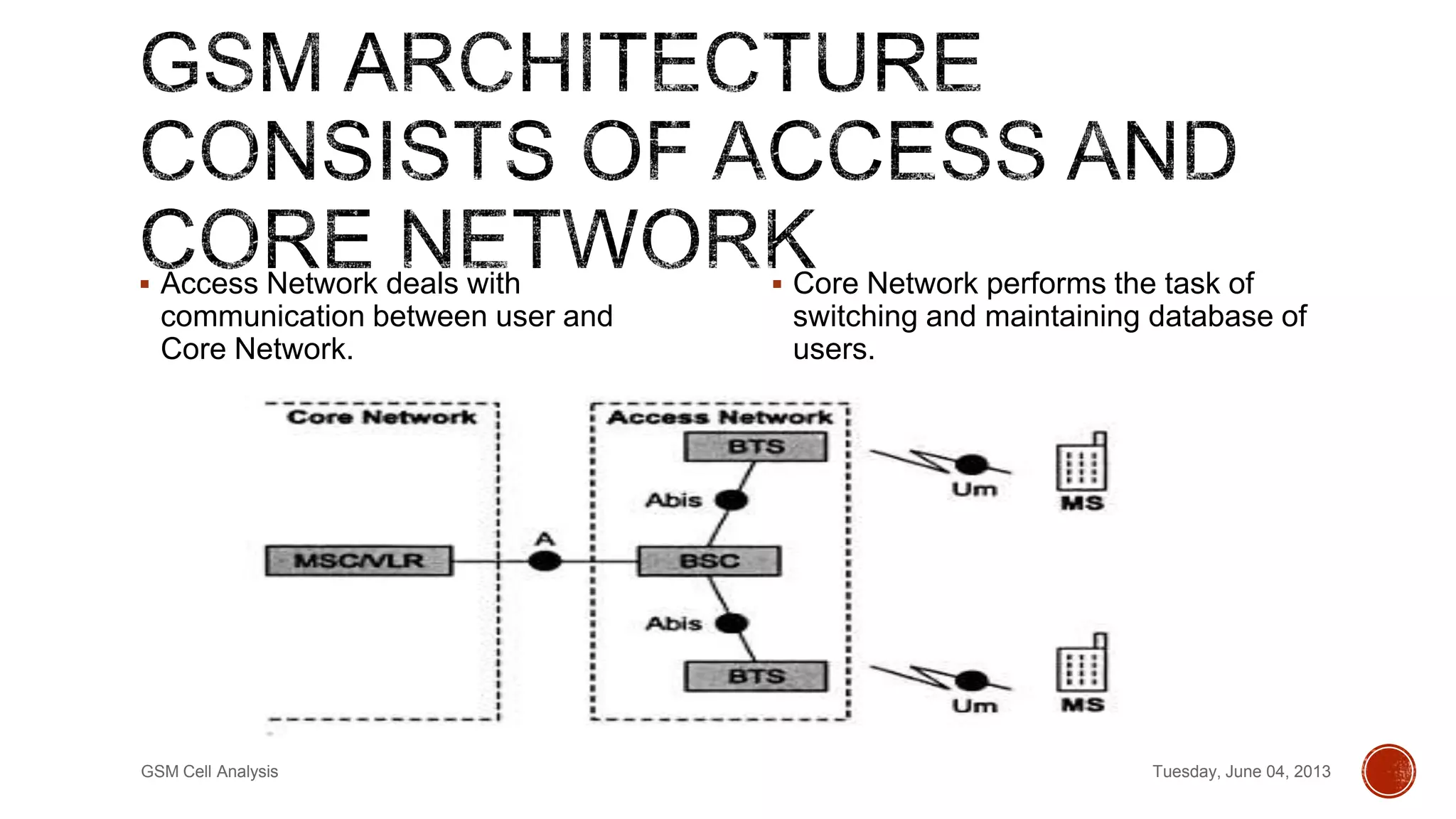
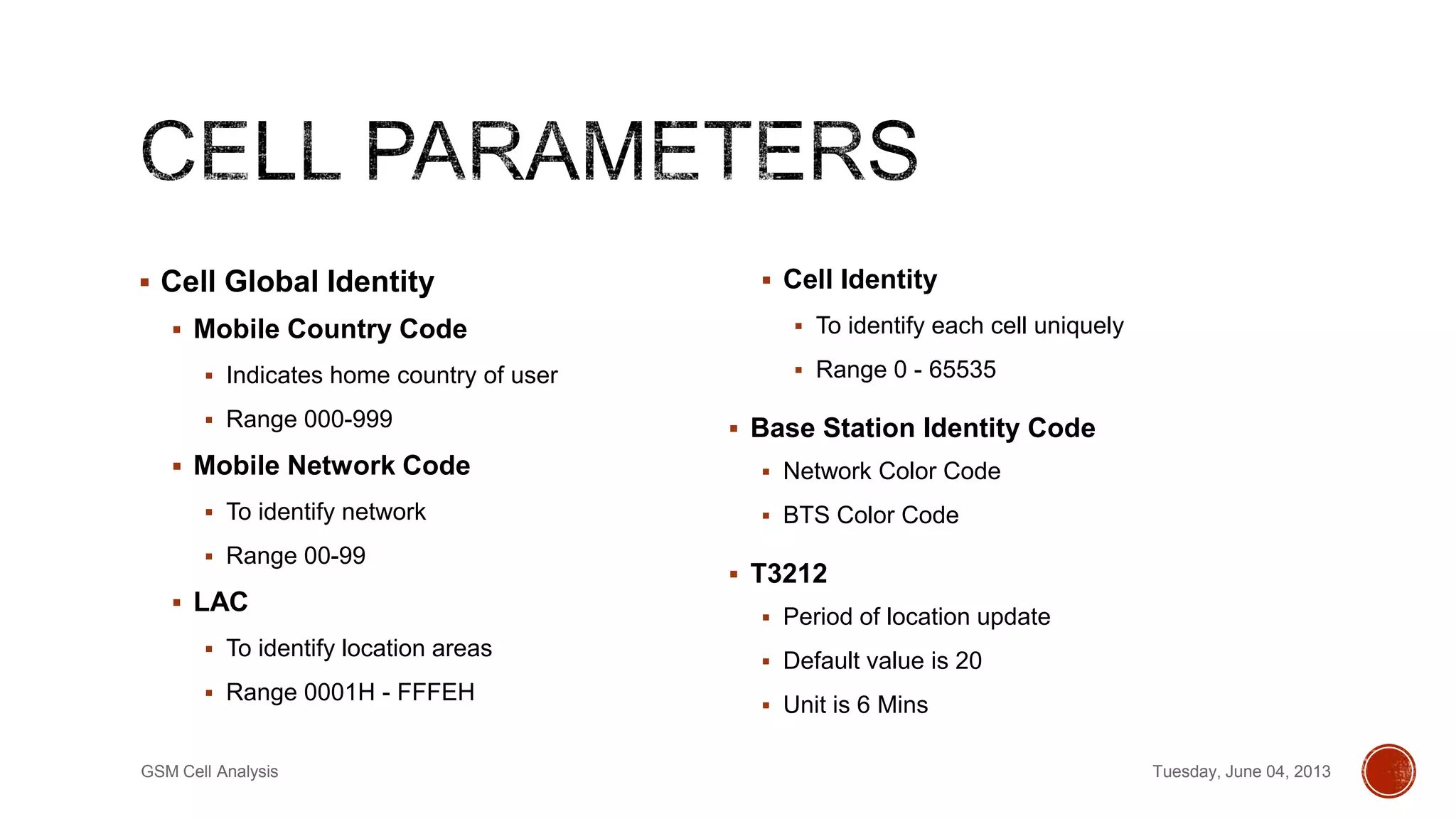
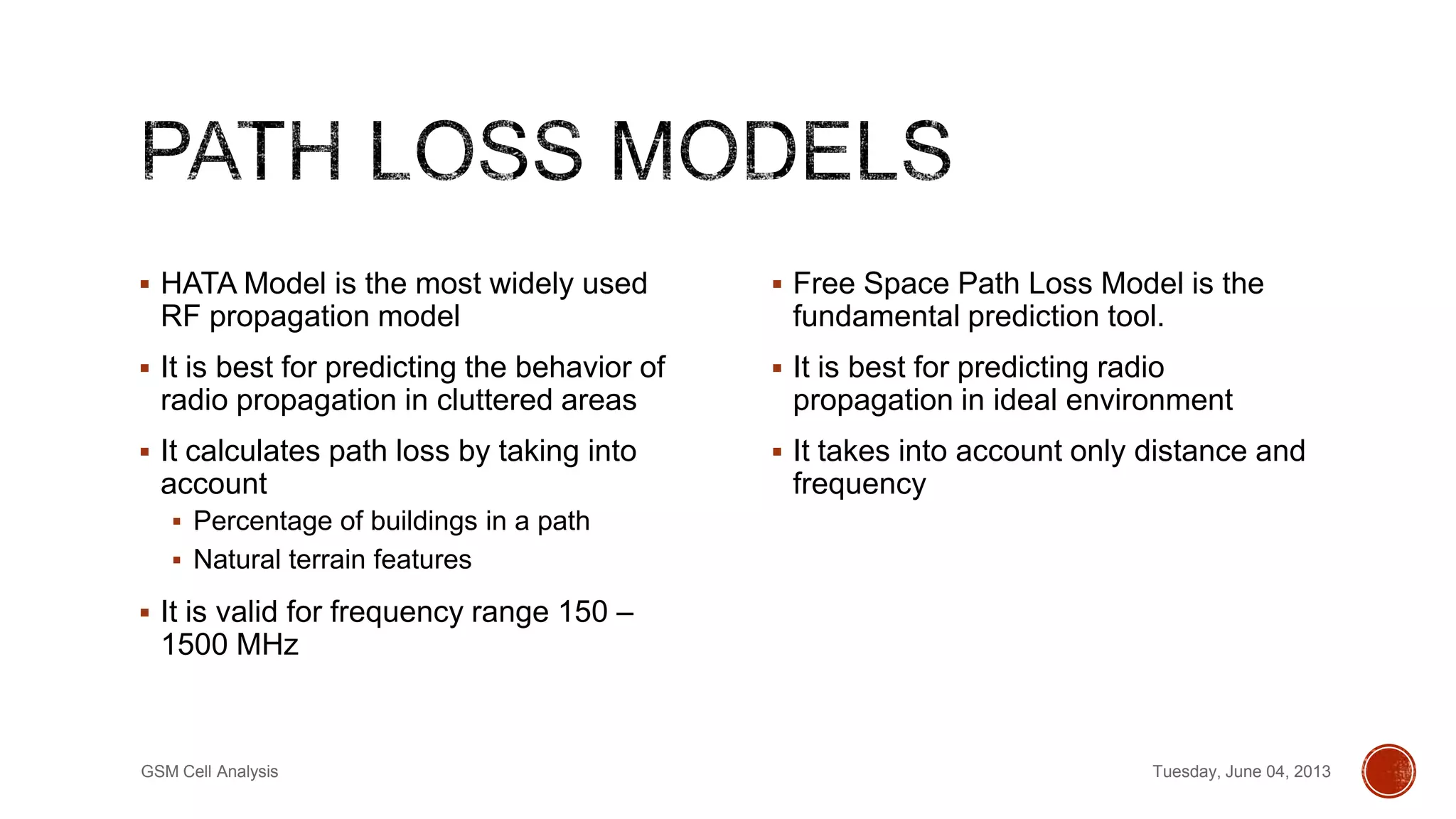
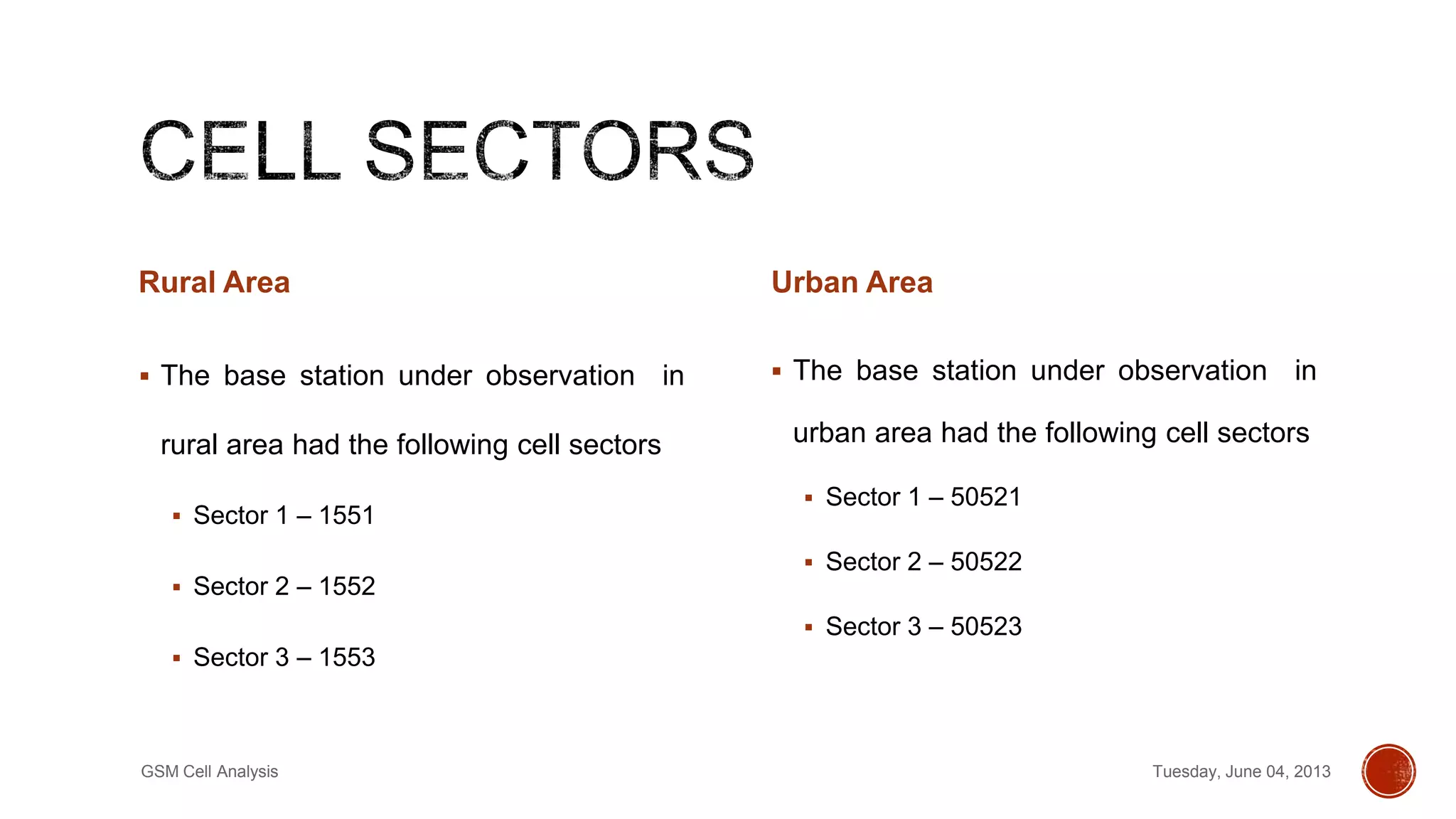
This document discusses a project analyzing GSM cell parameters and calculating path loss using propagation models. It provides background on GSM, describes conducting drive tests to collect cell data in rural and urban areas, and analyzing the data using HATA and Free Space Path Loss models. Key information collected includes cell identity, location area code, GPS coordinates, and signal strength. The rural base station had sectors 1551, 1552, 1553 and the urban station had 50521, 50522, 50523. Path loss was calculated using the models to predict radio signal propagation.