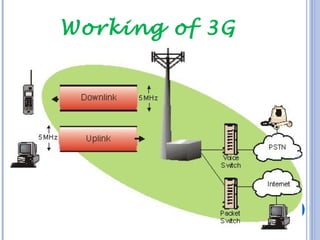
The document discusses the evolution and standards of wireless technology from 1G to 3G, highlighting the need for higher data rates and multimedia services. It outlines the features, applications, advantages, and disadvantages of 3G technology, as well as briefly touches on 4G and 5G advancements. The content is guided by a literature survey and includes specific technical details and performance metrics.