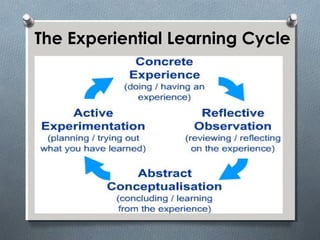
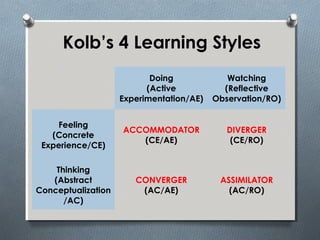
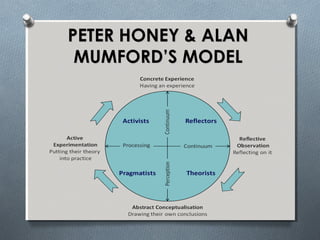
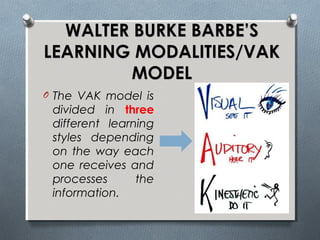
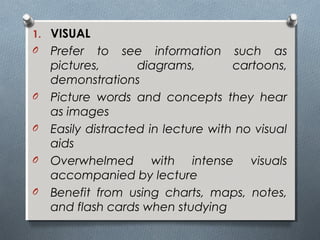
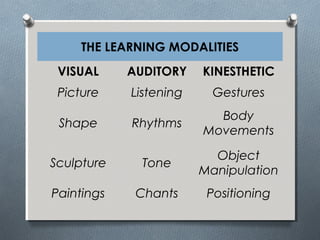
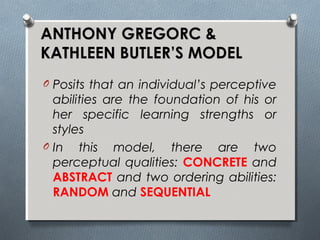
The document discusses various learning styles, emphasizing the differences in individual learning preferences and the influence on teaching methods. It highlights models by Kolb, Honey & Mumford, Barbe, Gregorc & Butler, and the NASSP, detailing specific styles and their characteristics. The educational implications suggest that educators should tailor activities to fit different learning styles to enhance effectiveness.