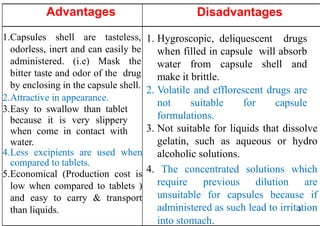
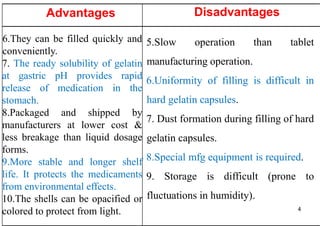
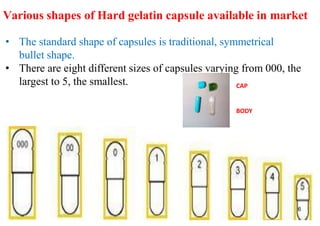
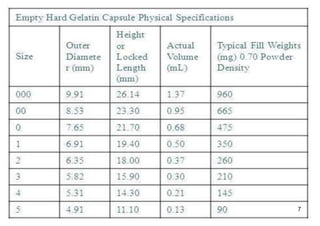
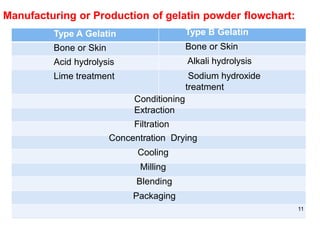
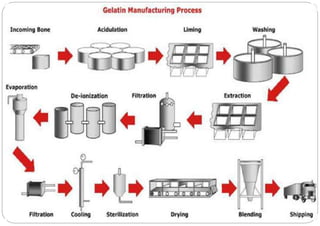
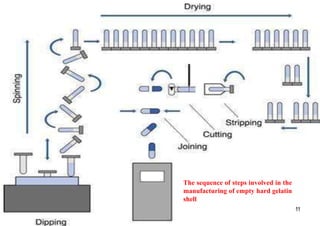
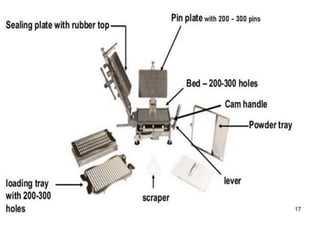
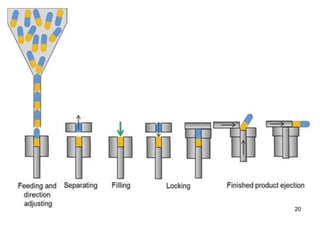
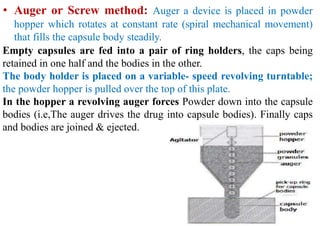
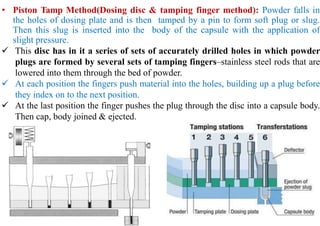
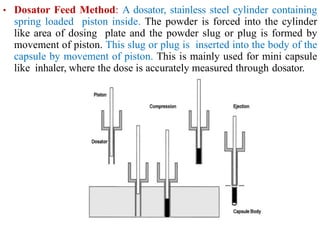
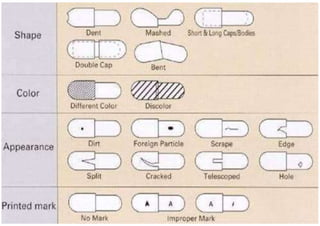
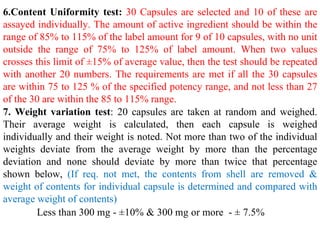
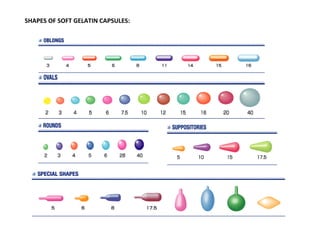
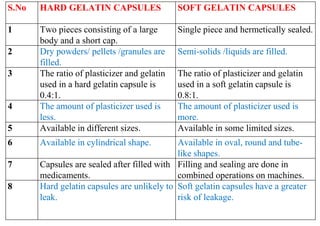
The document discusses capsules and their manufacturing process. It describes hard gelatin capsules and their production, including dipping pins in gelatin solution, drying, stripping capsules off pins, trimming, joining, polishing and sorting. The key steps in filling hard capsules are separating caps and bodies, filling bodies with powder, replacing caps, cleaning, and ejecting. Quality tests evaluate thickness, size, moisture content, and solubility. Soft gelatin capsules and pellets are also briefly mentioned.