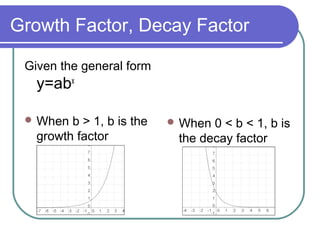
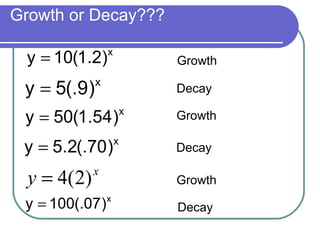
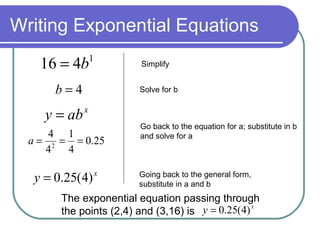
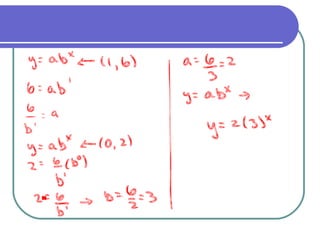
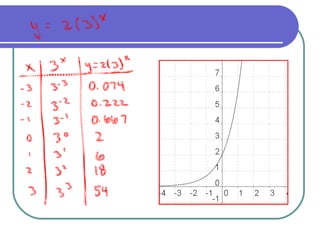
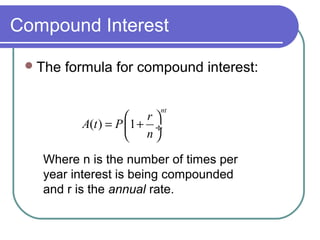
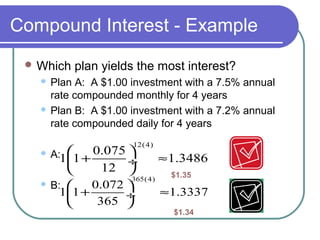
The document discusses exponential equations and their applications. Exponential equations take the form y=abx, where a and b are constants. When b>1, b is the growth factor, and when 0<b<1, b is the decay factor. Examples are provided to demonstrate how to write an exponential equation that passes through two given points. The concepts are then applied to modeling growth and decay scenarios using exponential equations. Compound interest is also discussed, with the formula A(t)=P(1+r/n)nt provided, where n is the number of times interest is compounded per year.