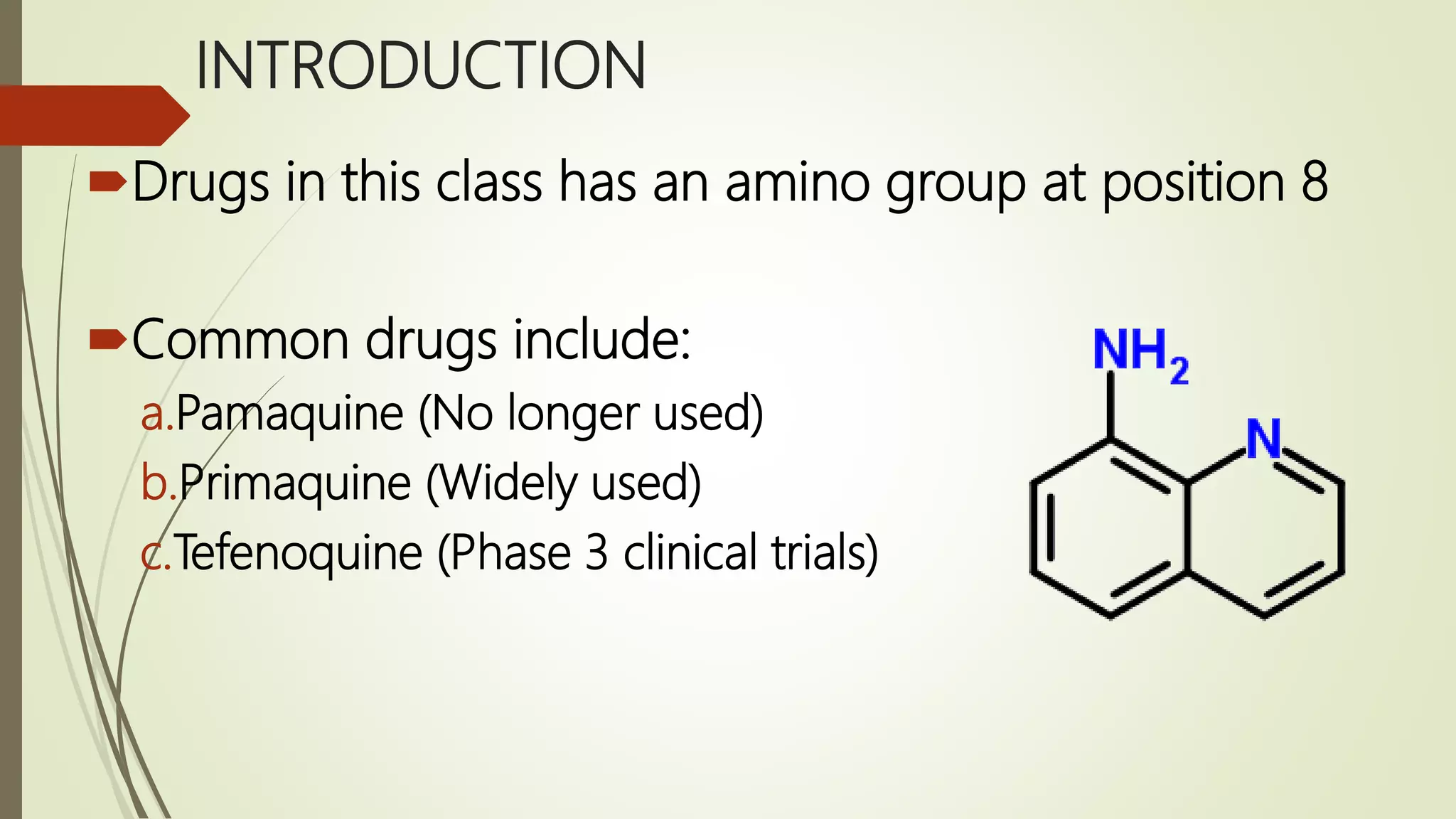
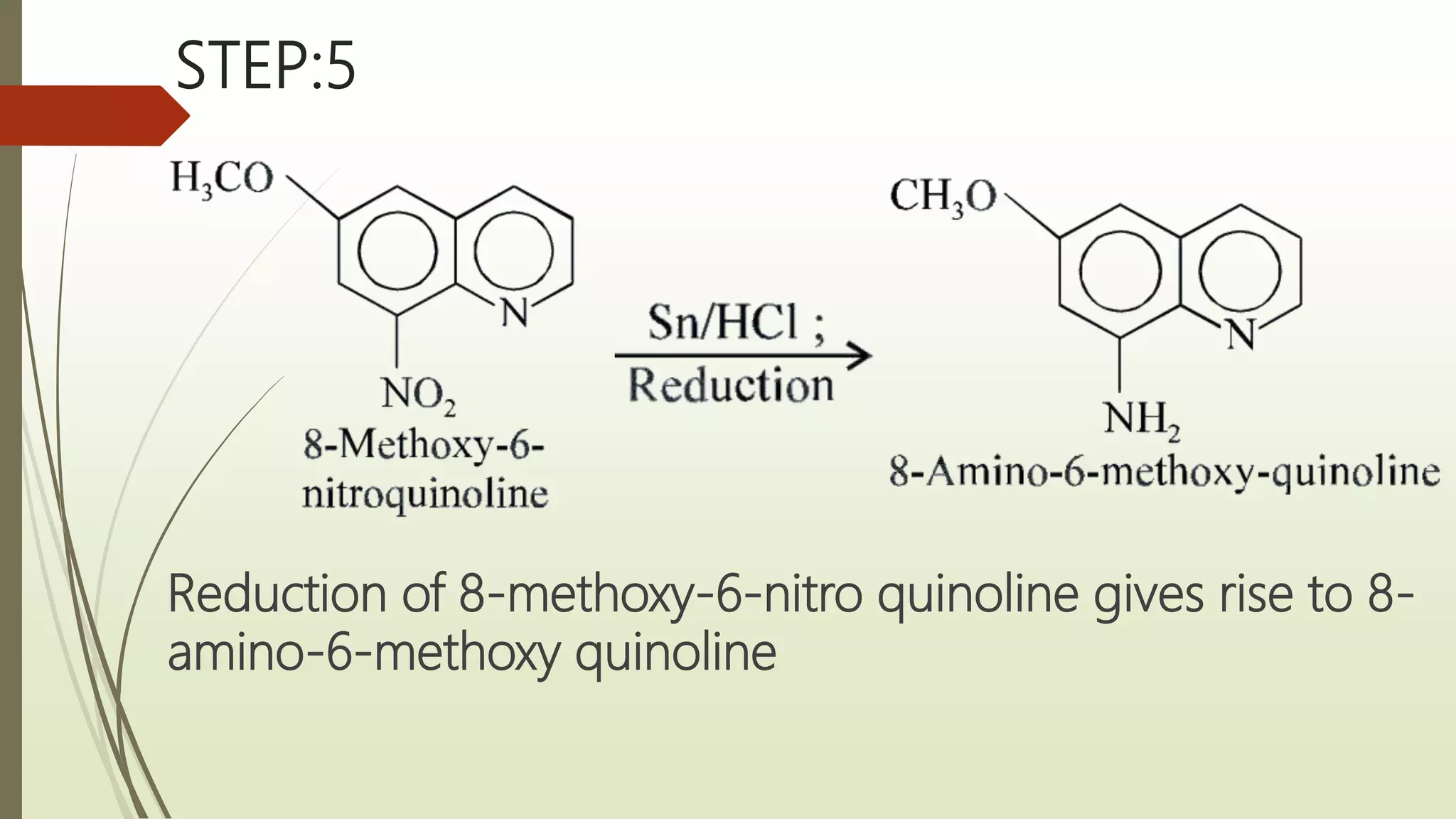
This document discusses anti-malarial drugs in the 8-aminoquinoline class. It describes the synthesis of primaquine through a multi-step process involving the quinoline nucleus and side chain. Structure-activity relationships are examined, noting the importance of the quinolone ring, pentyl side chain, primary amino group, and methoxy substitution. The pharmacology of primaquine is explained by its interference with the parasite's mitochondria and DNA. It is indicated for eradicating hypnozoites and prophylaxis but contraindicated in G6PD deficient patients due to risk of fatal hemolysis.