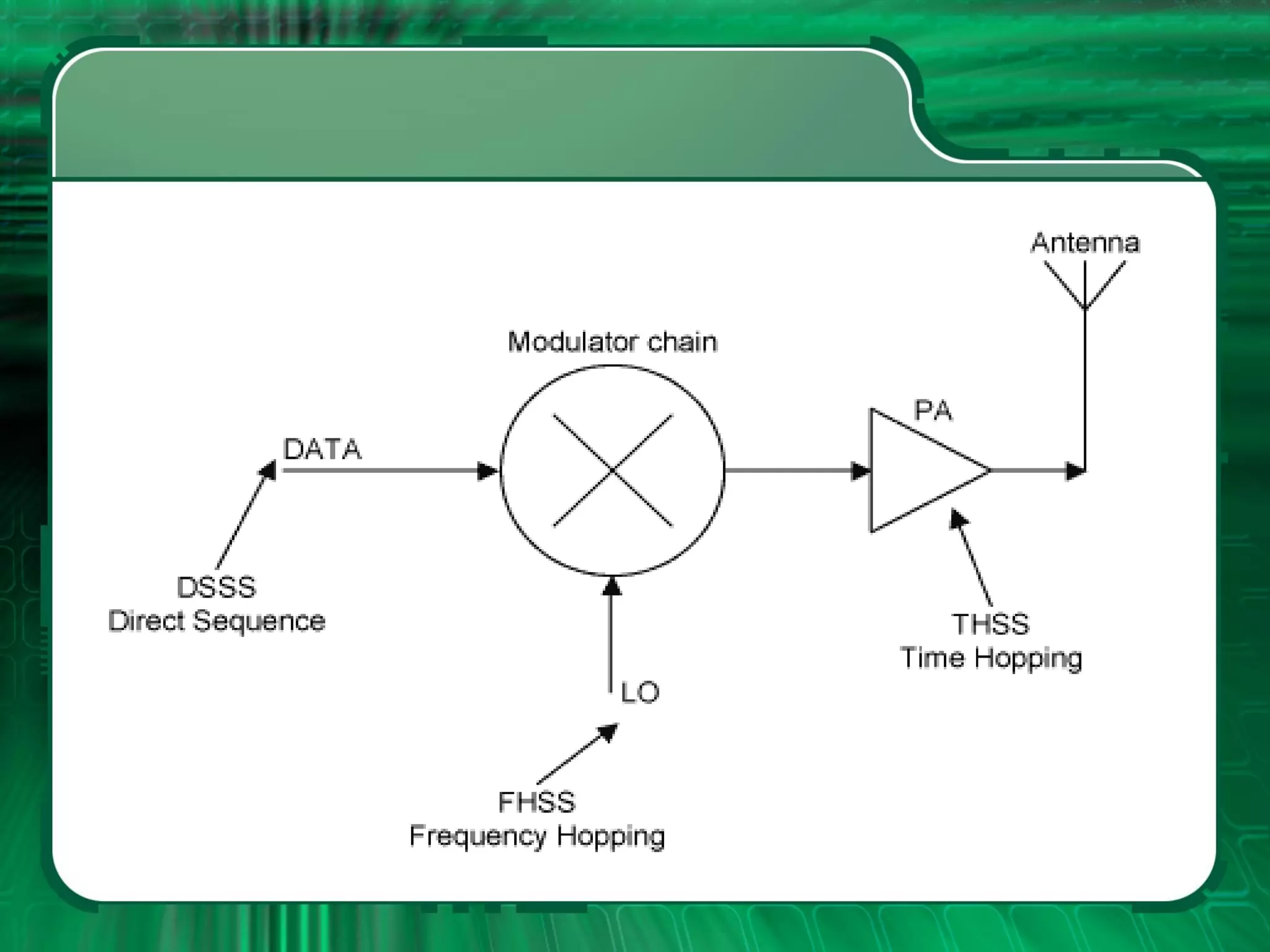
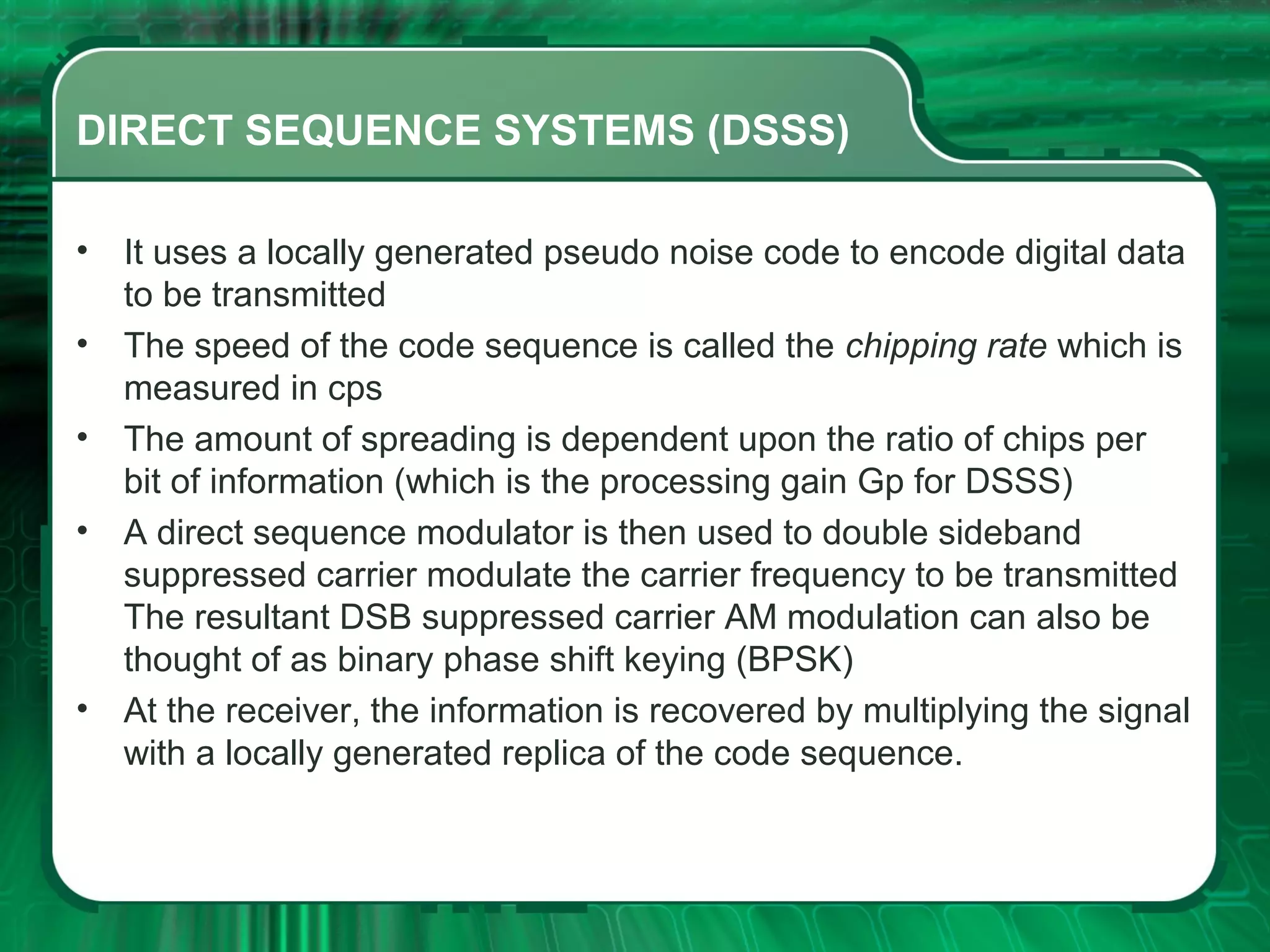
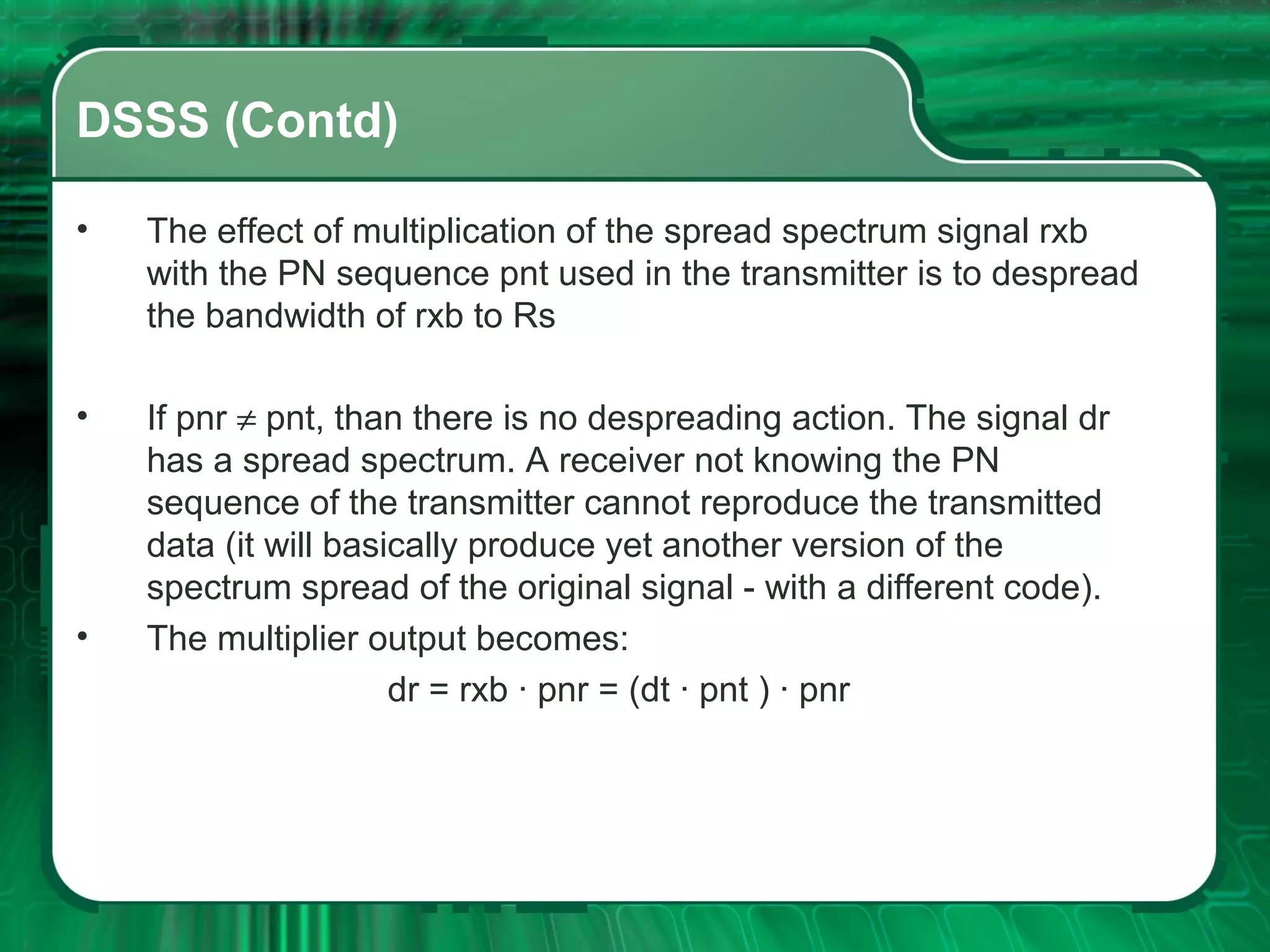
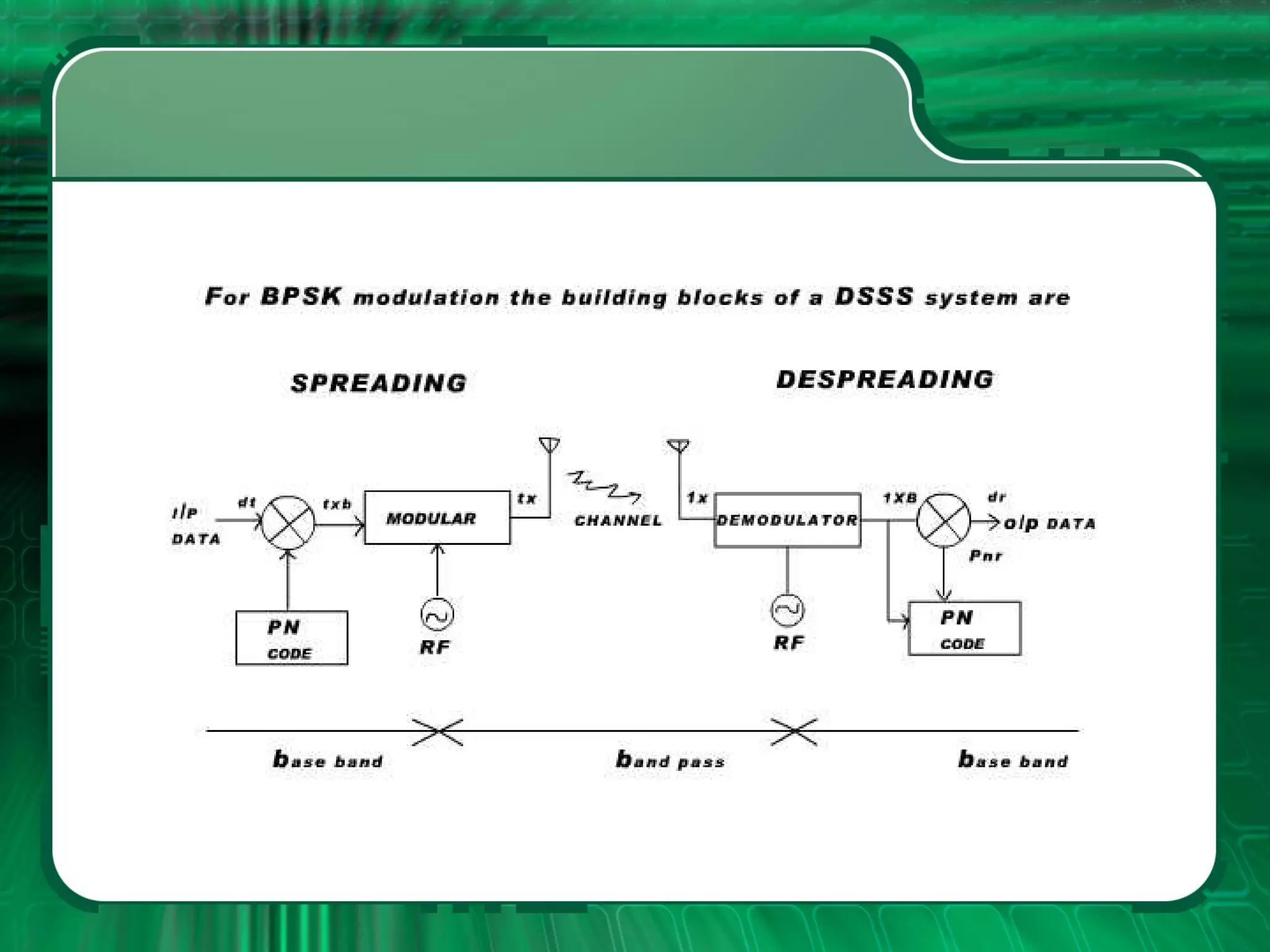
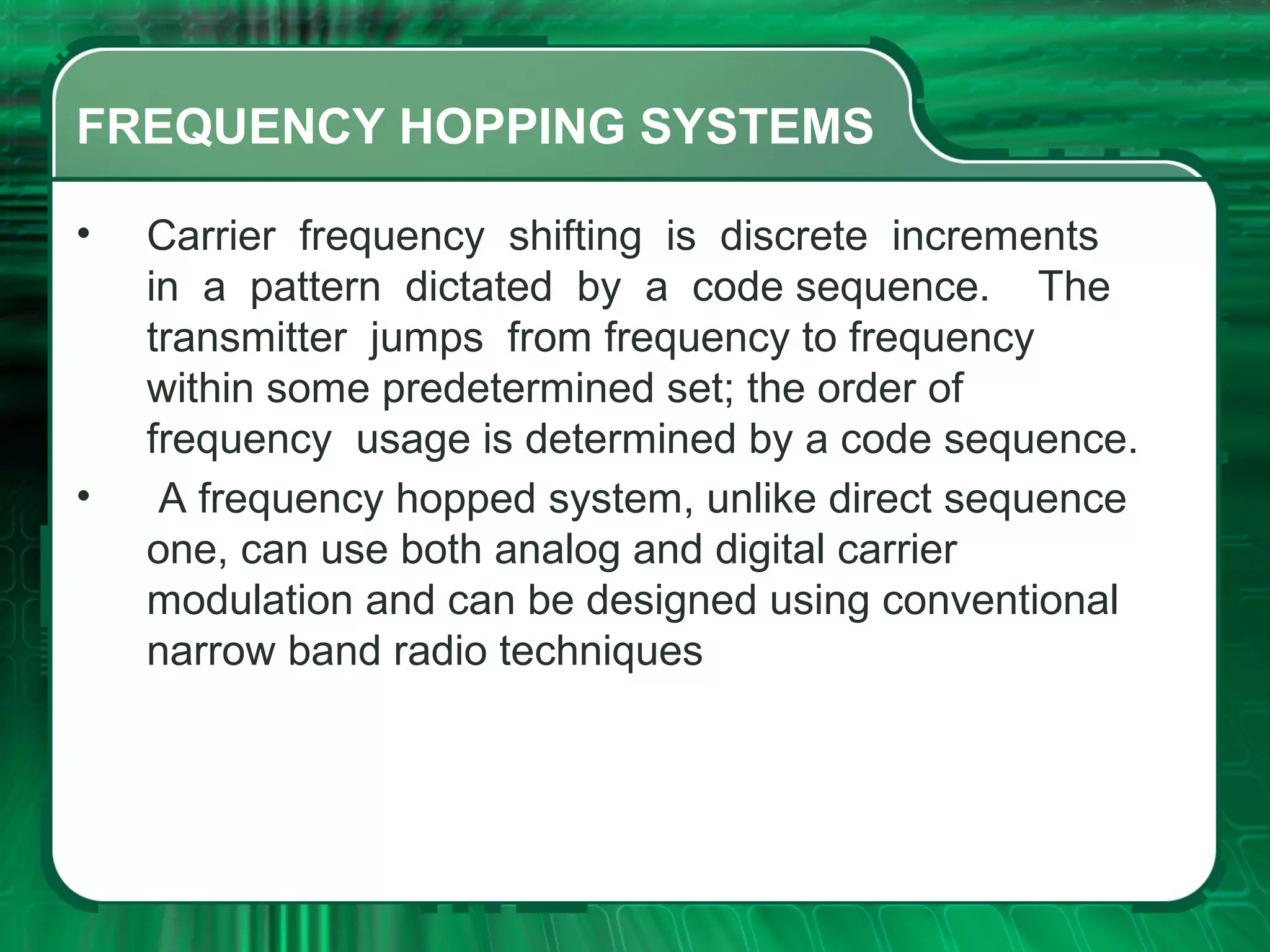
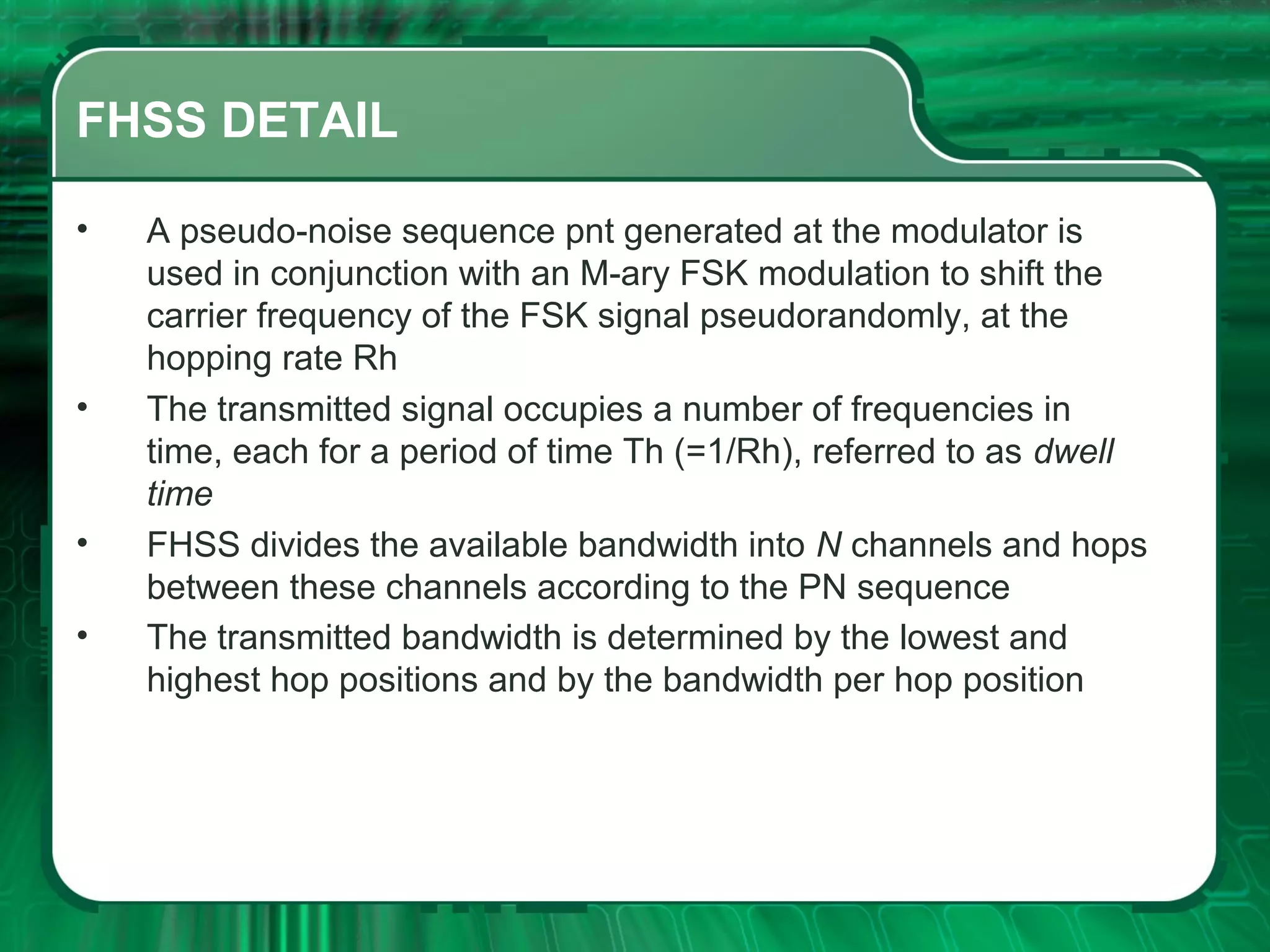
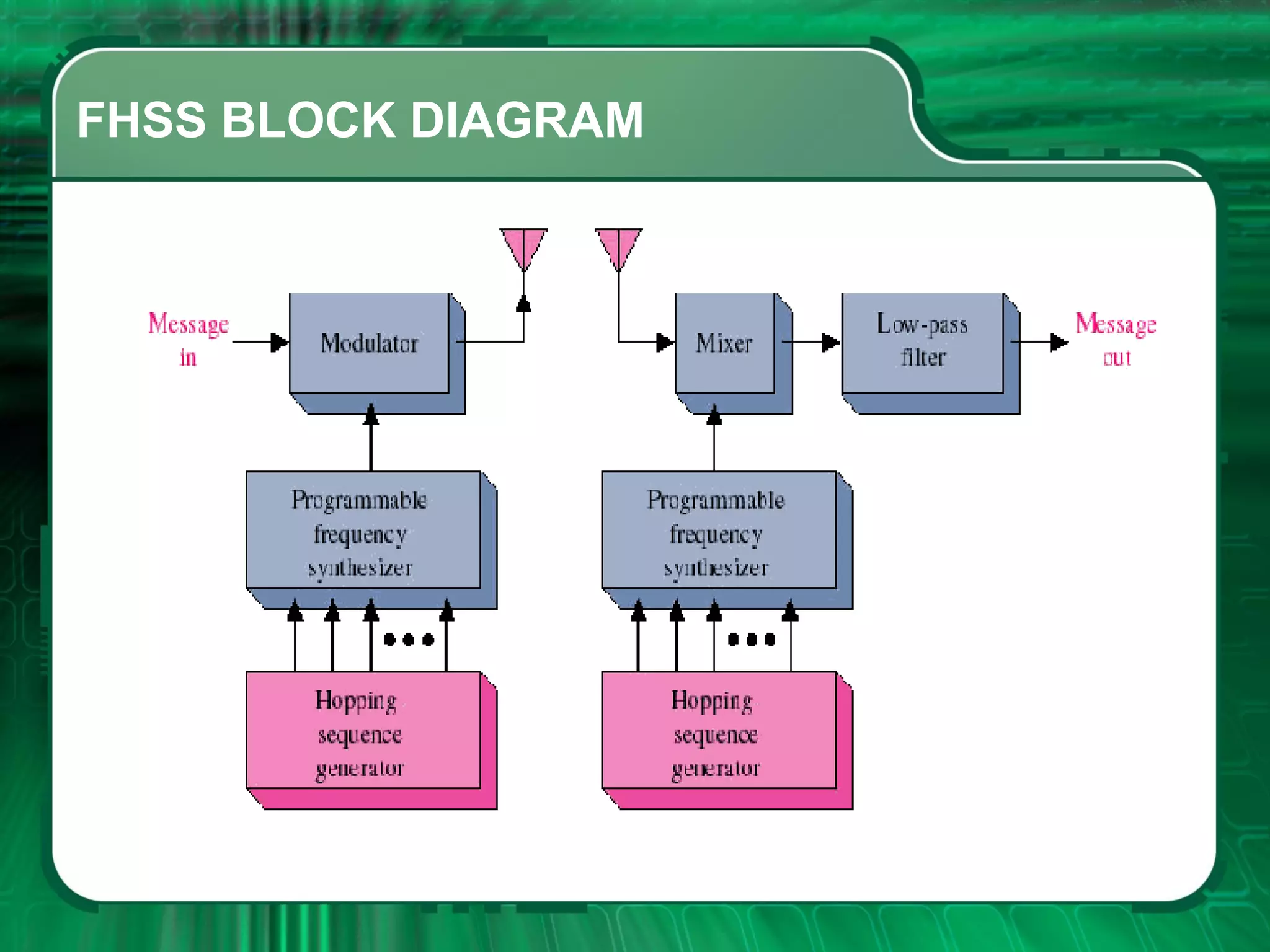
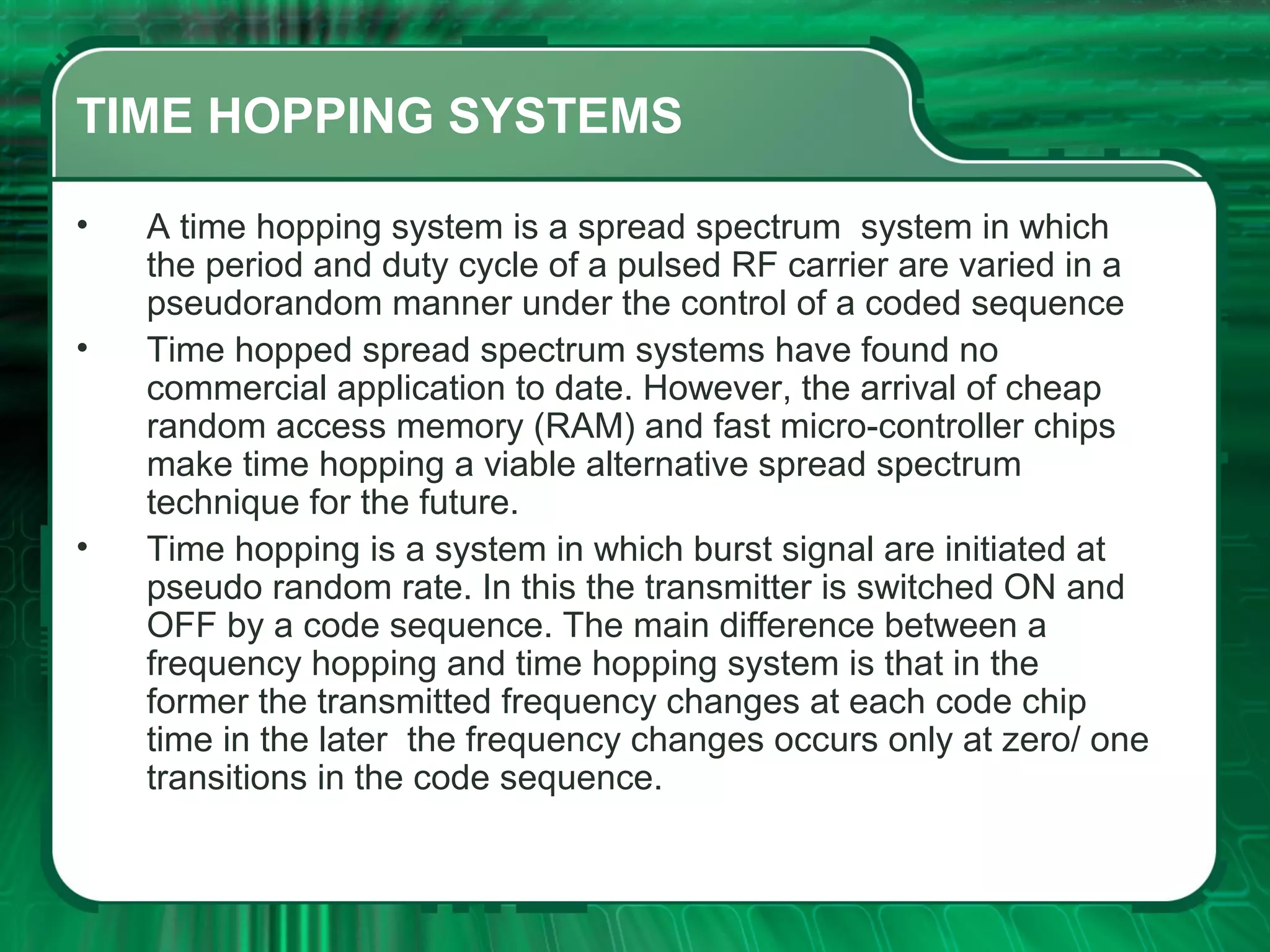
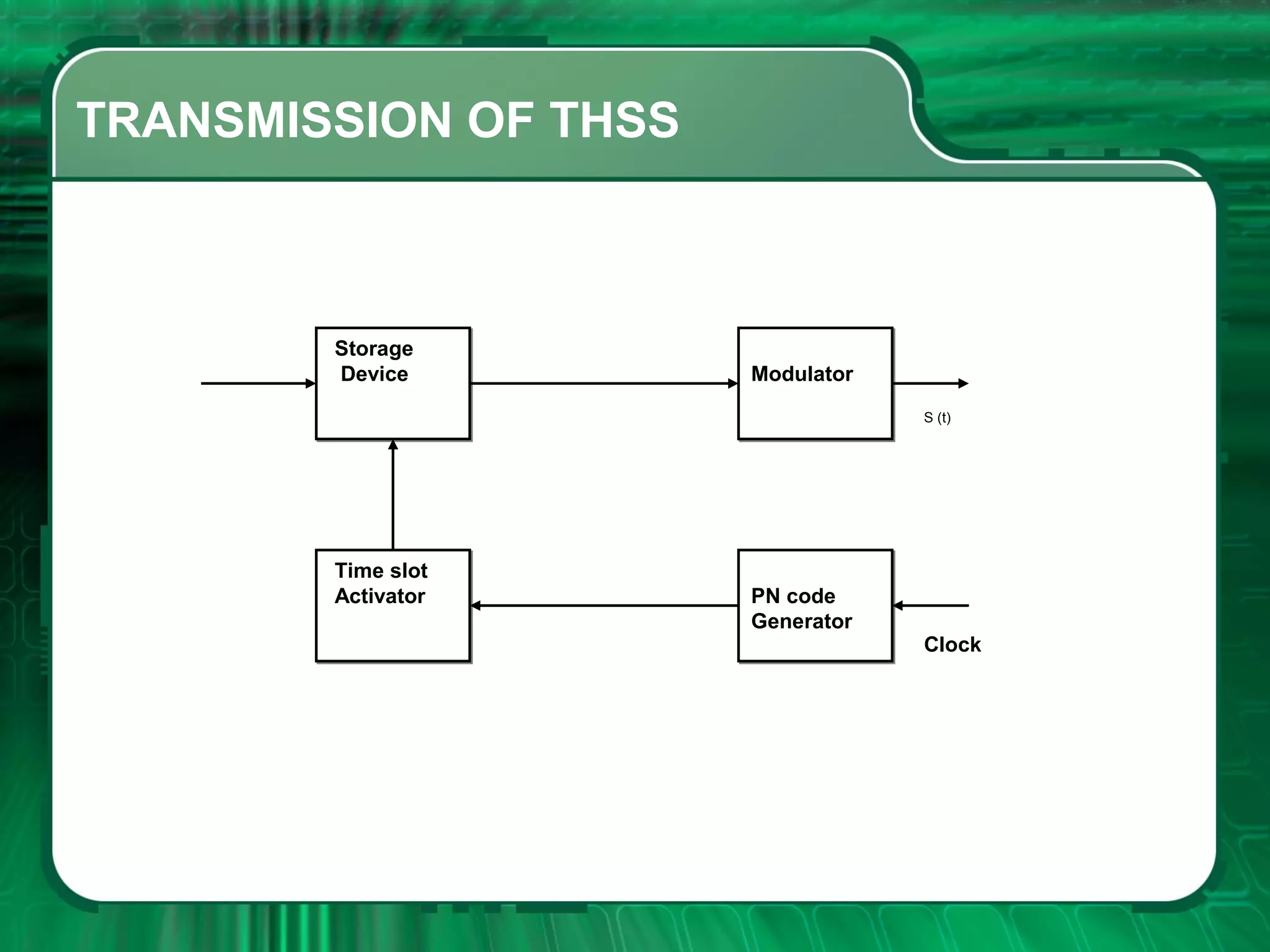
There are four main types of spread spectrum techniques: direct sequence spread spectrum (DSSS), frequency hopping spread spectrum (FHSS), time hopping spread spectrum (THSS), and hybrid techniques. DSSS uses a pseudo-noise code to spread the bandwidth of digital data. FHSS discretely shifts the carrier frequency in a pattern determined by a code sequence. THSS varies the period and duty cycle of a pulsed RF carrier in a pseudo-random manner. Hybrid techniques combine methods, such as DSSS and FHSS, to leverage advantages from multiple techniques.