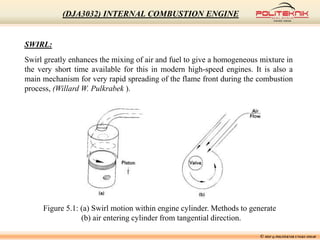
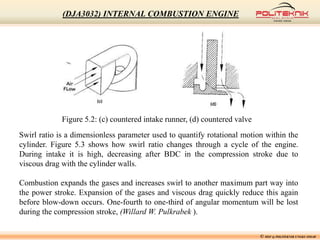
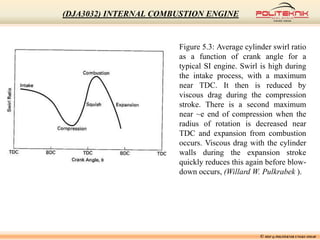
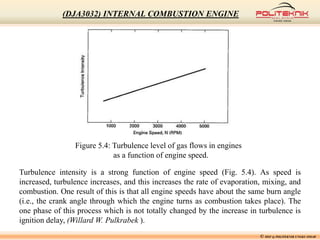
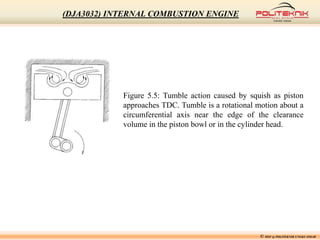
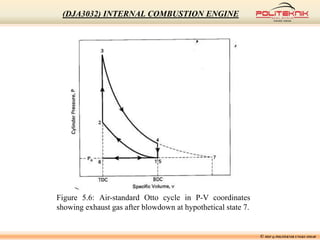
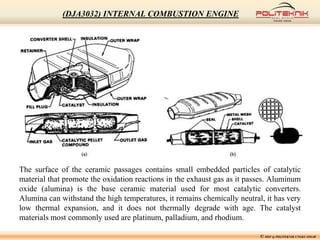
This document discusses fluid motion within internal combustion engines. It describes several types of fluid motion that occur during the engine cycle, including swirl, squish, tumble, and blowdown. Swirl enhances air-fuel mixing and combustion speed. Squish and tumble generate additional rotational and radial motions near top dead center to further mix the fuel and air. Turbulence throughout the cycle aids various engine processes. The exhaust gases exit the cylinder during blowdown and pass through the exhaust manifold, catalytic converter, tailpipe and muffler before being vented outside.