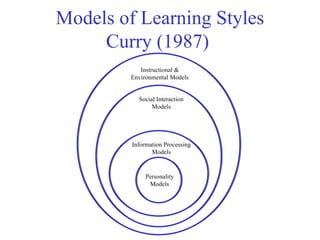
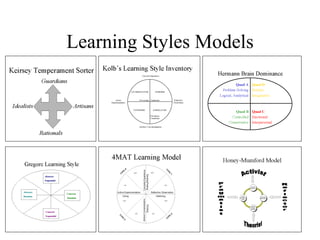
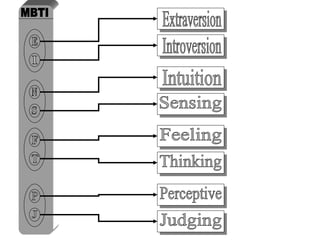
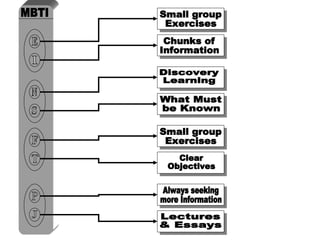
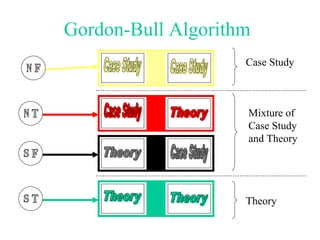
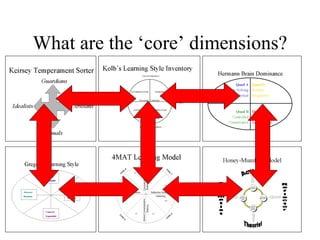
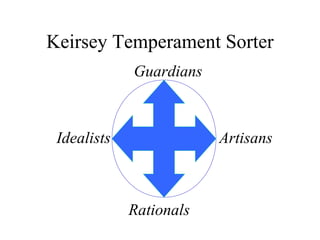
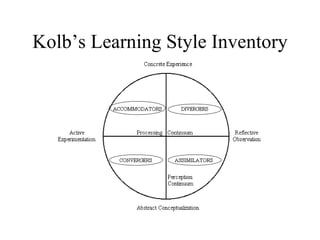
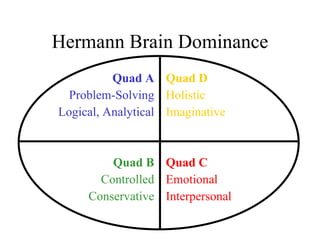
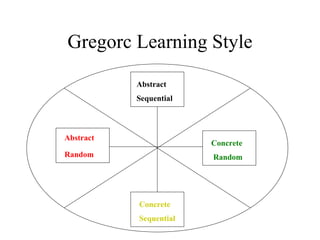
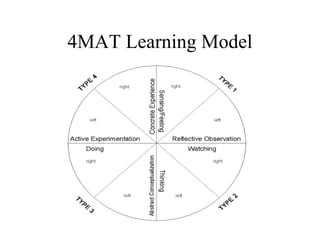
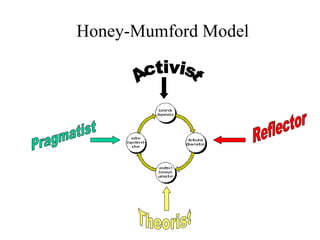
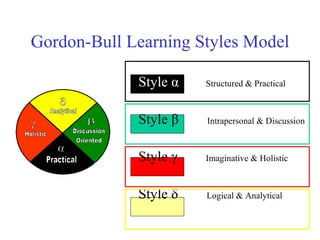
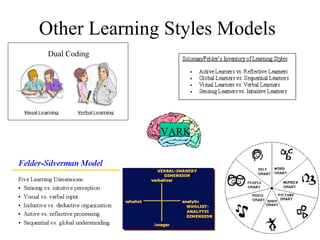
The document discusses learning styles and proposes a generalized model of learning styles. It summarizes several existing learning styles models and identifies some common dimensions across models. These include information processing styles, personality types, and social interaction styles. The document also addresses criticisms of learning styles, such as a lack of stability over time and skills. It proposes that learning styles models should be evolutionary and retested. It also suggests educating learners and teachers to avoid stereotyping.