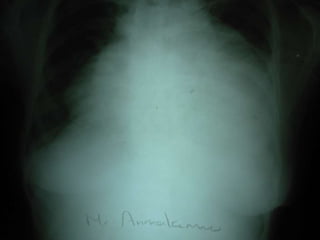
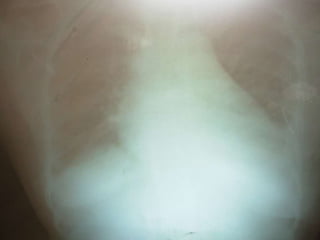
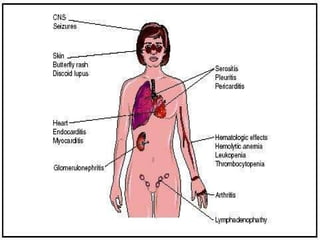
A 45-year-old woman presented with left leg swelling for 30 days, right abdominal pain for 20 days, and breathlessness for 4 days. Examination found signs of deep vein thrombosis in the left leg, pericardial effusion, pleural effusion, and ascites. Tests showed positive lupus anticoagulant and ANA antibodies, consistent with antiphospholipid antibody syndrome secondary to systemic lupus erythematosus. She was diagnosed with DVT of the left lower limb due to a hypercoagulable state from her autoimmune condition. Treatment included anticoagulation and management of her serositis.