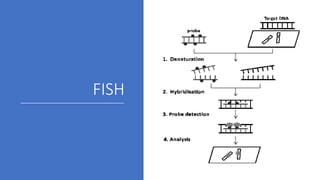
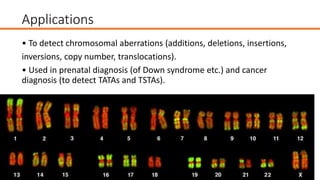
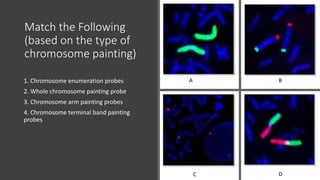
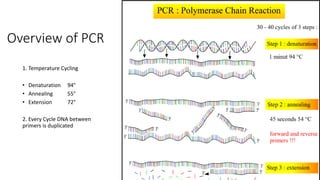
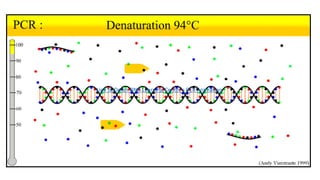
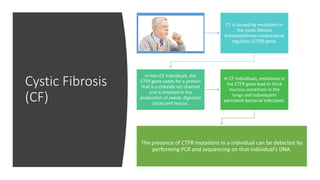
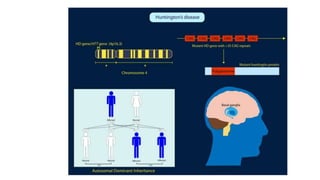
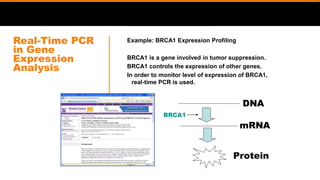
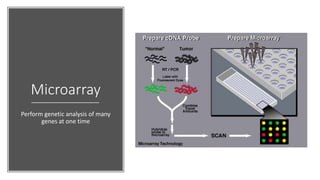
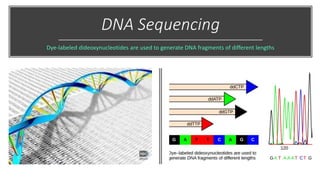
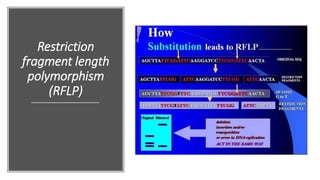
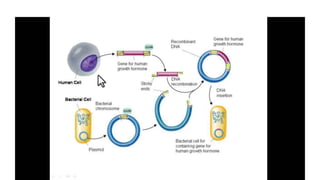
This document discusses diagnostic techniques for genetic disorders, including cytogenetic tests like fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) and karyotyping, as well as molecular tests like polymerase chain reaction (PCR), DNA microarray, DNA sequencing, and restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP). It provides examples of how each technique can be used to detect genetic abnormalities associated with diseases like cystic fibrosis, cancer, and HIV/AIDS. Real-time PCR is also described as a method for quantifying gene expression levels and monitoring viral load during HIV treatment.