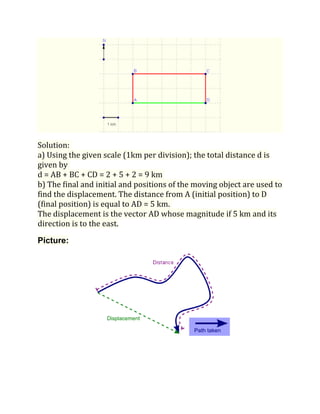
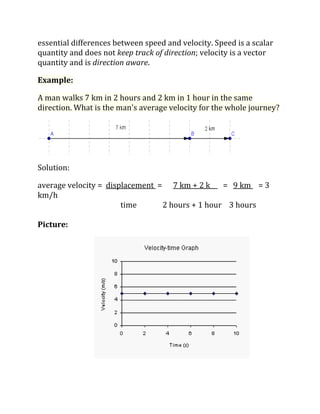
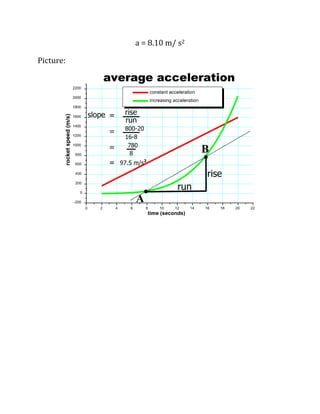
Distance is a scalar quantity that refers to how far an object has traveled, while displacement is a vector quantity referring to the shortest distance between initial and final positions. Speed is the distance traveled per unit time, while velocity is a vector quantity referring to the rate of change of an object's position and includes direction. Acceleration refers to the rate of change of an object's velocity. It can be calculated using the change in velocity over the change in time.