and acceleration must be considered carefully.