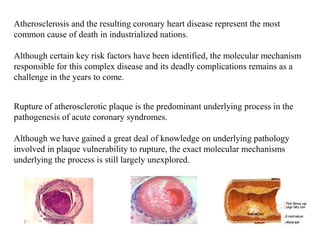
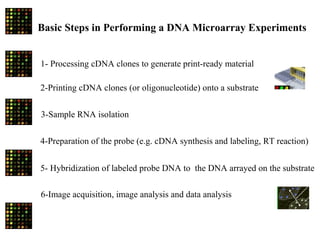
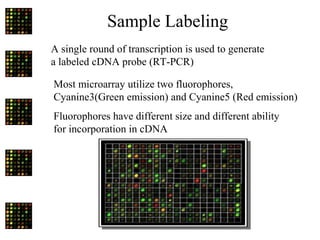
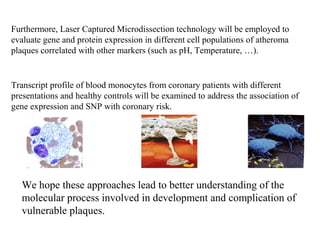
This document discusses the use of DNA microarrays in vulnerable plaque research. It provides background on atherosclerosis and identifies DNA microarrays as a tool that can be used to investigate the molecular mechanisms underlying plaque vulnerability. The document outlines the basic steps of a DNA microarray experiment and discusses considerations for experimental design, data analysis, and validation of results. It also summarizes several studies that have used DNA microarrays or related techniques to examine gene expression in atherosclerosis.