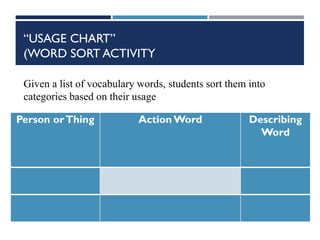
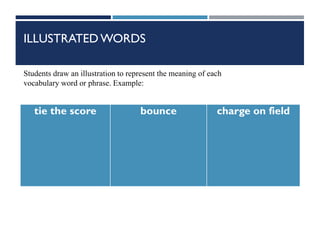
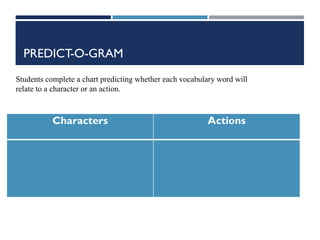
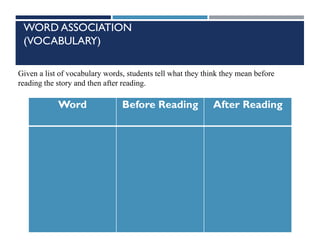
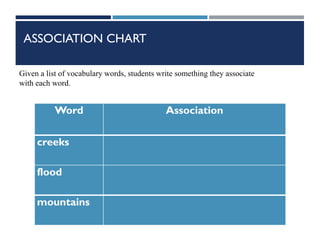
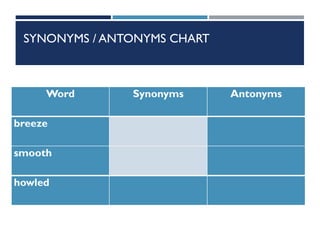
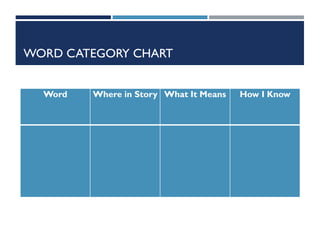
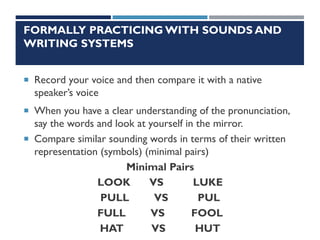
This document provides information on cognitive strategies that can be explicitly taught to students to help them become more strategic, flexible learners. It discusses that cognitive strategies must be taught and practiced multiple times to become powerful tools. The document then lists and describes various cognitive strategies for readers, such as planning and goal setting, tapping prior knowledge, asking questions, monitoring comprehension, and reflecting on what was read. It also provides examples of strategy exercises teachers can use, such as word sorts, Venn diagrams, predicting, and synonym activities. The document emphasizes the importance of practicing strategies naturally and using resources to support reading comprehension.