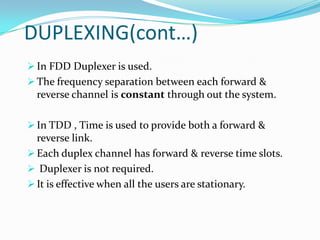
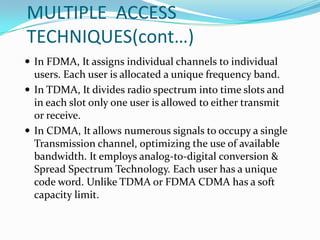
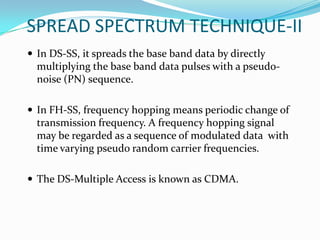
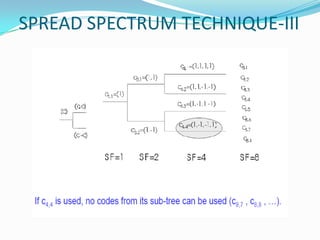
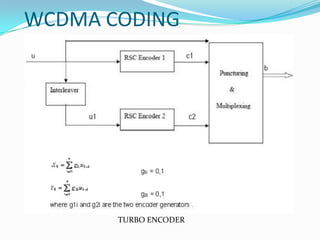
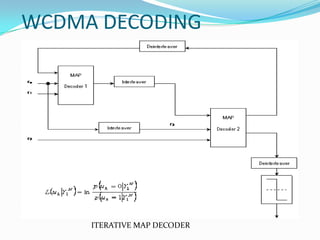
W-CDMA is a 3G mobile technology that provides higher data speeds than previous technologies. It was developed by 3GPP and first launched commercially by NTT DoCoMo in Japan. W-CDMA uses CDMA to allow multiple signals over one channel, with each user assigned a unique code. It employs spread spectrum techniques like direct sequence SS and frequency hopping SS. The presentation provides information on W-CDMA history, duplexing, multiple access techniques, coding and decoding, applications, and concludes it is a growing mobile technology.