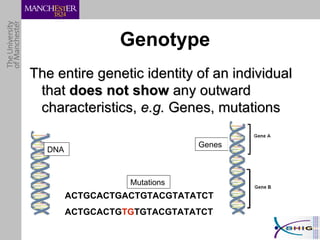
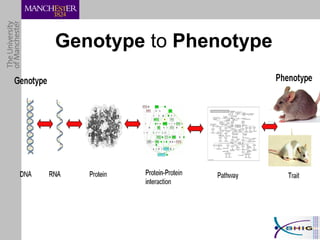
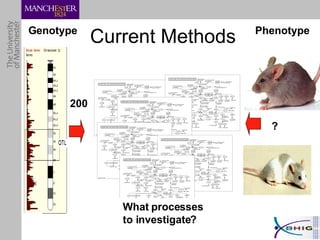
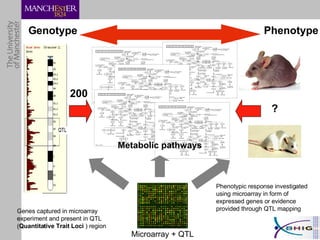
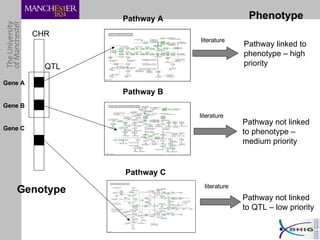
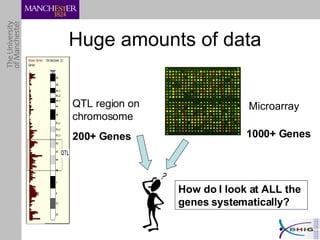
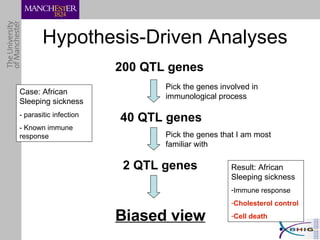
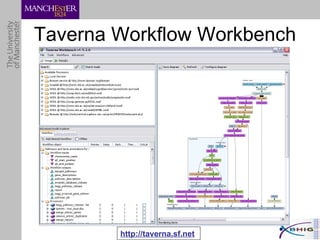
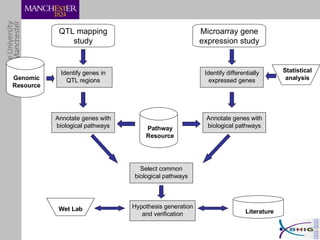
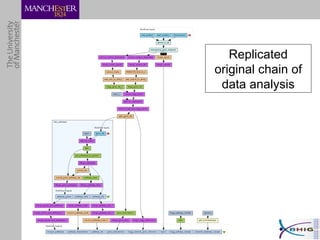
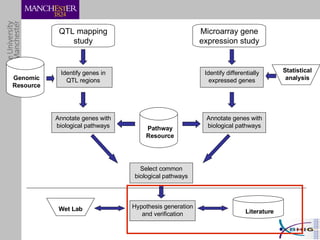
The document outlines a systematic approach for analyzing genotype-phenotype correlations, particularly in the context of African trypanosomiasis. It critiques current manual methods for their inefficiency and suggests automating analysis through workflows and text mining to improve accuracy and scalability. The case study demonstrates that a more structured methodology can lead to the discovery of significant candidate genes that traditional methods may overlook.