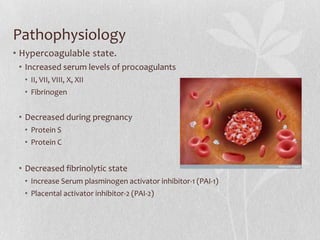
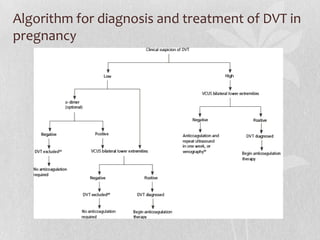
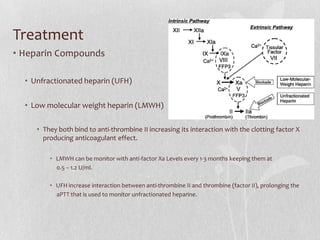
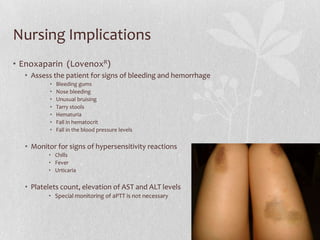
This document discusses the pharmacologic management of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) in pregnancy and related nursing implications. It notes that DVT is a leading cause of maternal death in the US, with an incidence of 1 in 500-2000 deliveries. Risk factors include physiological changes of pregnancy as well as acquired and inherited factors. Treatment involves therapeutic anticoagulation with low molecular weight heparin or unfractionated heparin, which are safe in pregnancy. Nursing implications include monitoring for signs of bleeding or allergic reaction and educating patients on prevention measures.