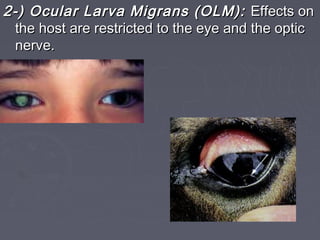
Toxocariasis is caused by the roundworm Toxocara canis or T. cati infecting humans. The worms normally infect dogs and cats as definitive hosts. Humans can become infected by ingesting embryonated eggs from contaminated soil or surfaces. This causes the larvae to hatch and migrate through the body, potentially causing visceral larva migrans or ocular larva migrans. Albendazole is the recommended treatment for toxocariasis.