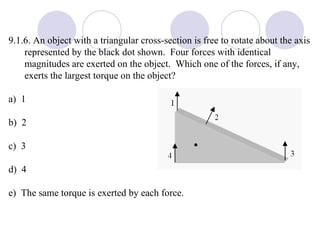
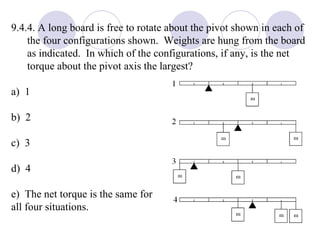
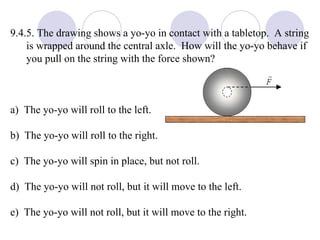
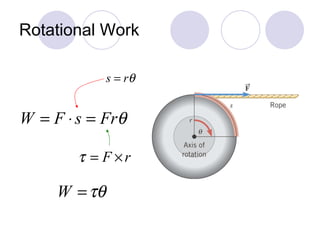
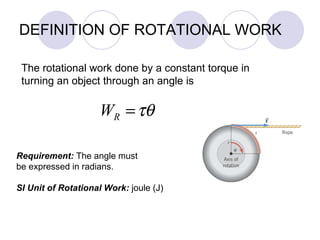
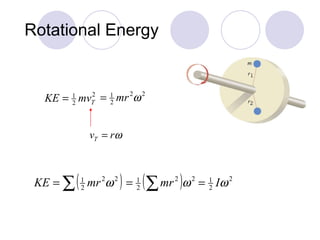
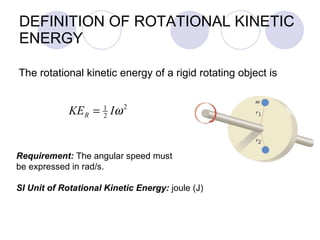
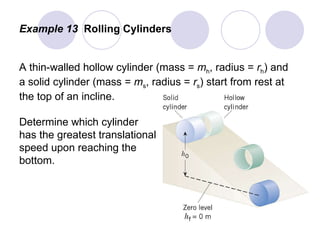
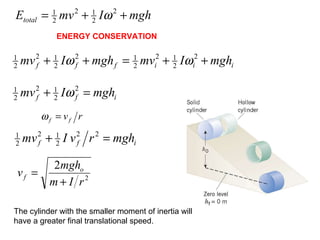
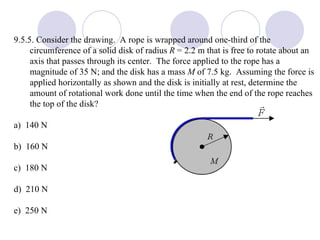
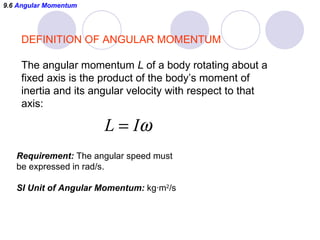
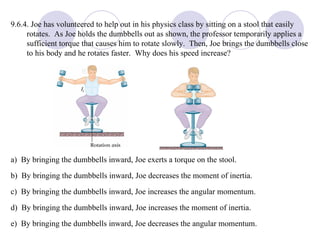
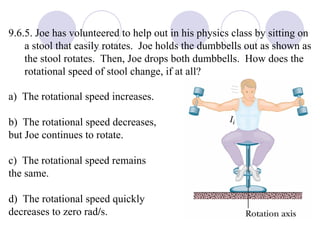
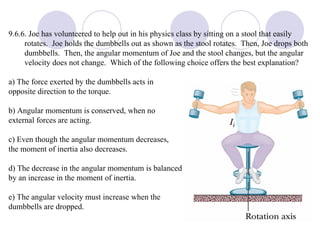
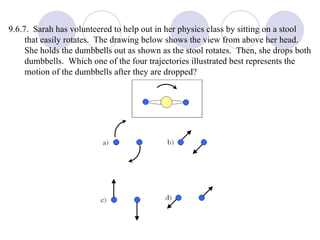
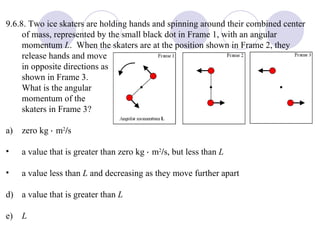
This document summarizes key concepts from a chapter on rotational dynamics:
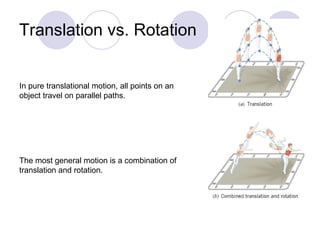
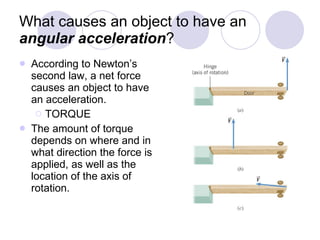
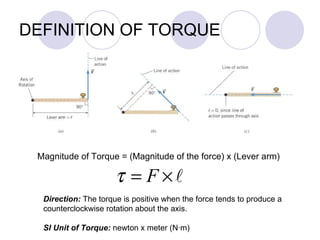
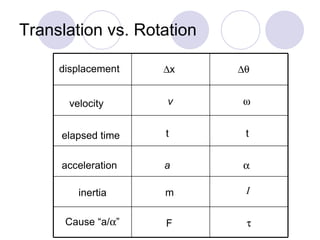
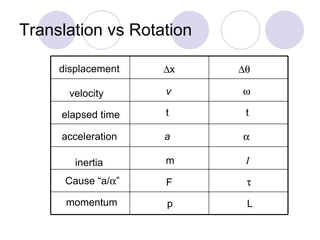
- It discusses rotational motion versus translational motion and defines torque as the cause of angular acceleration.
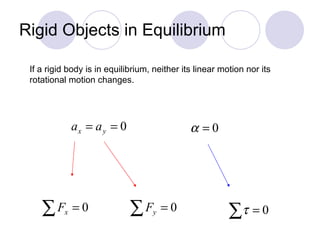
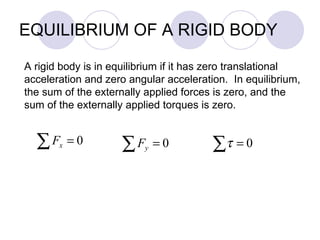
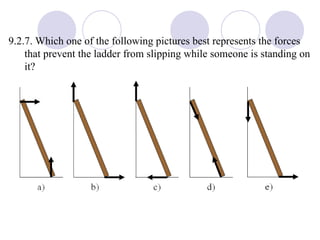
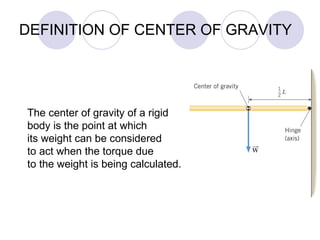
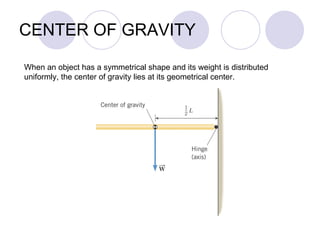
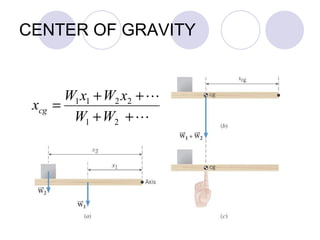
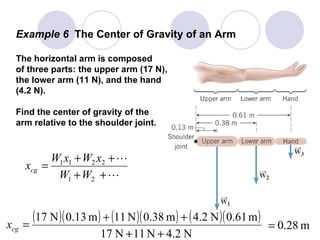
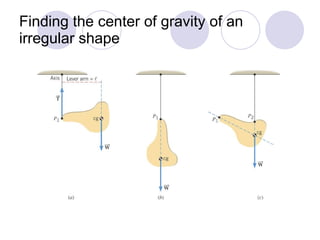
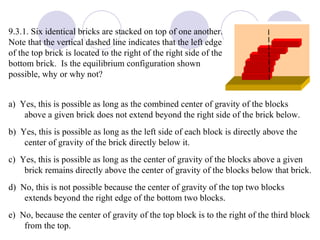
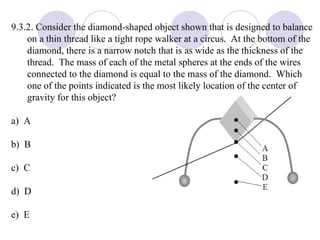
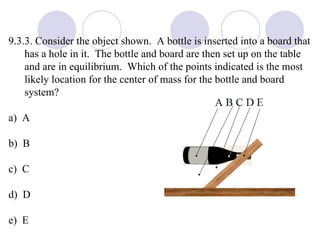
- Rigid objects in equilibrium are analyzed using the concepts of torque and center of gravity.
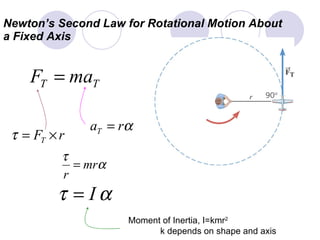
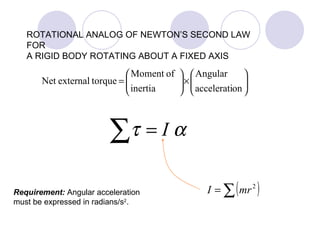
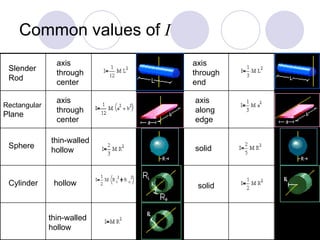
- Newton's second law is extended to rotational motion, defining moment of inertia and relating torque to angular acceleration.
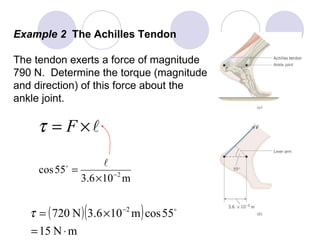
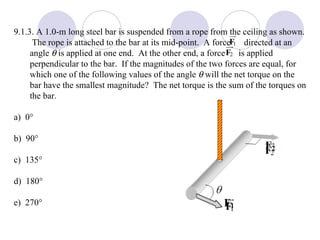
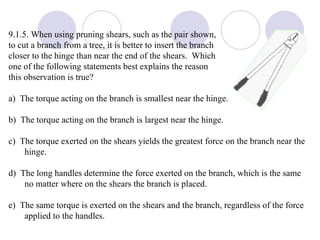
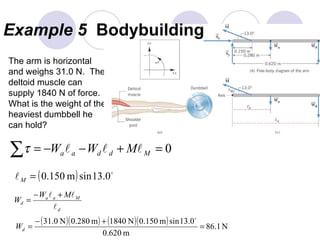
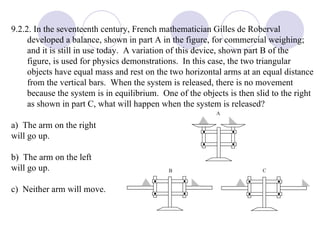
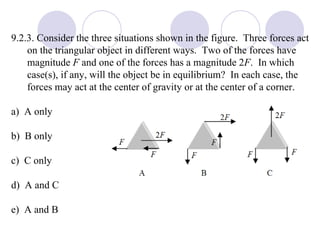
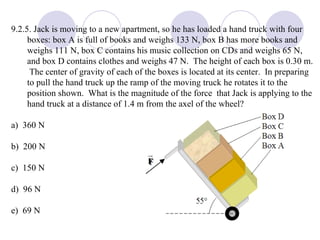
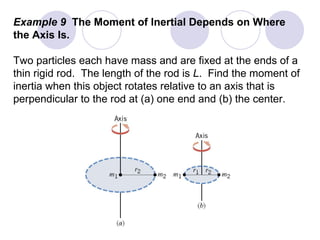
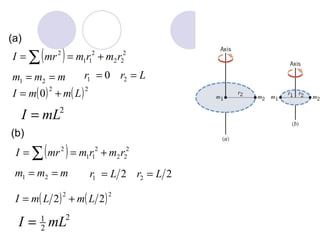
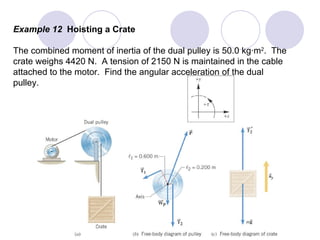
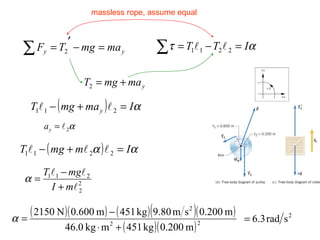
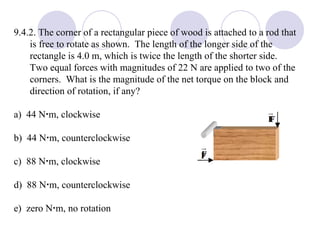
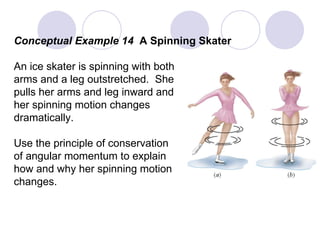
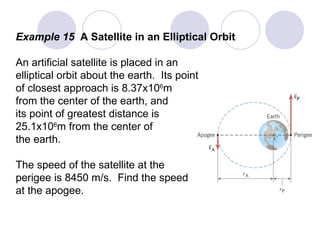
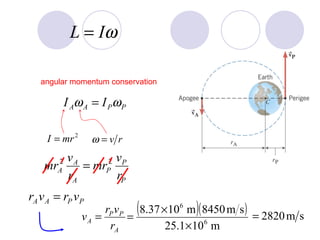
- Several example problems demonstrate calculating torque, center of gravity, and rotational motion and equilibrium for various objects.