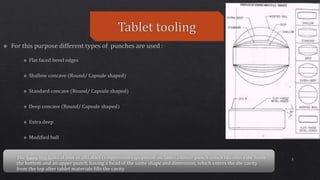
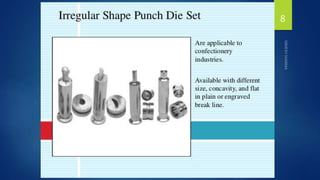
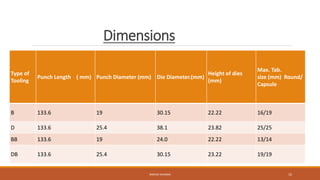
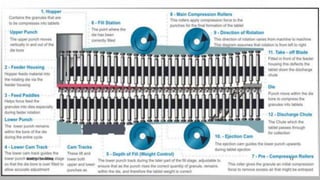
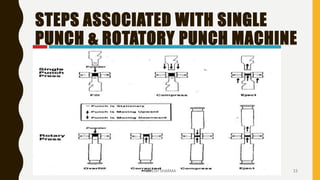
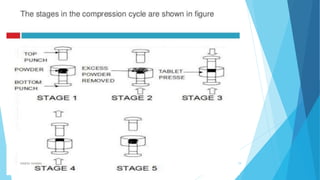
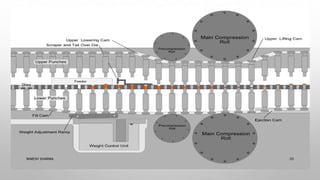
This document discusses tablet tooling and the tablet compression process. It describes the main types of tablet tooling, including 'B', 'D', 'BB', and 'DB' tooling, and provides their dimensions and specifications. It also outlines the basic components of a tablet press, including the hopper, dies, punches, cam tracks, and feeding mechanism. Finally, it explains the three main steps of the tablet compression process: filling and dosing the dies, compressing the tablets, and ejecting and exiting the tablets from the press.