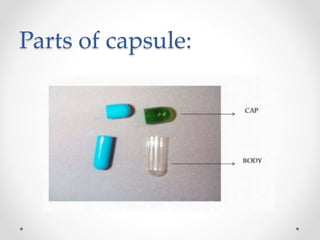
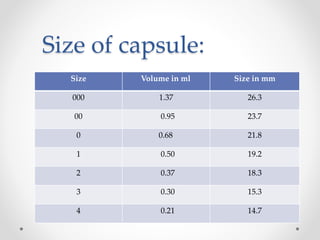
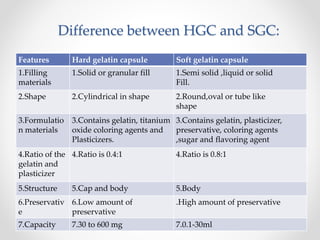
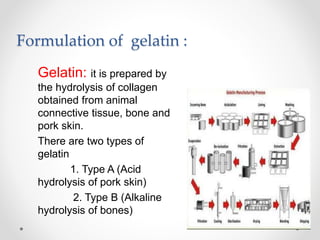
This document presents information on a student group project about hard gelatin capsules. It includes sections on the introduction, parts of capsules, types of capsules focusing on hard gelatin capsules. Details are provided on the ingredients, sizes, criteria, differences between hard and soft gelatin capsules. The document also discusses the formulation of gelatin, manufacturing process, filling methods, advantages, disadvantages, evaluation methods and concludes with thanks.