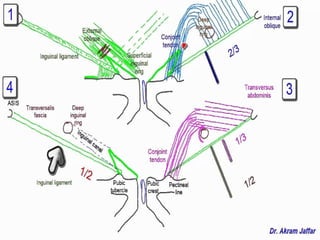
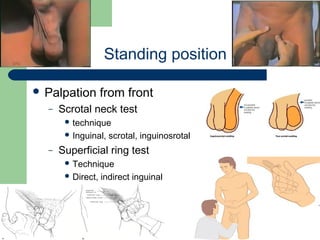
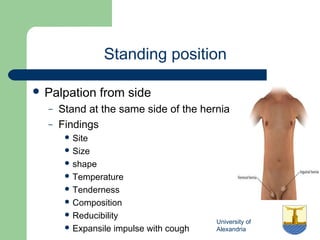
This document provides guidance on examining patients for inguinal hernias. It details the steps of the examination including inspection, palpation techniques, and tests to determine the type and characteristics of any hernia present. The examination is described in both standing and supine positions. Differential diagnoses are also listed. The goal of the examination is to determine factors such as location, size, reducibility, and complications in order to accurately diagnose the presence of an inguinal hernia.